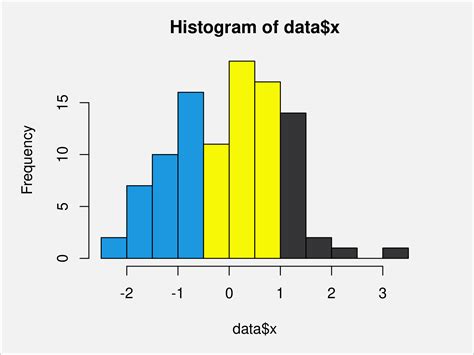
Understanding histograms is a crucial skill for anyone involved in data analysis, photography, or any field where visual representation of data is key. A histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data, making it easier to understand the data's underlying structure. For those looking to improve their skills in reading histograms, here are five essential tips to consider:
Key Points
- Identify the axes: Understand what the x-axis and y-axis represent in the histogram.
- Analyze the distribution: Look for the shape of the distribution, including whether it's symmetric, skewed, or bimodal.
- Find the central tendency: Identify the mean, median, and mode, and understand how they relate to the distribution.
- Examine the variability: Assess the spread of the data, including the range, variance, and standard deviation.
- Look for outliers: Identify any data points that are significantly different from the rest, as these can affect the interpretation of the histogram.
Understanding the Basics of Histograms
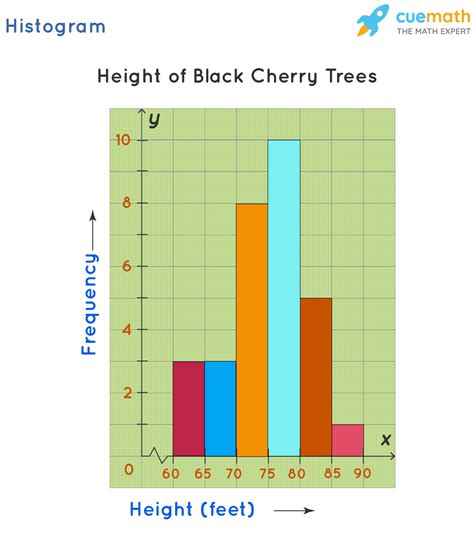
A histogram is essentially a bar chart that represents the distribution of a set of data. It’s divided into bins or ranges of values, and the height of each bar corresponds to the frequency of data points within that bin. The x-axis represents the value of the data, and the y-axis represents the frequency or density of the data. Understanding the axes is the first step in reading a histogram.
Identifying the Shape of the Distribution
The shape of the histogram can tell you a lot about the data. A symmetric distribution will look the same on both sides of the center, while a skewed distribution will have a longer tail on one side. A bimodal distribution will have two distinct peaks, indicating that the data can be divided into two distinct groups. The shape can also indicate the presence of outliers or anomalies in the data.
For instance, in photography, a histogram can help you understand the exposure of your image. A histogram with a peak on the left side indicates underexposure, while a peak on the right side indicates overexposure. Understanding the shape of the histogram can help you adjust your camera settings to achieve the perfect exposure.
Calculating Central Tendency and Variability
Central tendency refers to the measures of the “middle” of the distribution, including the mean, median, and mode. The mean is the average value of the data, the median is the middle value when the data is arranged in order, and the mode is the most frequent value. Variability refers to the spread of the data, including the range, variance, and standard deviation. Understanding these concepts can help you interpret the histogram more effectively.
| Type of Central Tendency | Description |
|---|---|
| Mean | The average value of the data |
| Median | The middle value when the data is arranged in order |
| Mode | The most frequent value in the data |
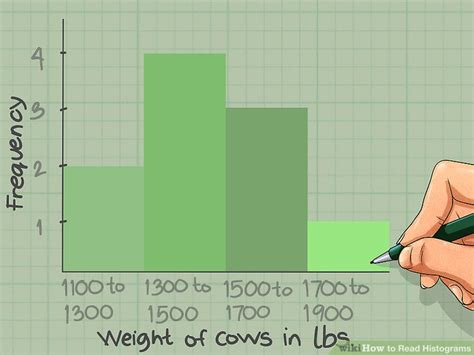
Advanced Techniques for Reading Histograms
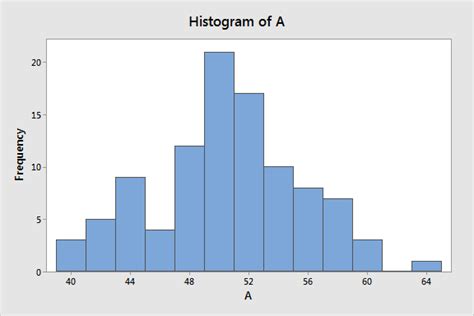
Once you have a good understanding of the basics, you can move on to more advanced techniques for reading histograms. This includes analyzing the histogram for outliers, skewness, and kurtosis. Outliers are data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data, and can affect the interpretation of the histogram. Skewness refers to the asymmetry of the distribution, while kurtosis refers to the “tailedness” of the distribution.
Identifying Outliers and Anomalies
Outliers and anomalies can significantly affect the interpretation of a histogram. An outlier is a data point that is significantly different from the rest of the data, and can be due to errors in measurement or unusual phenomena. Anomalies, on the other hand, are patterns or structures in the data that are not expected. Identifying outliers and anomalies can help you to better understand the data and make more accurate interpretations.
For example, in data analysis, outliers can be identified by looking for data points that are more than 1.5 times the interquartile range (IQR) away from the first quartile (Q1) or third quartile (Q3). This can help you to identify data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data.
What is the purpose of a histogram in data analysis?
+A histogram is used to visualize the distribution of a set of data, making it easier to understand the underlying structure of the data.
How do you identify outliers in a histogram?
+Outliers can be identified by looking for data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data, such as those that are more than 1.5 times the interquartile range (IQR) away from the first quartile (Q1) or third quartile (Q3).
What is the difference between a histogram and a bar chart?
+A histogram is a type of bar chart that represents the distribution of a set of data, while a bar chart is a more general type of chart that can be used to compare categorical data.
In conclusion, reading histograms is a valuable skill that can help you to better understand and interpret data. By following these five tips, you can improve your skills in reading histograms and gain a deeper understanding of the data. Whether you’re working in data analysis, photography, or any other field, understanding histograms can help you to make more accurate interpretations and informed decisions.