Determining whether a function is even or odd is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus. This distinction is crucial as it influences the function's behavior, its graph's symmetry, and how it interacts with other mathematical operations. In this article, we'll delve into the definitions of even and odd functions, explore their properties, and discuss how to identify them.
Key Points
- Definition and identification of even and odd functions
- Properties of even and odd functions, including symmetry and algebraic behavior
- Methods for determining if a function is even, odd, or neither
- Examples of even and odd functions in mathematics and real-world applications
- Importance of understanding function parity in mathematical analysis and modeling
Definition of Even and Odd Functions
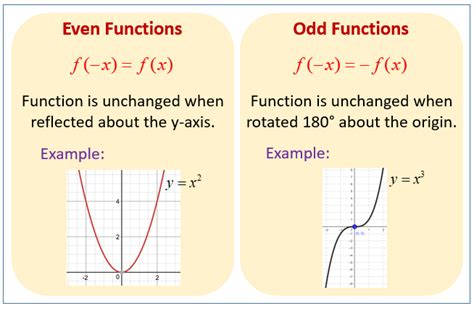
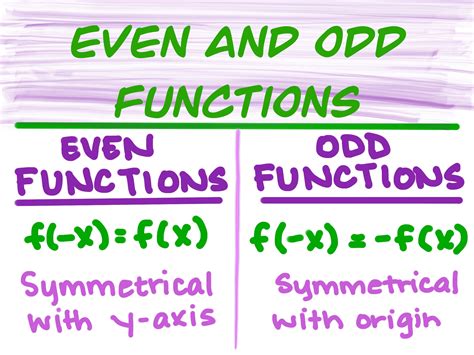
An even function is one where f(x) = f(-x) for all x in the domain of the function. This means that if we replace x with -x, the function’s value remains unchanged. A classic example of an even function is f(x) = x^2, because f(-x) = (-x)^2 = x^2 = f(x). Even functions are symmetric with respect to the y-axis.
On the other hand, an odd function satisfies the condition $f(-x) = -f(x)$ for all x in its domain. This implies that replacing $x$ with $-x$ changes the sign of the function's value but not its magnitude. A simple example of an odd function is $f(x) = x$, since $f(-x) = -x = -f(x)$. Odd functions are symmetric with respect to the origin.
Properties of Even and Odd Functions
Even functions have several distinct properties, including symmetry about the y-axis. This means if a point (x, y) is on the graph of an even function, then the point (-x, y) is also on the graph. For odd functions, the symmetry is about the origin; if (x, y) is on the graph, then (-x, -y) is also on it.
When it comes to integration, the definite integral of an even function from $-a$ to $a$ is twice the integral from $0$ to $a$. For an odd function, the definite integral from $-a$ to $a$ is $0$, because the areas on either side of the origin cancel each other out.
| Function Type | Definition | Symmetry |
|---|---|---|
| Even Function | $f(x) = f(-x)$ | Symmetric about the y-axis |
| Odd Function | $f(-x) = -f(x)$ | Symmetric about the origin |
Determining if a Function is Even, Odd, or Neither
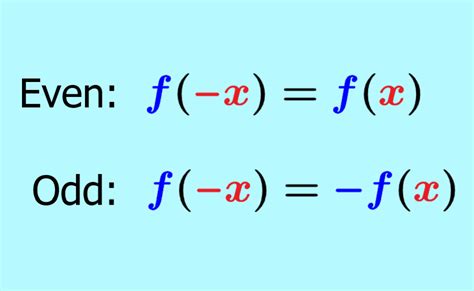
To determine if a function is even, odd, or neither, we substitute -x for x in the function’s equation and simplify:
- If $f(-x) = f(x)$, the function is even.
- If $f(-x) = -f(x)$, the function is odd.
- If neither condition is met, the function is neither even nor odd.
For example, consider $f(x) = 3x^2 + 2x$. Substituting $-x$ for $x$ gives $f(-x) = 3(-x)^2 + 2(-x) = 3x^2 - 2x$. Since $f(-x) \neq f(x)$ and $f(-x) \neq -f(x)$, this function is neither even nor odd.
Examples and Applications
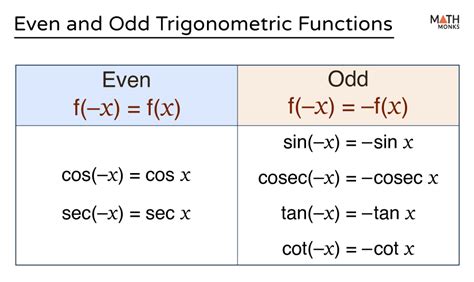
Even functions like f(x) = \cos(x) and odd functions like f(x) = \sin(x) are fundamental in trigonometry and have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and signal processing. The symmetry properties of these functions make them particularly useful for modeling periodic phenomena and analyzing wave patterns.
In conclusion, understanding whether a function is even or odd is crucial for a deep comprehension of its properties and behavior. This knowledge facilitates mathematical manipulations, simplifies problem-solving, and enhances our ability to model and analyze real-world phenomena accurately.
What is the difference between an even and an odd function?
+An even function satisfies f(x) = f(-x) and is symmetric about the y-axis, while an odd function satisfies f(-x) = -f(x) and is symmetric about the origin.
How do I determine if a function is even, odd, or neither?
+Substitute -x for x in the function’s equation. If f(-x) = f(x), it’s even. If f(-x) = -f(x), it’s odd. If neither condition is true, the function is neither even nor odd.
What are some common examples of even and odd functions?
+Common even functions include f(x) = x^2 and f(x) = \cos(x), while f(x) = x and f(x) = \sin(x) are examples of odd functions.