The concept of velocity is a fundamental aspect of physics and engineering, referring to the rate of change of an object's position with respect to time. Calculating velocity is crucial in understanding the motion of objects, whether it's a car moving down the road, a ball thrown through the air, or a spacecraft soaring through the cosmos. In this article, we will delve into the world of velocity, exploring the different types, formulas, and methods for calculating it, as well as providing practical examples and applications.
Understanding Velocity

Velocity is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude (amount of movement) and direction. It is typically denoted by the symbol “v” and is measured in units of distance per unit time, such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h). There are two main types of velocity: instantaneous velocity, which is the velocity of an object at a specific point in time, and average velocity, which is the total displacement of an object divided by the total time taken.
Key Points
- Velocty is a vector quantity with magnitude and direction
- Instantaneous velocity is the velocity at a specific point in time
- Average velocity is the total displacement divided by total time
- Velocity is measured in units of distance per unit time
- Calculating velocity is crucial in understanding object motion
Formulas for Calculating Velocity
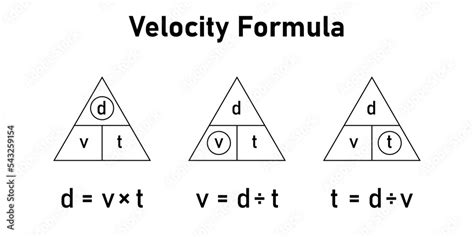
The formula for calculating velocity depends on the type of velocity being measured. For instantaneous velocity, the formula is v = dx/dt, where v is the velocity, dx is the infinitesimal displacement, and dt is the infinitesimal time interval. For average velocity, the formula is v_avg = Δx / Δt, where v_avg is the average velocity, Δx is the total displacement, and Δt is the total time taken.
| Velocity Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Instantaneous Velocity | v = dx/dt |
| Average Velocity | v_avg = Δx / Δt |

In addition to these formulas, there are also equations of motion that can be used to calculate velocity, such as the equation v = u + at, where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration, and t is the time. These equations are essential in understanding the motion of objects under the influence of forces such as gravity or friction.
Practical Applications of Velocity
Velocity plays a critical role in various fields, including physics, engineering, and sports. In physics, velocity is used to describe the motion of particles, waves, and objects. In engineering, velocity is used to design and optimize systems, such as engines, gears, and brakes. In sports, velocity is used to analyze and improve athletic performance, such as the velocity of a baseball pitch or the velocity of a sprinter.
For example, in the context of space exploration, calculating the velocity of a spacecraft is crucial in determining its trajectory and ensuring a successful mission. The velocity of a spacecraft must be carefully controlled to achieve orbit, escape Earth's gravity, or land safely on another planet. Similarly, in the context of automotive engineering, understanding the velocity of a vehicle is essential in designing safety features, such as airbags and anti-lock braking systems.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Velocity
When calculating velocity, there are several common mistakes to avoid. One of the most common mistakes is confusing velocity with speed, which is a scalar quantity that only has magnitude. Another mistake is failing to consider the reference frame in which the object is moving, which can lead to incorrect calculations. Additionally, neglecting to account for external forces, such as friction or air resistance, can also lead to errors in calculating velocity.
What is the difference between velocity and speed?
+Velocity is a vector quantity with magnitude and direction, while speed is a scalar quantity with only magnitude.
How do I calculate the velocity of an object?
+The formula for calculating velocity depends on the type of velocity being measured. For instantaneous velocity, use v = dx/dt, and for average velocity, use v_avg = Δx / Δt.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when calculating velocity?
+Common mistakes include confusing velocity with speed, failing to consider the reference frame, and neglecting to account for external forces.
In conclusion, velocity is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering that plays a critical role in understanding the motion of objects. By mastering the formulas and methods for calculating velocity, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the world around them and develop practical applications in various fields. Whether you’re a student, engineer, or simply a curious individual, understanding velocity can help you navigate the complexities of motion and unlock new insights into the natural world.