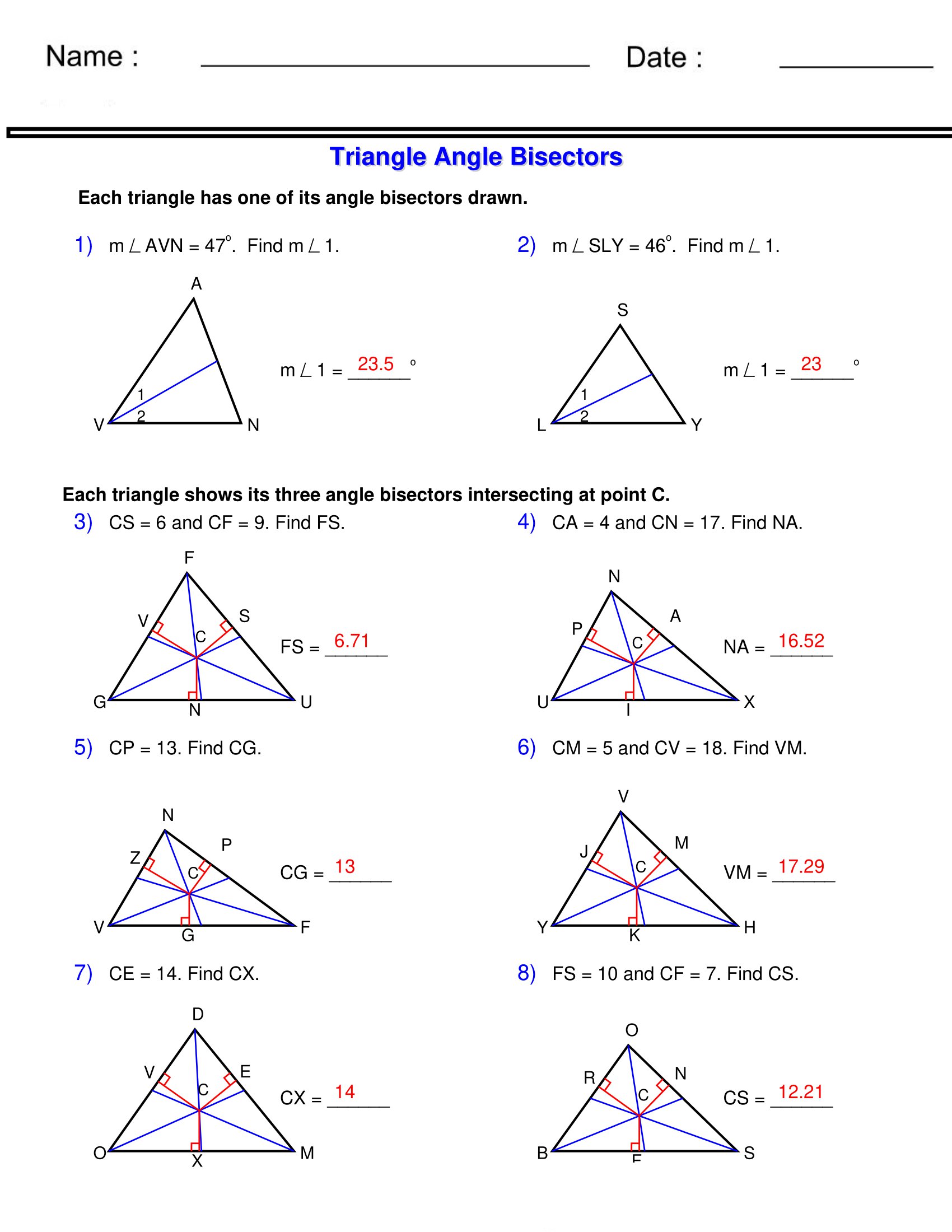
When it comes to geometry, one of the most fundamental concepts is the triangle, and understanding its angles is crucial for a wide range of applications, from architecture to engineering. Finding the angles of a triangle can seem daunting at first, but with the right approach and formulas, it becomes straightforward. In this article, we will delve into the world of triangles, exploring how to find their angles easily and efficiently, using both basic principles and advanced techniques.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic properties of triangles, including the sum of angles equaling 180 degrees.
- Using the Law of Cosines to find angles when all sides are known.
- Applying the Law of Sines for triangles where at least one angle and the lengths of two sides are known.
- Utilizing trigonometric ratios in right-angled triangles.
- Practical applications of triangle angle calculations in real-world scenarios.
Basic Principles of Triangles
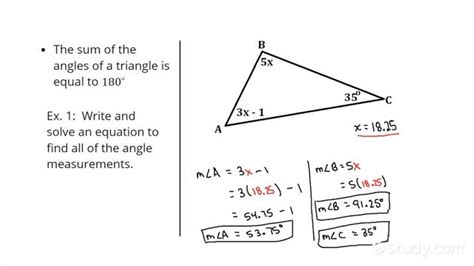
A triangle is defined by three points, known as vertices, which are connected by three lines, known as sides. One of the fundamental principles of triangles is that the sum of their interior angles is always 180 degrees. This principle is crucial for finding missing angles in a triangle. For instance, if you know two angles of a triangle, you can easily calculate the third by subtracting the sum of the known angles from 180 degrees.
Using the Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines is a powerful formula that allows you to find the length of any side of a triangle, given the lengths of the other two sides and the angle between them. It can also be rearranged to solve for an angle when all three sides are known. The formula is: (c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab\cos©), where (c) is the side opposite angle (C), and (a) and (b) are the other two sides. This formula can be particularly useful in scenarios where you have the dimensions of a triangle but need to find one of its angles.
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab\cos(C) | Law of Cosines to find side or angle |
| \frac{a}{\sin(A)} = \frac{b}{\sin(B)} = \frac{c}{\sin(C)} | Law of Sines to relate angles and sides |
Applying the Law of Sines
The Law of Sines is another essential formula for solving triangles. It states that the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is constant for all three sides and angles. This is expressed as (\frac{a}{\sin(A)} = \frac{b}{\sin(B)} = \frac{c}{\sin©}). The Law of Sines is particularly useful when you know at least one angle and the lengths of two sides, or when dealing with oblique triangles where the Law of Cosines might be more cumbersome to apply.
Trigonometric Ratios in Right-Angled Triangles
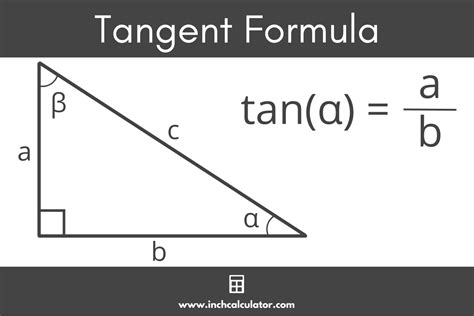
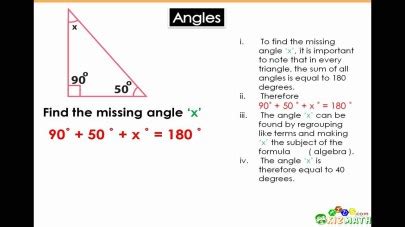
In right-angled triangles, where one angle is 90 degrees, trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent are invaluable for finding angles. These ratios are defined as the ratios of the lengths of the sides of the triangle. For example, (\sin(A) = \frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{hypotenuse}}), (\cos(A) = \frac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}}), and (\tan(A) = \frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{adjacent}}). By using these ratios, you can easily find the angles of a right-angled triangle if you know the lengths of its sides.
Practical Applications
Understanding how to find the angles of a triangle has numerous practical applications in various fields. In architecture, for example, calculating the angles of roofs or the stress on building frames is crucial for ensuring structural integrity. In surveying, triangle angle calculations are used to determine property boundaries and the layout of infrastructure projects. Moreover, in engineering, precise angle calculations are necessary for the design and construction of bridges, roads, and other critical infrastructure.
What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle?
+The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
How do I find an angle in a triangle if I know all the sides?
+You can use the Law of Cosines to find an angle in a triangle if you know all the sides. The formula is c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab\cos(C), where c is the side opposite angle C, and a and b are the other two sides.
What is the difference between the Law of Cosines and the Law of Sines?
+The Law of Cosines is used to find the length of a side of a triangle when you know the lengths of the other two sides and the angle between them, or to find an angle when all three sides are known. The Law of Sines, on the other hand, relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the sines of its angles, and is useful when you know at least one angle and the lengths of two sides.
In conclusion, finding the angles of a triangle is a fundamental skill that can be achieved through various methods, depending on the information available. Whether using the basic principle that the sum of angles in a triangle is 180 degrees, the Law of Cosines, the Law of Sines, or trigonometric ratios in right-angled triangles, each approach offers a powerful tool for solving triangle problems. By mastering these techniques and understanding their applications, individuals can tackle a wide range of problems in geometry and beyond, contributing to advancements in fields such as architecture, engineering, and surveying.
Meta Description: Learn how to find triangle angles easily using basic principles, the Law of Cosines, the Law of Sines, and trigonometric ratios. Discover practical applications and expert insights in geometry.