The concept of discriminant is a fundamental aspect of various mathematical and statistical disciplines, including algebra, calculus, and machine learning. In essence, the discriminant is a value that can be calculated from the coefficients of a polynomial equation or a statistical model, and it provides crucial information about the nature of the solutions or the model's performance. Here, we will delve into five distinct ways to find the discriminant, each applicable to different contexts and mathematical constructs.
Introduction to Discriminant

The discriminant is perhaps most famously known for its role in quadratic equations, where it determines the nature of the roots. However, its application extends far beyond, into areas such as conic sections, cubic equations, and even into the realm of machine learning and data analysis. The ability to calculate and interpret the discriminant is a critical skill for anyone working with mathematical or statistical models.
Key Points
- The discriminant can be used to determine the nature of the roots of a polynomial equation.
- In machine learning, the discriminant is used in discriminant analysis to classify data points into categories.
- The formula for the discriminant varies depending on the context, such as quadratic equations, cubic equations, or statistical models.
- Understanding the discriminant is crucial for solving equations, analyzing data, and making informed decisions in various fields.
- The discriminant can also provide insights into the performance and reliability of statistical models.
1. Quadratic Equations
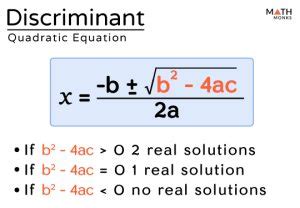
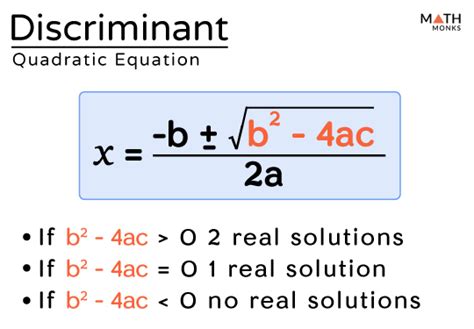
In the context of quadratic equations of the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, the discriminant is given by the formula \Delta = b^2 - 4ac. This value is pivotal in determining the nature of the roots of the equation. If \Delta > 0, the equation has two distinct real roots. If \Delta = 0, the equation has one real root (or two identical real roots). And if \Delta < 0, the equation has no real roots, implying the existence of complex roots.
Calculation Example
For the quadratic equation x^2 + 5x + 6 = 0, the coefficients are a = 1, b = 5, and c = 6. Plugging these values into the discriminant formula yields \Delta = 5^2 - 4(1)(6) = 25 - 24 = 1. Since \Delta > 0, the equation has two distinct real roots.
| Coefficient | Value |
|---|---|
| a | 1 |
| b | 5 |
| c | 6 |
| Discriminant ($\Delta$) | $b^2 - 4ac = 5^2 - 4(1)(6) = 1$ |
2. Cubic Equations
For cubic equations of the form ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d = 0, the discriminant is more complex and is given by \Delta = 18abcd - 4b^3d + b^2c^2 - 4ac^3 - 27a^2d^2. This discriminant can be used to determine the nature of the roots of the cubic equation, although its interpretation is more nuanced than in the quadratic case.
Interpretation of Discriminant in Cubic Equations
The discriminant of a cubic equation can tell us if the equation has any repeated roots. If \Delta > 0, the equation has three distinct real roots. If \Delta = 0, the equation has a repeated root (at least two roots are the same). If \Delta < 0, the equation has one real root and two complex conjugate roots.
3. Conic Sections
In the context of conic sections, the discriminant can be used to determine the type of conic section represented by a given equation. For an equation of the form Ax^2 + Bxy + Cy^2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0, the discriminant is B^2 - 4AC. The value of this discriminant determines whether the conic section is an ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola.
Classification Based on Discriminant
If B^2 - 4AC < 0, the conic section is an ellipse. If B^2 - 4AC = 0, it is a parabola. And if B^2 - 4AC > 0, the conic section is a hyperbola. This classification is essential in understanding the geometric properties and behaviors of conic sections.
4. Machine Learning and Discriminant Analysis

In machine learning, discriminant analysis is a technique used for classifying data points into categories. The discriminant in this context is a function that combines the features of the data in such a way that the classes are well-separated. The most common form of discriminant analysis is linear discriminant analysis (LDA), where the discriminant function is linear.
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
LDA seeks to find linear combinations of features that characterizes or separates classes of data. The discriminant function in LDA is derived to maximize the ratio of the between-class variance to the within-class variance, ensuring that the classes are as distinct as possible.
5. Statistical Models
In statistical modeling, particularly in regression analysis, the discriminant can refer to the ability of a model to distinguish between different outcomes or classes. For logistic regression, a common statistical model for binary classification, the discriminant is related to the log-odds of an event occurring.
Logistic Regression and Discriminant
The logistic regression model estimates probabilities using a logistic function, which can be interpreted as a discriminant function that maps the input features to a probability of belonging to a particular class. The model’s ability to discriminate between classes is fundamental to its predictive power.
What is the primary use of the discriminant in quadratic equations?
+The primary use of the discriminant in quadratic equations is to determine the nature of the roots, whether they are real and distinct, real and identical, or complex.
How does the discriminant in cubic equations differ from that in quadratic equations?
+The discriminant in cubic equations is more complex and is used to determine if the equation has any repeated roots, unlike in quadratic equations where it simply determines the nature of the roots.
What role does the discriminant play in machine learning, specifically in discriminant analysis?
+In machine learning, the discriminant in discriminant analysis is a function that combines features to separate classes of data. It is used for classifying data points into categories based on their features.
In conclusion, the concept of discriminant is versatile and applies to various mathematical and statistical contexts, each with its unique formula and interpretation. Understanding the discriminant and how to calculate it is essential for solving equations, analyzing data, and making informed decisions in fields ranging from algebra and calculus to machine learning and statistical modeling.