The concept of mass is a fundamental aspect of physics, and understanding it is crucial for a wide range of applications, from engineering to cosmology. Finding mass easily is a matter of applying the right techniques and formulas, depending on the context and the information available. In this article, we will explore the different methods for determining mass, discussing the principles behind each approach and providing examples to illustrate their application.
Key Points
- Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, and it can be determined using various methods, including weight, density, and volume calculations.
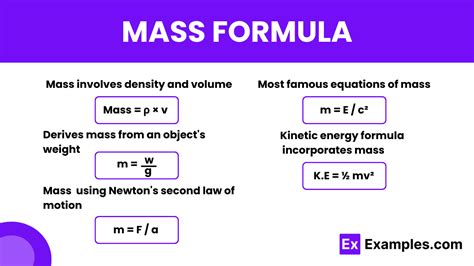
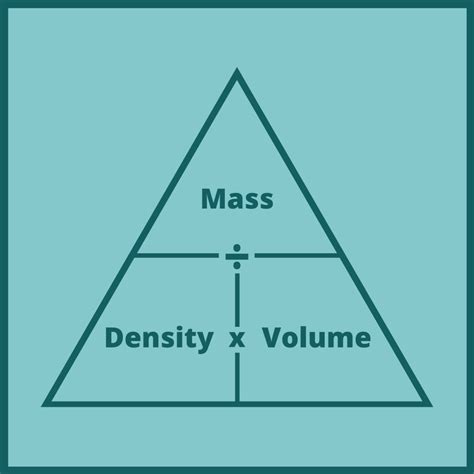
- The formula for mass, m = ρV, relates mass to density and volume, and it is a key concept in understanding how to find mass easily.
- Inertial mass is a measure of an object's resistance to changes in its motion, and it can be determined through experiments involving force and acceleration.
- Gravitational mass is the measure of the strength of an object's gravitational pull, and it is what gives rise to weight.
- Understanding the distinction between mass and weight is crucial, as weight is a force that depends on both mass and gravity, while mass is an intrinsic property of an object.
Understanding Mass and Its Measurement
Mass is a fundamental property of objects that determines their resistance to changes in motion (inertial mass) and their gravitational interaction with other objects (gravitational mass). The SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg), and it is defined as the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram, a platinum-iridium alloy cylinder stored at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in France.
Methods for Finding Mass
There are several methods for finding mass, each with its own set of applications and limitations. One of the most common methods is to use a balance or scale, which compares the weight of an object to a set of standard masses. This method is straightforward but requires that the object be accessible and that the balance be calibrated correctly.
Another method for finding mass is to use the formula m = ρV, where m is the mass, ρ (rho) is the density, and V is the volume of the object. This method requires knowledge of the object's density and volume, which can be determined through various means, such as measurement or calculation based on the object's geometry.
| Method | Description | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Balance or Scale | Compares the weight of an object to standard masses. | Requires access to the object and a calibrated balance. |
| Density and Volume Calculation | Uses the formula m = ρV to calculate mass from density and volume. | Requires knowledge of density and volume, which can be difficult to determine for complex shapes or heterogeneous materials. |
| Inertial Mass Experiment | Measures an object's resistance to changes in motion. | Requires a controlled environment and precise measurement of force and acceleration. |
Applications and Implications
The ability to find mass easily has numerous applications across various fields, from engineering and physics to biology and chemistry. In engineering, knowing the mass of components is essential for designing and optimizing systems, whether it’s a bridge, a car, or a rocket. In physics, mass is a critical parameter in understanding the behavior of particles and objects under different conditions, such as gravity, electromagnetism, and relativity.
In addition to its practical applications, understanding mass also has deep implications for our understanding of the universe. The distribution of mass within galaxies and galaxy clusters, for example, helps us understand the nature of dark matter and dark energy, which are thought to make up a large portion of the universe's mass-energy budget.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, finding mass easily is a matter of applying the right techniques and formulas, depending on the context and the information available. By understanding the principles behind each method and considering the limitations and requirements of each approach, one can ensure accurate and reliable measurements of mass. As our understanding of the universe and its underlying laws continues to evolve, the importance of mass as a fundamental property will only continue to grow, driving further research and innovation in fields ranging from cosmology to materials science.
What is the difference between mass and weight?
+Mass is an intrinsic property of an object that determines its resistance to changes in motion and its gravitational interaction with other objects. Weight, on the other hand, is a force that depends on both mass and gravity. While mass remains constant regardless of location, weight can vary depending on the strength of the gravitational field.
How do you calculate mass using density and volume?
+The formula to calculate mass using density and volume is m = ρV, where m is the mass, ρ (rho) is the density, and V is the volume. By rearranging this formula, you can solve for mass if you know the density and volume of the object.
What are some common units of mass?
+Common units of mass include the kilogram (kg), gram (g), milligram (mg), and tonne (t). The kilogram is the SI unit of mass and is defined as the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram.