The concept of finding the pKa from pH is a fundamental aspect of chemistry, particularly in the fields of biochemistry and pharmacology. Understanding the relationship between pKa and pH is crucial for predicting the behavior of molecules in different environments. In this article, we will delve into the principles behind pKa and pH, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to calculate pKa from pH.
Introduction to pKa and pH

pKa, also known as the acid dissociation constant, is a measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It represents the pH at which the concentration of the acid is equal to the concentration of its conjugate base. On the other hand, pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The relationship between pKa and pH is described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, which is a fundamental concept in chemistry.
The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
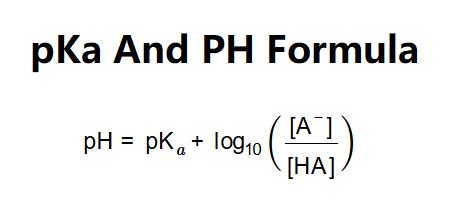
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is given by: pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]), where [A-] is the concentration of the conjugate base and [HA] is the concentration of the acid. This equation provides a simple way to calculate the pKa of an acid from its pH and the concentrations of the acid and its conjugate base.
Key Points
- The pKa is a measure of the strength of an acid in solution.
- The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation describes the relationship between pKa and pH.
- The equation is given by: pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]).
- The pKa can be calculated from the pH and the concentrations of the acid and its conjugate base.
- Understanding the relationship between pKa and pH is crucial for predicting the behavior of molecules in different environments.
Calculating pKa from pH

To calculate the pKa from pH, we need to rearrange the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to solve for pKa. This gives us: pKa = pH - log([A-]/[HA]). We can then plug in the values of pH, [A-], and [HA] to calculate the pKa.
Example Calculation
Suppose we have a solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH) with a pH of 4.5 and a concentration of 0.1 M. The concentration of the conjugate base (CH3COO-) is 0.01 M. We can calculate the pKa of acetic acid using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: pKa = 4.5 - log(0.01/0.1) = 4.5 - log(0.1) = 4.5 - (-1) = 5.5.
| Acid | pKa | pH | [A-] | [HA] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid | 5.5 | 4.5 | 0.01 M | 0.1 M |
Practical Applications
Understanding the relationship between pKa and pH has numerous practical applications in chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology. For example, in drug development, the pKa of a drug can affect its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties. A drug with a pKa close to the physiological pH (7.4) will be more likely to be absorbed and distributed effectively.
Biological Relevance
In biological systems, the pKa of an acid can affect its interaction with proteins, membranes, and other biomolecules. For example, the pKa of a drug can affect its binding affinity to a protein receptor, which can impact its efficacy and toxicity.
What is the relationship between pKa and pH?
+The relationship between pKa and pH is described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]).
How do I calculate the pKa from pH?
+To calculate the pKa from pH, rearrange the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to solve for pKa: pKa = pH - log([A-]/[HA]).
What is the practical significance of pKa in chemistry and biochemistry?
+Understanding the relationship between pKa and pH has numerous practical applications in chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, including drug development, protein binding, and biological interactions.
In conclusion, calculating the pKa from pH is a straightforward process using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. Understanding the relationship between pKa and pH is essential for predicting the behavior of molecules in different environments, with numerous practical applications in chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology.
Meta description: Learn how to calculate the pKa from pH using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, and understand the practical significance of pKa in chemistry and biochemistry. (150 characters)