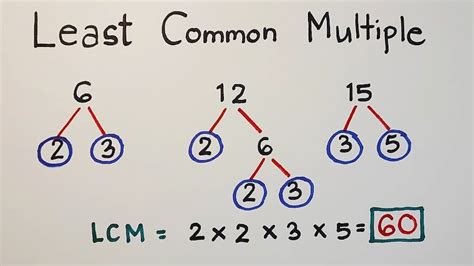
When dealing with multiple numbers, finding the least common multiple (LCM) can be a challenging task, especially for large numbers. However, with the right approach and understanding of the concept, it can be made easier. The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of each of the given numbers. In this article, we will explore the methods to find the LCM easily and efficiently.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of LCM and its importance in mathematics
- Using the prime factorization method to find LCM
- Applying the division method to calculate LCM
- Utilizing online tools and calculators for quick LCM calculation
- Practicing with examples to master the LCM calculation
Understanding LCM and Its Importance

The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory. It is used to find the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more given numbers. The LCM has numerous applications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science. For instance, LCM is used in finding the common period of two or more periodic functions, in calculating the greatest common divisor (GCD), and in solving linear congruences.
Prime Factorization Method
One of the most effective methods to find the LCM is the prime factorization method. This method involves finding the prime factors of each given number and then taking the product of the highest powers of all the prime factors. The prime factorization of a number can be found by dividing it by prime numbers starting from 2 until the quotient is 1. For example, to find the LCM of 12 and 15, we need to find their prime factorizations: 12 = 2^2 * 3 and 15 = 3 * 5. Then, the LCM is calculated as 2^2 * 3 * 5 = 60.
| Number | Prime Factorization | LCM |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 2^2 * 3 | 2^2 * 3 * 5 = 60 |
| 15 | 3 * 5 | 2^2 * 3 * 5 = 60 |
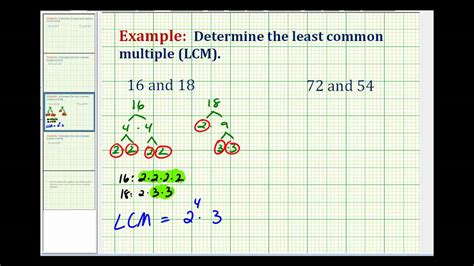
Division Method
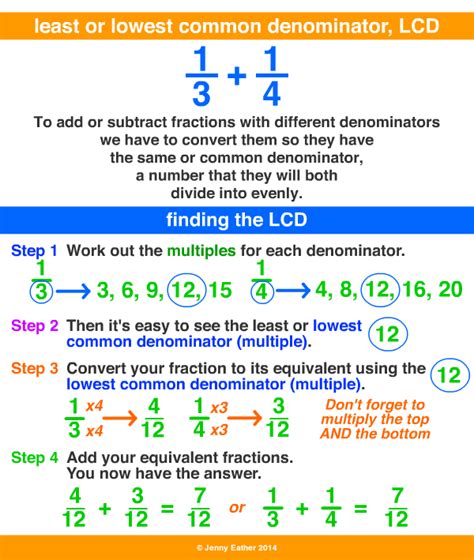
Another method to find the LCM is the division method. This method involves dividing the given numbers by their common factors until the remainder is 1. The LCM is then calculated as the product of the divisors. For example, to find the LCM of 12 and 15 using the division method, we start by dividing 12 by 3, which gives a quotient of 4 and a remainder of 0. Then, we divide 15 by 3, which gives a quotient of 5 and a remainder of 0. Finally, we multiply the divisors (4 and 5) to get the LCM, which is 60.
Using Online Tools and Calculators
In today’s digital age, there are numerous online tools and calculators available that can calculate the LCM quickly and efficiently. These tools can be particularly useful when dealing with large numbers or when time is of the essence. Some popular online LCM calculators include the LCM calculator by Mathway, the LCM calculator by Wolfram Alpha, and the LCM calculator by CalculatorSoup. These tools can save time and effort, allowing users to focus on other aspects of their work or study.
Practicing with Examples
As with any mathematical concept, practice is key to mastering the LCM calculation. It’s essential to practice with various examples, starting with simple numbers and gradually moving on to more complex ones. This will help build confidence and fluency in calculating the LCM. Some examples to try include finding the LCM of 24 and 30, the LCM of 48 and 60, and the LCM of 120 and 180.
What is the LCM of two prime numbers?
+The LCM of two prime numbers is their product, since they have no common factors other than 1.
How do I find the LCM of three or more numbers?
+To find the LCM of three or more numbers, find the LCM of the first two numbers, and then find the LCM of the result and the third number, and so on.
What is the relationship between LCM and GCD?
+The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the numbers themselves, i.e., LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b.
In conclusion, finding the LCM can be made easier by using the prime factorization method, the division method, or online tools and calculators. Practicing with examples and understanding the concept of LCM are essential to mastering its calculation. With this knowledge, users can efficiently calculate the LCM and apply it to various mathematical and real-world problems.