Understanding the relationship between moles and grams is a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for calculations and experiments in various fields, including pharmacology, biochemistry, and materials science. The conversion between moles and grams is based on the molar mass of a substance, which is the mass of one mole of that substance. In this article, we will delve into the process of converting moles to grams and grams to moles, discussing the steps involved, the importance of accurate calculations, and providing examples to illustrate the process.
Introduction to Moles and Molar Mass

The mole (mol) is the unit of measurement in the International System of Units (SI) for the amount of substance. It is defined as the amount of substance that contains as many particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) as there are atoms in 0.012 kilograms of carbon-12. The molar mass of a substance is a measure of the mass of one mole of that substance and is expressed in units of grams per mole (g/mol). For elements, the molar mass is the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms in one molecule of the element. For compounds, it is the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms in one molecule of the compound.
Key Points
- The mole is the SI unit for the amount of substance.
- Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in g/mol.
- Conversions between moles and grams require the molar mass of the substance.
- Accurate calculations are crucial in chemical experiments and applications.
- Understanding the relationship between moles and grams is fundamental in chemistry.
Converting Moles to Grams
To convert moles to grams, you multiply the number of moles by the molar mass of the substance. The formula for this conversion is: mass in grams = number of moles * molar mass. For example, if you want to find the mass in grams of 2 moles of sodium chloride (NaCl), you first need to know the molar mass of NaCl. The atomic mass of sodium (Na) is approximately 22.99 g/mol, and the atomic mass of chlorine (Cl) is approximately 35.45 g/mol. Therefore, the molar mass of NaCl is 22.99 g/mol + 35.45 g/mol = 58.44 g/mol. Using the formula, the mass in grams of 2 moles of NaCl is 2 moles * 58.44 g/mol = 116.88 grams.
| Substance | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Number of Moles | Mass in Grams |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | 58.44 | 2 | 116.88 |
| Oxygen (O2) | 31.9988 | 1.5 | 47.9982 |
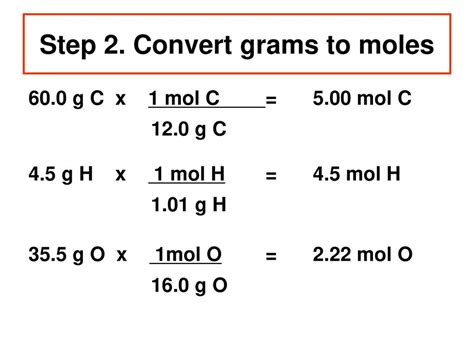
Converting Grams to Moles
To convert grams to moles, you divide the mass in grams by the molar mass of the substance. The formula for this conversion is: number of moles = mass in grams / molar mass. For instance, if you have 100 grams of water (H2O) and you want to find out how many moles of water you have, you first need to calculate the molar mass of H2O. The atomic mass of hydrogen (H) is approximately 1.008 g/mol, and the atomic mass of oxygen (O) is approximately 15.999 g/mol. Therefore, the molar mass of H2O is (2*1.008 g/mol) + 15.999 g/mol = 18.015 g/mol. Using the formula, the number of moles of 100 grams of H2O is 100 g / 18.015 g/mol = approximately 5.55 moles.
Importance of Accurate Calculations

Accurate calculations are critical in chemistry and related fields because small errors can lead to significant differences in outcomes, especially in experiments or when preparing solutions. In pharmacology, for example, the dose of a medication is often calculated in moles or grams, and incorrect calculations can result in ineffective treatment or adverse effects. Similarly, in materials science, the properties of materials can be highly sensitive to the stoichiometry of their components, making accurate mole-to-gram conversions essential.
Real-World Applications
The conversion between moles and grams has numerous real-world applications. In biochemistry, understanding the amount of substance in moles is crucial for studying metabolic pathways and enzymatic reactions. In environmental science, calculating the amount of pollutants in moles can help in assessing their impact on ecosystems. Furthermore, in the production of chemicals and pharmaceuticals, precise control over the amount of reactants and products in moles is necessary to ensure the quality and consistency of the final product.
What is the primary unit for measuring the amount of substance in chemistry?
+The mole (mol) is the primary unit for measuring the amount of substance in chemistry, defined as the amount of substance that contains as many particles as there are atoms in 0.012 kilograms of carbon-12.
How do you convert moles to grams?
+To convert moles to grams, you multiply the number of moles by the molar mass of the substance. The formula is: mass in grams = number of moles * molar mass.
What is the importance of accurate calculations in chemistry?
+Accurate calculations are crucial in chemistry because small errors can lead to significant differences in outcomes, especially in experiments or when preparing solutions, which can affect the safety, efficacy, and quality of products and processes.
In conclusion, the conversion between moles and grams is a fundamental concept in chemistry, essential for a wide range of applications from laboratory experiments to industrial production. Understanding this conversion and being able to perform it accurately is critical for achieving desired outcomes and ensuring safety and efficacy in various fields. By grasping the principles behind the mole and molar mass, and by practicing the conversion between moles and grams, individuals can enhance their proficiency in chemistry and related disciplines, contributing to advancements in science, technology, and healthcare.



