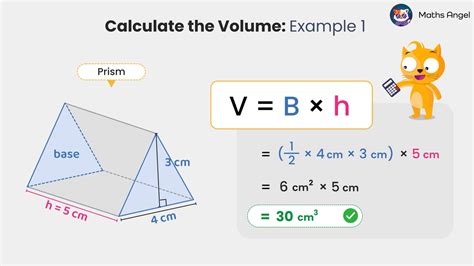
Calculating the volume of an object is a fundamental concept in mathematics and physics, with applications in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and science. The volume of an object is a measure of the amount of space it occupies, and it can be calculated using different formulas depending on the shape of the object. In this article, we will explore five ways to find the volume of different objects, highlighting the formulas, techniques, and examples for each method.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic formulas for calculating volume, including length times width times height for rectangular prisms and (4/3)πr³ for spheres.
- Applying the concept of displacement to find the volume of irregularly shaped objects by measuring the volume of fluid displaced.
- Using integration to calculate the volume of complex shapes, such as cones, pyramids, and other solids of revolution.
- Employing the method of similar figures to compare volumes of similar objects and scale factors.
- Utilizing technology, such as 3D modeling software and calculators, to compute volumes of intricate shapes and designs.
Rectangular Prisms and the Basic Volume Formula
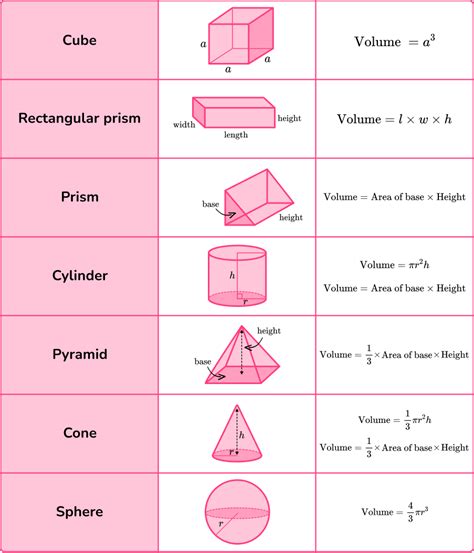
The most straightforward method to calculate volume is by using the formula for rectangular prisms, which is length times width times height (V = lwh). This formula applies to any object that has a rectangular shape, such as boxes, bricks, and books. For example, if you have a box with a length of 5 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 2 cm, the volume would be 5 cm * 3 cm * 2 cm = 30 cubic cm. This basic formula is the foundation for calculating the volume of more complex shapes.
Displacement Method for Irregular Shapes
For objects with irregular shapes, calculating volume directly can be challenging. However, the principle of fluid displacement provides a practical solution. According to Archimedes’ Principle, the volume of an object is equal to the volume of the fluid it displaces. By submerging the object in a fluid (like water) and measuring the volume of the displaced fluid, you can determine the volume of the object. This method is particularly useful for objects with complex shapes where direct calculation is not feasible.
| Shape | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangular Prism | V = lwh | 30 cubic cm (5 cm * 3 cm * 2 cm) |
| Sphere | V = (4/3)πr³ | Approx. 113.10 cubic cm (r = 3 cm) |

Integration for Complex Shapes
For shapes like cones, pyramids, and other solids of revolution, the volume can be found using integration. This method involves breaking down the shape into infinitesimally small disks or slices and summing up their volumes. The formula for the volume of a cone, for instance, is derived from integrating the area of circular slices with respect to the height of the cone, resulting in V = (1⁄3)πr²h. Similarly, the volume of a pyramid is V = (1⁄3)Bh, where B is the area of the base and h is the height. Integration provides a powerful tool for calculating the volumes of complex shapes that cannot be easily decomposed into simpler geometric figures.
Similar Figures and Scaling Factors
When dealing with similar figures, the concept of scaling factors becomes crucial. If two objects are similar, the ratio of their volumes is the cube of the ratio of their corresponding linear dimensions (like side lengths or heights). This principle allows for the comparison and calculation of volumes based on known scaling factors. For example, if one object is twice as large as another in all dimensions, its volume will be 2³ = 8 times larger. This method is useful in architecture, engineering, and design, where scaling models or prototypes is a common practice.
Technology and 3D Modeling
In modern times, technology plays a significant role in calculating volumes, especially for intricate shapes and designs. Software like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) programs, 3D modeling tools, and even certain calculators can compute volumes with high precision. These tools allow for the creation of complex models and the calculation of their volumes using algorithms and mathematical formulas, making the process faster and more accurate than manual calculations. This approach is invaluable in fields like aerospace, automotive, and product design, where precision and efficiency are paramount.
What is the formula for the volume of a sphere?
+The formula for the volume of a sphere is V = (4/3)πr³, where r is the radius of the sphere.
How do you calculate the volume of an irregularly shaped object?
+The volume of an irregularly shaped object can be calculated by measuring the volume of the fluid it displaces, according to Archimedes' Principle.
What role does integration play in finding volumes of complex shapes?
+Integration is used to find the volumes of complex shapes like cones and pyramids by summing up the volumes of infinitesimally small slices or disks that make up the shape.
In conclusion, calculating the volume of objects is a versatile task that can be approached from multiple angles, depending on the shape and complexity of the object. From the basic formula for rectangular prisms to the use of integration for complex shapes, and from the displacement method for irregular objects to the application of technology for intricate designs, each method has its place and utility. Understanding these different approaches not only enhances one’s mathematical and physical insight but also equips individuals with the skills to tackle a wide range of problems in various disciplines.