To find the average atomic mass of an element, you need to consider the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes and their relative abundances. This process involves understanding the concept of isotopes, which are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, leading to different masses. The average atomic mass is a weighted average that reflects the proportion of each isotope in a sample of the element.
Understanding Isotopes and Their Abundances
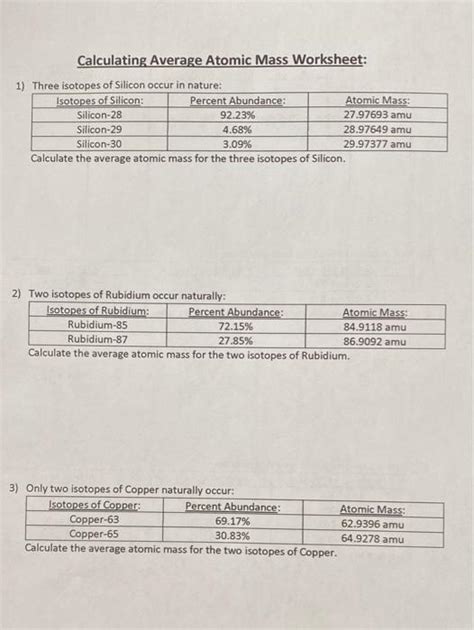
Isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties due to the same number of electrons (which is equal to the number of protons in a neutral atom), but they differ in physical properties such as mass due to the varying number of neutrons in the nucleus. For example, carbon has two main isotopes: carbon-12 (with 6 protons and 6 neutrons) and carbon-13 (with 6 protons and 7 neutrons), along with a trace amount of carbon-14 (with 6 protons and 8 neutrons). The average atomic mass of carbon is not simply the mass of one of these isotopes but a calculated value that takes into account the relative abundance of each isotope in nature.
Calculating Average Atomic Mass
The formula to calculate the average atomic mass (Aavg) of an element is given by the sum of the product of the mass of each isotope (mi) and its fractional abundance (fi): Aavg = Σ(mi * fi). For instance, if we consider the isotopes of neon: neon-20 (with a mass of approximately 19.9924 u and an abundance of about 90.48%), neon-21 (with a mass of approximately 20.9938 u and an abundance of about 0.27%), and neon-22 (with a mass of approximately 21.9914 u and an abundance of about 9.25%), we can calculate the average atomic mass of neon using these values.
| Isotope | Mass (u) | Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Neon-20 | 19.9924 | 90.48 |
| Neon-21 | 20.9938 | 0.27 |
| Neon-22 | 21.9914 | 9.25 |
Practical Application and Importance

The average atomic mass is crucial in chemistry for calculating the amount of substance (moles) of an element or compound in a given mass of sample. This is essential for stoichiometric calculations in chemical reactions, ensuring the right proportions of reactants are used to achieve the desired products. Moreover, understanding isotopic compositions and their averages can provide insights into geological and biological processes, such as dating of archaeological samples or tracing the source of environmental pollutants.
Key Points
- The average atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes.
- Isotopes have the same chemical properties but differ in mass due to different numbers of neutrons.
- The calculation of average atomic mass involves the masses and relative abundances of the isotopes.
- Accurate values for isotope masses and abundances are necessary for precise calculations.
- The average atomic mass is vital for stoichiometric calculations and understanding various scientific phenomena.
Evidence-Based Analysis
Evidence from various fields, including physics, chemistry, and geology, supports the importance of average atomic mass in understanding elemental composition and reactions. For example, the average atomic mass of carbon is approximately 12.011 u, which reflects the predominance of carbon-12. This value is critical in biochemical reactions, where carbon plays a central role, and in environmental science, where understanding the carbon cycle is essential for addressing climate change.
In conclusion, finding the average atomic mass involves a straightforward yet nuanced process that requires understanding the isotopic composition of elements and applying the formula that weights these isotopes by their abundance. This concept is fundamental to chemistry and has far-reaching implications in various scientific disciplines.
What is the purpose of calculating the average atomic mass of an element?
+The average atomic mass is essential for calculating the amount of substance (in moles) of an element or compound in a given mass of sample, which is critical for stoichiometric calculations in chemical reactions.
How do isotopes affect the average atomic mass of an element?
+Isotopes of an element have different masses due to varying numbers of neutrons, and their relative abundances contribute to the overall average atomic mass of the element.
Where can accurate values for isotope masses and abundances be found?
+Accurate values for isotope masses and abundances can be found in scientific literature or databases maintained by reputable scientific organizations, such as the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).