The proton, a fundamental particle in the universe, plays a crucial role in the structure and properties of matter. With a positive charge, protons reside in the nucleus of atoms, alongside neutrons, and their interactions determine the chemical behavior of elements. Let's delve into five fascinating facts about protons that highlight their significance and intriguing characteristics.
Introduction to Protons and Their Role in Atomic Structure

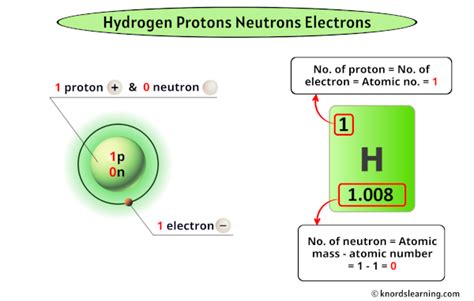
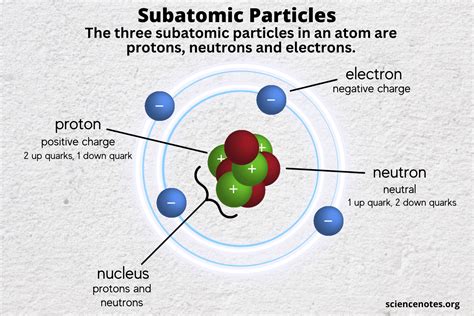
Protons are among the three main particles that make up atoms, the others being electrons and neutrons. While electrons orbit the nucleus, protons and neutrons are found within it. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines the element of an atom, with each element having a unique number of protons in its atoms, known as the atomic number. For instance, hydrogen has one proton, helium has two, and so on. This characteristic makes protons essential for defining the chemical properties of elements.
Key Points
- Protons have a positive charge, which is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the charge of electrons.
- The mass of a proton is approximately 1836 times the mass of an electron, indicating a significant difference in their physical properties.
- Protons are stable particles, meaning they do not decay into other particles under normal conditions.
- The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines the chemical element of the atom, making it a fundamental characteristic of an element.
- Protons participate in nuclear reactions, such as fusion and fission, which are crucial for energy production in stars and nuclear power plants.
Proton Charge and Mass
A key characteristic of protons is their positive charge. The charge of a proton is +1 elementary charge, which is a fundamental constant in physics. This charge is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the charge of an electron, facilitating the formation of neutral atoms when electrons and protons combine. Moreover, the mass of a proton is significantly larger than that of an electron, with a mass ratio of approximately 1836:1. This substantial mass difference affects the physical properties and behaviors of atoms and molecules.
| Particle | Charge | Mass (in electron masses) |
|---|---|---|
| Proton | +1 elementary charge | 1836 |
| Electron | -1 elementary charge | 1 |

Nuclear Reactions and Proton Stability
Protons are stable particles under normal conditions, meaning they do not spontaneously decay into other particles. This stability is crucial for the existence of atoms and molecules as we know them. However, in high-energy environments, such as those found in particle accelerators or the cores of stars, protons can participate in nuclear reactions. These reactions include fusion, where two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy in the process, and fission, where a heavy nucleus splits into lighter nuclei, also releasing a significant amount of energy.
Implications of Proton Properties for Energy Production
The properties of protons, including their charge, mass, and stability, have profound implications for energy production. Nuclear fusion, the process that powers the sun and other stars, involves the combination of protons (along with neutrons) to form heavier nuclei, releasing vast amounts of energy in the process. Efforts to replicate this process on Earth, such as in nuclear fusion reactors, are underway, promising a potentially limitless and clean source of energy. On the other hand, nuclear fission is already used in power plants around the world, although it comes with significant challenges related to safety, waste disposal, and proliferation.
In conclusion, protons are fundamental to our understanding of matter and energy. Their unique properties, including their positive charge, significant mass, and stability, underpin the structure of atoms and the periodic table of elements. Moreover, their role in nuclear reactions highlights their importance in both natural phenomena, such as the lifecycle of stars, and human endeavors, such as the development of nuclear energy. As research continues to uncover more about the universe and its fundamental particles, the proton remains a fascinating subject of study, offering insights into the intricacies of physics and chemistry.
What is the role of protons in the structure of atoms?
+Protons, found in the nucleus of an atom, determine the atomic number of an element, which in turn defines the chemical properties of the element. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus is unique to each element and is the basis for the organization of the periodic table.
How do protons participate in nuclear reactions?
+Protons participate in nuclear reactions such as fusion and fission. In fusion, protons combine with neutrons to form heavier nuclei, releasing energy. In fission, a heavy nucleus splits into lighter nuclei, also releasing a significant amount of energy. These reactions are crucial for energy production in stars and potential sources of clean energy on Earth.
What is the significance of proton stability?
+The stability of protons is crucial for the existence of atoms and molecules as we know them. If protons were unstable, they would decay into other particles, making the formation of stable atoms impossible. This stability also underpins the potential for nuclear reactions that can be harnessed for energy production.