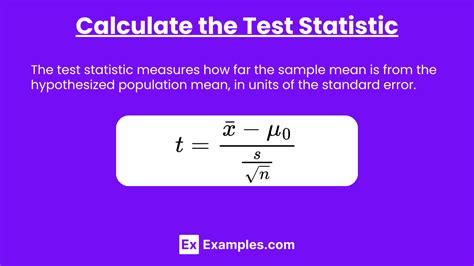
When it comes to statistical analysis, calculating the test statistic is a crucial step in determining the significance of the results. In this article, we will explore the concept of test statistics, their importance in statistical inference, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to calculate them easily. Whether you are a student, researcher, or data analyst, understanding test statistics is essential for making informed decisions based on data.
Key Points
- The test statistic is a numerical value that helps determine the significance of the results in a statistical test.
- There are different types of test statistics, including the z-score, t-score, and F-score, each used in different scenarios.
- Calculating the test statistic involves using a formula specific to the type of test being conducted.
- Interpreting the test statistic requires comparing it to a critical value or using a p-value to determine statistical significance.
- Statistical software and calculators can simplify the process of calculating test statistics.
Understanding Test Statistics

A test statistic is a numerical value that is used to determine whether the null hypothesis should be rejected or failed to be rejected. The null hypothesis is a statement of no effect or no difference, and the alternative hypothesis is a statement of an effect or difference. The test statistic is calculated from the sample data and is used to determine the probability of observing the results, or more extreme, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
Types of Test Statistics
There are several types of test statistics, each used in different scenarios. The most common types include:
- Z-score: Used for large samples (n > 30) and when the population standard deviation is known.
- T-score: Used for small samples (n ≤ 30) and when the population standard deviation is unknown.
- F-score: Used for analysis of variance (ANOVA) and regression analysis.
Calculating Test Statistics
Calculating the test statistic involves using a formula specific to the type of test being conducted. Here are the formulas for the z-score, t-score, and F-score:
| Test Statistic | Formula |
|---|---|
| Z-score | z = (x̄ - μ) / (σ / √n) |
| T-score | t = (x̄ - μ) / (s / √n) |
| F-score | F = (MSbetween / MSwithin) |
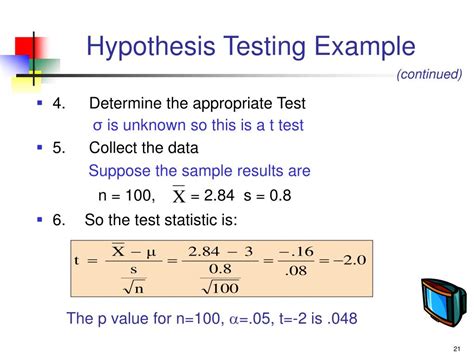
Where:
- x̄ = sample mean
- μ = population mean
- σ = population standard deviation
- s = sample standard deviation
- n = sample size
- MSbetween = mean square between groups
- MSwithin = mean square within groups
Interpreting Test Statistics
Once the test statistic is calculated, it needs to be interpreted. This involves comparing the test statistic to a critical value or using a p-value to determine statistical significance. The critical value is a pre-determined value that the test statistic must exceed in order to reject the null hypothesis. The p-value is the probability of observing the results, or more extreme, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
Using Statistical Software and Calculators
Calculating test statistics can be a tedious and time-consuming process, especially for large datasets. Fortunately, there are many statistical software programs and calculators available that can simplify the process. Some popular options include:
- R
- Python
- Excel
- SPSS
- SAS
These programs can perform a wide range of statistical tests, including hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and analysis of variance.
What is the purpose of a test statistic?
+The purpose of a test statistic is to determine whether the null hypothesis should be rejected or failed to be rejected. It helps to determine the significance of the results in a statistical test.
How do I choose the correct test statistic?
+The choice of test statistic depends on the research question, the type of data, and the level of measurement. For example, the z-score is used for large samples and when the population standard deviation is known, while the t-score is used for small samples and when the population standard deviation is unknown.
Can I use statistical software to calculate test statistics?
+Yes, there are many statistical software programs available that can calculate test statistics, including R, Python, Excel, SPSS, and SAS. These programs can simplify the process of calculating test statistics and perform a wide range of statistical tests.
In conclusion, test statistics are a crucial component of statistical inference, and understanding how to calculate and interpret them is essential for making informed decisions based on data. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily calculate test statistics and determine the significance of your results. Remember to choose the correct test statistic, consider the context of the study, and use statistical software and calculators to simplify the process.