Absolute value inequalities are a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus. These inequalities involve the absolute value of a quantity, which can make them slightly more complex to solve compared to linear or quadratic inequalities. However, with a systematic approach, solving absolute value inequalities can become straightforward. This article will guide you through five ways to solve absolute value inequalities, providing a comprehensive understanding of the methods and their applications.
Key Points
- Understanding the definition and properties of absolute value
- Basic method of solving absolute value inequalities
- Graphical method for visualizing solutions
- Using algebraic manipulations to simplify inequalities
- Applying case analysis for more complex inequalities
Understanding Absolute Value Inequalities

The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero, regardless of direction. Thus, |x| = y means that the distance of x from 0 is y. Absolute value inequalities involve comparisons between absolute values and numbers. For example, |x| < 5 means that the distance of x from 0 is less than 5, implying -5 < x < 5.
Basic Method of Solving Absolute Value Inequalities
The basic method involves translating the absolute value inequality into a double inequality without absolute values. For |x| < a, the solution is -a < x < a. For |x| > a, the solution is x < -a or x > a. This method works because the absolute value function essentially reflects negative values to be positive, and vice versa, creating a symmetric boundary around zero.
| Absolute Value Inequality | Solution |
|---|---|
| |x| < 3 | -3 < x < 3 |
| |x| > 2 | x < -2 or x > 2 |
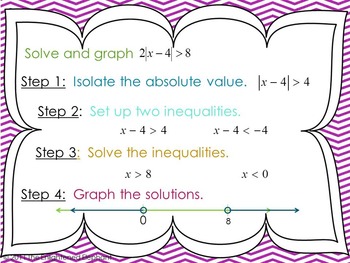
Graphical Method for Visualizing Solutions
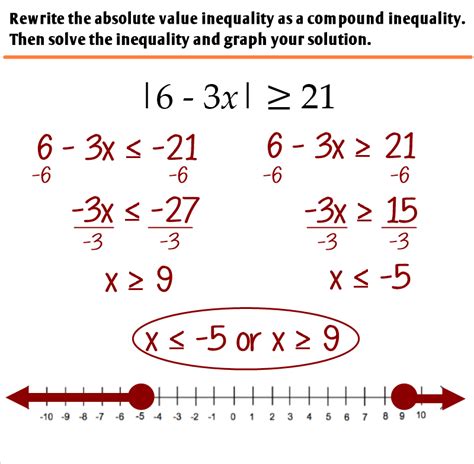
A graphical approach can provide a visual understanding of the solution set. By plotting the function y = |x| and comparing it to the given value (e.g., y = 2), one can see the points where |x| intersects or is above/below the value, depending on the inequality. For |x| < 2, the area between -2 and 2 on the x-axis represents the solution. For |x| > 2, the areas outside -2 and 2 represent the solution.
Using Algebraic Manipulations
Algebraic manipulations can simplify inequalities and make them easier to solve. For instance, if we have |2x + 1| < 3, we first solve the inequality without the absolute value by setting up two equations: 2x + 1 < 3 and 2x + 1 > -3. Solving these gives -2 < 2x + 1 < 2, and then -2 - 1 < 2x < 2 - 1, resulting in -3⁄2 < x < 1⁄2.
Applying Case Analysis
For more complex inequalities involving absolute values, such as those with multiple absolute value expressions or within other functions, a case analysis approach can be useful. This involves breaking down the problem into manageable cases based on the sign of the expressions within the absolute values. For example, solving |x| + |y| > 1 involves considering the cases when x and y are positive, negative, or a mix, and then finding the common solution that satisfies the inequality across these cases.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
When dealing with higher-order equations or inequalities within absolute values, advanced algebraic techniques, such as substitution or elimination methods, may be necessary. Additionally, considering the domain and range of functions involved can provide insights into possible solutions and restrictions.
What is the main challenge in solving absolute value inequalities?
+The main challenge is often understanding how to translate the absolute value into a form that can be easily compared or manipulated, especially when the inequality involves complex expressions or multiple absolute values.
How do you choose the best method for solving an absolute value inequality?
+The choice of method depends on the complexity of the inequality and personal preference. Simple inequalities may be quickly solved using basic translation methods, while more complex ones may require graphical or algebraic manipulation techniques.
In conclusion, solving absolute value inequalities requires a combination of understanding the properties of absolute values, applying basic translation methods, utilizing graphical representations, employing algebraic manipulations, and sometimes, conducting case analyses. By mastering these techniques and understanding when to apply each, one can confidently tackle a wide range of absolute value inequalities, from the straightforward to the complex.