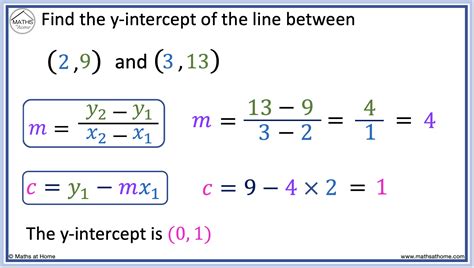
The process of finding the Y-intercept using two points involves understanding the slope-intercept form of a linear equation, which is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line, and b represents the Y-intercept. To find the Y-intercept, we first need to calculate the slope (m) using the two given points and then use one of the points along with the slope to solve for b, the Y-intercept.
Naturally Calculating Slope and Y-Intercept

Let’s assume the two points given are (x1, y1) and (x2, y2). The formula for calculating the slope (m) using these two points is m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1). Once we have the slope, we can substitute it back into the equation y = mx + b along with one of the points to solve for b, the Y-intercept.
Step-by-Step Calculation
For example, if the two points are (1, 3) and (2, 5), we first calculate the slope: m = (5 - 3) / (2 - 1) = 2 / 1 = 2. Now that we know the slope is 2, we can use one of the points, say (1, 3), and substitute into the equation to find b: 3 = 2(1) + b. Solving for b, we get b = 3 - 2 = 1. Therefore, the Y-intercept is 1.
| Point | X Coordinate | Y Coordinate |
|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Point 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Slope (m) | 2 | |
| Y-Intercept (b) | 1 | |
Key Points
- The slope (m) of a line can be found using the formula m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) with two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
- The Y-intercept (b) can be calculated by substituting the slope and one of the points into the equation y = mx + b and solving for b.
- Accuracy in identifying the points on the line is essential for correct slope and Y-intercept calculations.
- The equation y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the Y-intercept, is fundamental in understanding linear relationships.
- Real-world applications of slope and Y-intercept calculations are found in physics, engineering, economics, and more, where understanding rates of change and initial conditions is critical.
Understanding the Conceptual Framework

It’s also important to understand that the Y-intercept is not just a mathematical concept but has practical implications. For instance, in economics, the Y-intercept of a demand curve can indicate the maximum price consumers are willing to pay for a product when the quantity supplied is zero. Similarly, in physics, the Y-intercept of a velocity-time graph can represent the initial velocity of an object.
Evolutionary Developments and Methodological Approaches
Over time, the calculation of the Y-intercept has evolved with the development of more sophisticated mathematical tools and computational methods. However, the fundamental principle remains the same. The use of graphical calculators and computer software has made it easier to visualize and calculate the Y-intercept, especially for complex equations. Nonetheless, understanding the manual calculation process is essential for a deep comprehension of linear equations and their applications.
When dealing with non-linear equations, the concept of a Y-intercept still applies but may require more complex calculations or approximations. In such cases, numerical methods or graphical representations can be invaluable tools for estimating the Y-intercept.
What is the significance of the Y-intercept in real-world applications?
+The Y-intercept has significant implications in various fields, including physics, economics, and engineering, where it can represent initial conditions, maximum or minimum values, or points of reference.
How do you calculate the Y-intercept using two points?
+First, calculate the slope using the formula m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), then substitute the slope and one of the points into the equation y = mx + b to solve for b, the Y-intercept.
What is the equation for the slope of a line given two points?
+The equation for the slope (m) given two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1).
Meta Description: Find the Y-intercept with two points using the slope-intercept form of a linear equation, understanding the slope calculation, and solving for b with real-world applications and examples.