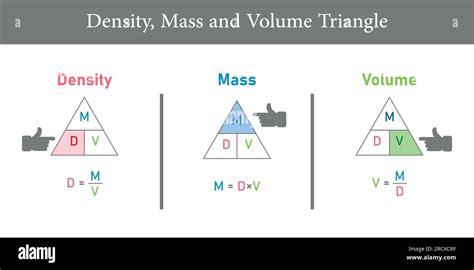
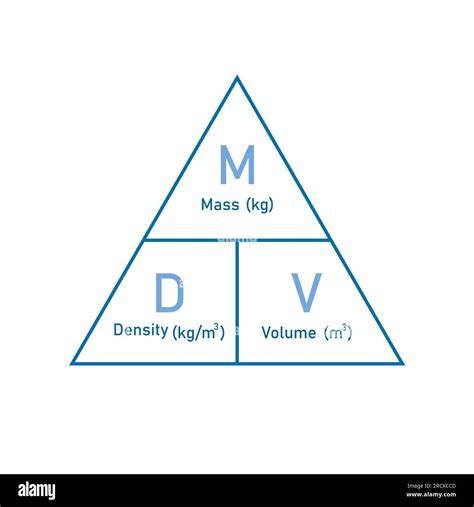
The calculation of mass from density and volume is a fundamental concept in physics, widely applied across various fields including engineering, chemistry, and materials science. Understanding this relationship is crucial for determining the properties of substances and objects. The formula that connects mass, density, and volume is straightforward yet powerful: mass equals density times volume (m = ρV), where m is the mass of the object, ρ (rho) is the density of the material, and V is the volume of the object.
Understanding Density and Volume

Before diving into the calculation, it’s essential to grasp the concepts of density and volume. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. It’s expressed in units such as grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). Volume, on the other hand, refers to the amount of space that a substance or object occupies, measured in units like cubic meters (m³), liters (L), or cubic centimeters (cm³).
Calculating Mass
Given the density and volume of an object, calculating its mass is straightforward using the formula m = ρV. For instance, if you know that the density of water is approximately 1 gram per cubic centimeter (1 g/cm³) and you have a container that holds 1000 cubic centimeters (1000 cm³) of water, you can calculate the mass of the water as follows: m = ρV = 1 g/cm³ * 1000 cm³ = 1000 grams, or 1 kilogram.
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density of Water | 1 | g/cm³ |
| Volume of Water | 1000 | cm³ |
| Calculated Mass | 1000 | grams or 1 kg |
Practical Applications

The application of the formula m = ρV is diverse, ranging from everyday calculations to complex engineering and scientific research. For instance, in the field of materials science, knowing the density of a material can help in understanding its properties and potential applications. In chemical engineering, calculating the mass of substances is critical for stoichiometric calculations and process design.
Addressing Limitations and Potential Objections
One potential limitation of this formula is the assumption that the density of the substance is uniform throughout, which may not always be the case, especially in mixtures or in materials that exhibit significant variations in density. Moreover, measuring volume and density accurately can sometimes be challenging, particularly for irregularly shaped objects or substances with complex compositions.
Key Points
- The formula m = ρV is used to calculate mass from density and volume.
- Density is mass per unit volume, expressed in units like g/cm³ or kg/m³.
- Volume refers to the space occupied by a substance or object, measured in units like m³, L, or cm³.
- Ensuring compatible units for density and volume is crucial for accurate calculations.
- The application of this formula is widespread, including materials science, chemical engineering, and everyday calculations.
Evidence-Based Analysis
Evidence from various scientific fields supports the use and accuracy of the formula m = ρV. Experimental data from physics, chemistry, and engineering consistently show that when density and volume are accurately measured, the calculated mass matches the actual mass of the object or substance. This consistency underscores the reliability of the formula for a wide range of applications.
Forward-Looking Implications
As research and technology advance, the importance of accurately calculating mass from density and volume will continue to grow. In fields like aerospace engineering, where materials with specific density properties are crucial, or in biomedicine, where understanding the density of tissues can aid in diagnosis and treatment, the precise calculation of mass will remain a fundamental aspect of scientific and engineering practice.
What is the formula to calculate mass from density and volume?
+The formula is m = ρV, where m is the mass, ρ is the density, and V is the volume.
Why is it important to match the units of density and volume?
+Matching the units ensures that the calculation is accurate and avoids errors due to unit mismatches.
What are some practical applications of calculating mass from density and volume?
+Applications include materials science, chemical engineering, and everyday calculations for determining the properties of substances and objects.
Meta Description: Calculate mass from density and volume using the formula m = ρV. Understand the concepts of density and volume, and apply them to various fields such as materials science and engineering.