Fractions are a fundamental concept in mathematics, and multiplying them is a crucial operation in various mathematical and real-world applications. When it comes to multiplying fractions, it's essential to understand the basics and apply them correctly to avoid errors. In this article, we'll explore five ways to multiply fractions, providing a comprehensive guide for students, teachers, and professionals alike.
Understanding the Basics of Fraction Multiplication

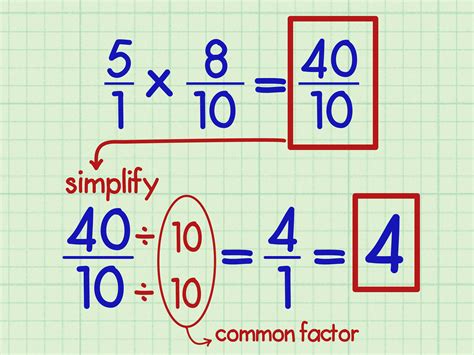
Before diving into the methods, let’s review the fundamental concept of multiplying fractions. When you multiply two fractions, you’re essentially multiplying the numerators (the numbers on top) and the denominators (the numbers on the bottom) separately. The resulting fraction is the product of the numerators divided by the product of the denominators. This can be represented by the formula: (a/b) × (c/d) = (ac)/(bd), where a, b, c, and d are the numerators and denominators of the fractions.
Key Points
- Multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators and denominators separately
- The formula for multiplying fractions is (a/b) × (c/d) = (ac)/(bd)
- Simplifying the resulting fraction is crucial to obtain the final answer
- Understanding the concept of equivalent ratios is essential for fraction multiplication
- Real-world applications of fraction multiplication include recipes, measurements, and financial calculations
Method 1: The Standard Method
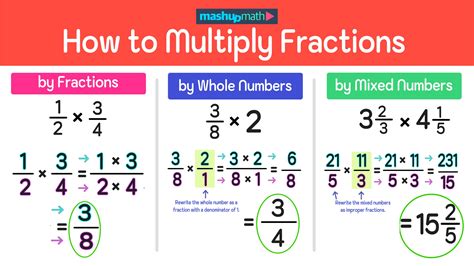
The standard method of multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators and denominators separately, as mentioned earlier. For example, to multiply 1⁄2 and 3⁄4, you would multiply the numerators (1 × 3 = 3) and the denominators (2 × 4 = 8), resulting in the fraction 3⁄8. This method is straightforward and easy to apply, making it a popular choice among students and professionals.
| Fraction 1 | Fraction 2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 3/4 | 3/8 |
| 2/3 | 4/5 | 8/15 |
Method 2: The Cross-Cancellation Method
The cross-cancellation method is a variant of the standard method that involves canceling out common factors between the numerators and denominators before multiplying. This method can simplify the calculation and reduce the risk of errors. For example, to multiply 2⁄3 and 3⁄4, you can cancel out the common factor of 3 between the numerator of the second fraction and the denominator of the first fraction, resulting in the fraction 2⁄4, which simplifies to 1⁄2.
Method 3: The Equivalent Ratios Method
The equivalent ratios method involves finding equivalent ratios for one or both of the fractions before multiplying. This method can be useful when dealing with complex fractions or fractions with large numbers. For example, to multiply 3⁄4 and 2⁄3, you can find an equivalent ratio for the first fraction, such as 6⁄8, and then multiply it by the second fraction, resulting in the fraction 12⁄24, which simplifies to 1⁄2.
Method 4: The Visual Method
The visual method involves using visual aids, such as diagrams or grids, to represent the fractions and multiply them. This method can be helpful for students who are visual learners or struggle with abstract concepts. For example, to multiply 1⁄2 and 3⁄4, you can draw a grid with 2 rows and 4 columns, shade in 1 row and 3 columns, and count the total number of shaded squares to find the result.
Method 5: The Real-World Application Method
The real-world application method involves using real-world examples to illustrate the concept of fraction multiplication. This method can make the concept more relatable and interesting for students. For example, if a recipe calls for 1⁄2 cup of sugar and you want to make 3⁄4 of the recipe, you can multiply the fractions to find the total amount of sugar needed.
What is the formula for multiplying fractions?
+The formula for multiplying fractions is (a/b) × (c/d) = (ac)/(bd), where a, b, c, and d are the numerators and denominators of the fractions.
How do I simplify the resulting fraction?
+To simplify the resulting fraction, find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator and divide both numbers by the GCD.
What are some real-world applications of fraction multiplication?
+Fraction multiplication has various real-world applications, including recipes, measurements, financial calculations, and science.
In conclusion, multiplying fractions is a fundamental concept in mathematics that can be applied in various ways. By understanding the standard method, cross-cancellation method, equivalent ratios method, visual method, and real-world application method, students and professionals can develop a deeper understanding of fraction multiplication and apply it to real-world problems. Remember to simplify the resulting fraction and use visual aids or real-world examples to make the concept more relatable and interesting.