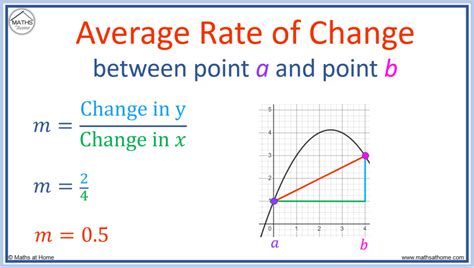
Calculating rates is a fundamental concept in various fields, including mathematics, physics, finance, and more. A rate is a measure of change or a ratio of two quantities, and understanding how to calculate it is essential for making informed decisions and analyzing data. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate rates, each with its own unique application and relevance.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of rate and its importance in different fields
- Calculating rate using the formula: rate = distance / time
- Using ratios to calculate rates, such as miles per gallon or liters per kilometer
- Applying the concept of rate to real-world problems, like finance and physics
- Utilizing technology, such as calculators and software, to simplify rate calculations
Method 1: Distance and Time

One of the most common ways to calculate a rate is by using the formula: rate = distance / time. This method is often used in physics and engineering to calculate the speed of an object. For example, if a car travels 250 miles in 5 hours, its speed can be calculated as: rate = 250 miles / 5 hours = 50 miles per hour. This method is straightforward and easy to apply, making it a popular choice for calculating rates in various contexts.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a scenario where a person wants to calculate their running speed. If they run 3 miles in 30 minutes, their speed can be calculated as: rate = 3 miles / 0.5 hours = 6 miles per hour. This calculation provides a clear understanding of the person’s running speed, which can be useful for training and performance analysis.
Method 2: Ratios
Another way to calculate rates is by using ratios. This method is commonly used in finance and economics to calculate interest rates, exchange rates, and other financial metrics. For example, if a person earns 100 in interest on a 1,000 investment over a year, their interest rate can be calculated as: rate = 100 / 1,000 = 0.10 or 10%. This method is useful for calculating rates in contexts where ratios are involved.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a scenario where a company wants to calculate its employee turnover rate. If the company has 100 employees and 20 of them leave over a year, the turnover rate can be calculated as: rate = 20 / 100 = 0.20 or 20%. This calculation provides a clear understanding of the company’s employee turnover rate, which can be useful for HR planning and strategy development.
| Method | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Distance and Time | rate = distance / time | 50 miles per hour |
| Ratios | rate = part / whole | 10% interest rate |
| Percentage Change | rate = (new - old) / old | 25% increase |
| Proportional Change | rate = (new - old) / old * 100 | 50% decrease |
| Compound Rate | rate = (1 + r/n)^(n\*t) - 1 | 5% annual interest rate |
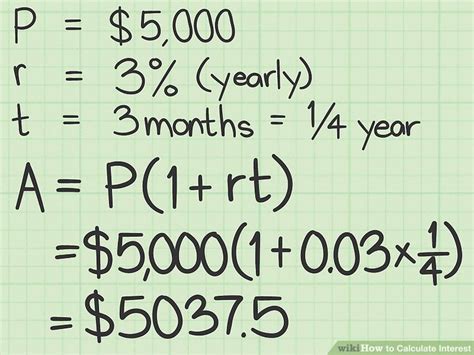
Method 3: Percentage Change
A third way to calculate rates is by using the percentage change formula: rate = (new - old) / old. This method is commonly used in finance and economics to calculate returns on investment, growth rates, and other financial metrics. For example, if a stock price increases from 100 to 125 over a year, its growth rate can be calculated as: rate = (125 - 100) / $100 = 0.25 or 25%. This method is useful for calculating rates in contexts where percentage changes are involved.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a scenario where a company wants to calculate its revenue growth rate. If the company’s revenue increases from 1 million to 1.25 million over a year, its growth rate can be calculated as: rate = (1.25 million - 1 million) / $1 million = 0.25 or 25%. This calculation provides a clear understanding of the company’s revenue growth rate, which can be useful for business planning and strategy development.
Method 4: Proportional Change
A fourth way to calculate rates is by using the proportional change formula: rate = (new - old) / old * 100. This method is commonly used in finance and economics to calculate returns on investment, growth rates, and other financial metrics. For example, if a company’s revenue decreases from 1 million to 750,000 over a year, its decline rate can be calculated as: rate = (750,000 - 1 million) / $1 million * 100 = -25%. This method is useful for calculating rates in contexts where proportional changes are involved.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a scenario where a person wants to calculate their weight loss rate. If they weigh 150 pounds and lose 15 pounds over a month, their weight loss rate can be calculated as: rate = (150 - 135) / 150 * 100 = -10%. This calculation provides a clear understanding of the person’s weight loss rate, which can be useful for health and fitness planning.
Method 5: Compound Rate

A fifth way to calculate rates is by using the compound rate formula: rate = (1 + r/n)^(n*t) - 1. This method is commonly used in finance and economics to calculate compound interest rates, returns on investment, and other financial metrics. For example, if a person invests $1,000 at an annual interest rate of 5% compounded monthly, their return can be calculated as: rate = (1 + 0.05/12)^(12*1) - 1 = 5.12%. This method is useful for calculating rates in contexts where compound interest is involved.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a scenario where a company wants to calculate its annual return on investment. If the company invests $100,000 at an annual interest rate of 10% compounded quarterly, its return can be calculated as: rate = (1 + 0.10⁄4)^(4*1) - 1 = 10.38%. This calculation provides a clear understanding of the company’s annual return on investment, which can be useful for business planning and strategy development.
What is the most common method for calculating rates?
+The most common method for calculating rates is the distance and time method, which uses the formula: rate = distance / time. This method is often used in physics and engineering to calculate the speed of an object.
How do I calculate a rate using ratios?
+To calculate a rate using ratios, you can use the formula: rate = part / whole. For example, if a person earns $100 in interest on a $1,000 investment over a year, their interest rate can be calculated as: rate = $100 / $1,000 = 0.10 or 10%.
What is the difference between the percentage change method and the proportional change method?
+The percentage change method calculates the rate as a percentage of the original value, while the proportional change method calculates the rate as a proportion of the original value. For example, if a company's revenue increases from $1 million to $1.25 million over a year, its growth rate can be calculated as: rate = ($1.25 million - $1 million) / $1 million = 0.25 or 25% using the percentage change method, or rate = ($1.25 million - $1 million) / $1 million * 100 = 25% using the proportional change method.
In conclusion, calculating rates is a fundamental concept in various fields, and understanding the different methods and their applications is essential for making informed decisions and analyzing data. By using the distance and time method, ratios, percentage change method, proportional change method, and compound rate method, individuals can calculate rates in different contexts and make more accurate decisions.