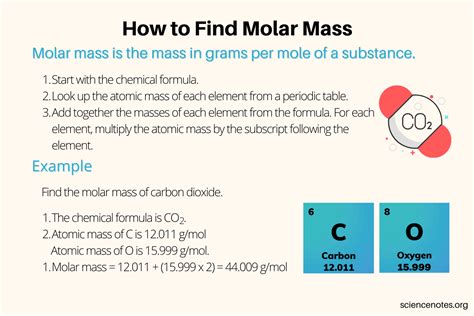
The calculation of molar mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry, essential for understanding the properties and behaviors of substances. Molar mass, also known as molecular weight, is the total mass of a molecule of a substance, expressed in units of grams per mole (g/mol). It is calculated by summing the atomic masses of the atoms in a molecule. The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of that element, and it can be found on the periodic table.
Understanding Atomic Mass and Its Role in Molar Mass Calculation
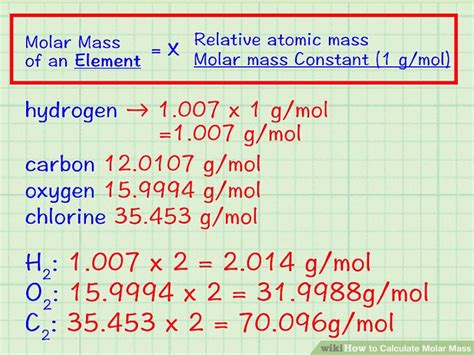
Atomic mass is a critical component in the calculation of molar mass. The periodic table provides the atomic masses of elements, which are used to calculate the molar mass of compounds. For instance, the atomic mass of carbon © is approximately 12.01 g/mol, and that of oxygen (O) is about 16.00 g/mol. To calculate the molar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2), one would add the atomic mass of one carbon atom to twice the atomic mass of oxygen, resulting in a molar mass of 12.01 g/mol + 2(16.00 g/mol) = 44.01 g/mol.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Molar Mass
Calculating the molar mass of a compound involves the following steps:
- Identify the chemical formula of the compound. This tells you how many atoms of each element are present in one molecule of the compound.
- Look up the atomic masses of the elements present in the compound using the periodic table.
- Calculate the total mass contributed by each element by multiplying the atomic mass of the element by the number of atoms of that element in the compound.
- Sum the masses contributed by all elements to get the molar mass of the compound.
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms | Total Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 12.01 | 1 | 12.01 |
| Oxygen (O) | 16.00 | 2 | 32.00 |
| Total Molar Mass of CO2 | 44.01 |

Challenges and Considerations in Molar Mass Calculations

While the calculation of molar mass is straightforward for simple compounds, challenges arise with more complex molecules. For instance, the calculation for proteins or other large biomolecules requires precise knowledge of their amino acid or nucleotide composition, respectively. Additionally, the presence of isotopes can affect the calculated molar mass, as different isotopes of the same element have slightly different masses. However, for most chemical calculations, the average atomic masses provided by the periodic table are sufficiently accurate.
Key Points
- Understanding atomic masses from the periodic table is crucial for calculating molar mass.
- The formula of a compound determines how many atoms of each element are present.
- Molar mass calculation involves summing the atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule.
- Complex molecules require detailed composition data for accurate molar mass calculation.
- The presence of isotopes can introduce minor variations in calculated molar masses.
Real-World Applications of Molar Mass Calculations
Molar mass calculations have numerous practical applications in chemistry, biochemistry, and related fields. They are essential for determining the amount of substance (in moles) needed for chemical reactions, which is critical in both laboratory settings and industrial production processes. Furthermore, understanding molar masses is vital in pharmaceuticals, where the dosing and efficacy of drugs can depend on their molecular weight and the molar concentrations at which they are administered.
What is the significance of molar mass in chemistry?
+Molar mass is significant because it allows chemists to calculate the amount of a substance needed for a reaction, understand the composition of compounds, and determine the physical and chemical properties of substances.
How does the presence of isotopes affect molar mass calculations?
+The presence of isotopes introduces minor variations in the atomic masses used for calculations. However, for most purposes, the average atomic masses listed on the periodic table are used, which account for the natural abundance of isotopes.
What are some real-world applications of molar mass calculations?
+Molar mass calculations are crucial in laboratory settings for preparing solutions, in industrial processes for scaling up reactions, and in pharmaceuticals for dosing and drug development.
In conclusion, calculating molar mass is a fundamental skill in chemistry, based on the principle of summing the atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule. Understanding this concept is essential for various applications, from simple laboratory preparations to complex industrial and pharmaceutical processes. By mastering the calculation of molar mass, individuals can better comprehend the chemical and physical properties of substances, facilitating advancements in numerous scientific and technological fields.