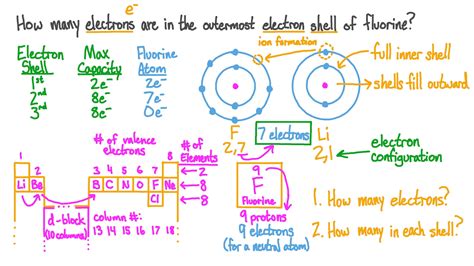
To determine the number of electrons in an atom, you need to understand the basic structure of atoms and how electrons are arranged. Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, which is the central part of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines the element of an atom and is known as the atomic number. For a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons, which means it is also equal to the atomic number.
Understanding Atomic Number and Electron Count
The atomic number is a unique identifier for each element and represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Since a neutral atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, knowing the atomic number allows you to determine the number of electrons. For example, if you look at the periodic table, you’ll see that hydrogen has an atomic number of 1. This means a neutral hydrogen atom has 1 proton and 1 electron. Similarly, oxygen has an atomic number of 8, indicating that a neutral oxygen atom has 8 protons and 8 electrons.
Ions and Electron Count
However, it’s important to note that the number of electrons can change when an atom becomes an ion. An ion is formed when an atom gains or loses electrons. If an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion (cation), and if it gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion (anion). For instance, if a sodium atom (atomic number 11) loses one electron, it becomes a sodium ion with 10 electrons. Conversely, if a chlorine atom (atomic number 17) gains one electron, it becomes a chloride ion with 18 electrons.
| Element | Atomic Number | Number of Electrons (Neutral) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 8 |
| Sodium | 11 | 11 |
| Chlorine | 17 | 17 |
Key Points
- The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus.
- Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons, changing their electron count.
- To find the number of electrons in an ion, adjust the atomic number based on the charge of the ion.
- For cations (positively charged ions), subtract the charge from the atomic number to find the number of electrons.
- For anions (negatively charged ions), add the charge to the atomic number to find the number of electrons.
Understanding how to calculate the number of electrons in an atom or ion is fundamental in chemistry. It helps in predicting the chemical properties and behaviors of elements and compounds. By remembering that the atomic number is the key to determining the number of electrons in a neutral atom and adjusting for ions based on their charge, you can easily determine the electron count for any atom or ion.
How do you find the number of electrons in a neutral atom?
+The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of the element, which represents the number of protons in the nucleus.
What happens to the number of electrons when an atom becomes an ion?
+When an atom becomes an ion, it either gains or loses electrons. If it loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion (cation) with fewer electrons than the atomic number. If it gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion (anion) with more electrons than the atomic number.
How do you calculate the number of electrons in an ion?
+For a cation, subtract the charge from the atomic number to find the number of electrons. For an anion, add the charge to the atomic number to find the number of electrons.