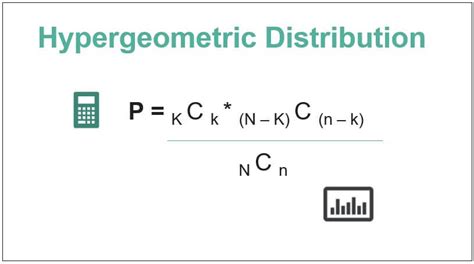
The hypergeometric distribution is a fundamental concept in statistics, used to model the probability of success in a fixed number of trials without replacement from a finite population. This distribution has numerous applications in fields such as quality control, medicine, and social sciences. To effectively apply the hypergeometric distribution, it is crucial to understand its underlying principles and parameters. In this article, we will delve into five essential tips for working with the hypergeometric distribution, providing a comprehensive guide for both beginners and advanced practitioners.
Understanding the Hypergeometric Distribution Parameters
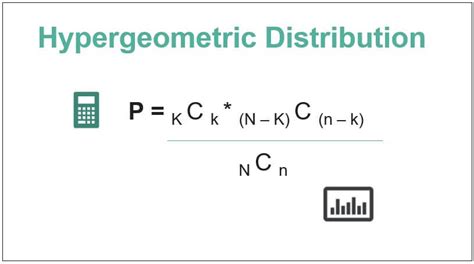
The hypergeometric distribution is characterized by three key parameters: the population size (N), the number of successes in the population (K), and the sample size (n). Understanding these parameters is vital for accurate application of the distribution. For instance, if we are sampling from a batch of 100 items (N=100) where 20 are defective (K=20), and we take a sample of 10 items (n=10), the hypergeometric distribution can tell us the probability of finding exactly k defective items in our sample. It’s also important to note that the distribution assumes sampling without replacement, which affects the probability of success in each trial.
Calculating Probabilities with the Hypergeometric Distribution
The probability mass function (PMF) of the hypergeometric distribution is given by the formula P(X = k) = [C(K, k) * C(N-K, n-k)] / C(N, n), where C(a, b) denotes the number of combinations of ‘a’ items taken ‘b’ at a time, and ‘k’ is the number of successes. This formula allows us to calculate the probability of observing exactly ‘k’ successes in ‘n’ trials. For example, to find the probability of getting exactly 2 defective items in our sample of 10 from the population described earlier, we would use the formula with N=100, K=20, n=10, and k=2.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Population Size (N) | 100 |
| Successes in Population (K) | 20 |
| Sample Size (n) | 10 |
| Number of Successes (k) | 2 |
Applying the Hypergeometric Distribution in Real-World Scenarios

The hypergeometric distribution has numerous real-world applications. For example, in quality control, it can be used to determine the probability of finding a certain number of defective items in a sample from a production batch. In medical research, it can model the probability of success in clinical trials where participants are selected from a finite population without replacement. Understanding how to apply this distribution to solve practical problems is essential for making informed decisions in these fields.
Interpreting Results and Drawing Conclusions
After calculating probabilities using the hypergeometric distribution, it’s essential to interpret these results in the context of the problem. This involves understanding what the probabilities signify and making decisions based on this information. For instance, if the probability of finding more than a certain number of defective items in a sample is very low, this might indicate that the batch from which the sample was taken has a high quality level. Conversely, a high probability of finding defective items could signal a quality control issue.
Key Points
- The hypergeometric distribution is used for modeling the probability of success in a fixed number of trials without replacement from a finite population.
- Understanding the parameters (N, K, n, k) is crucial for accurate application.
- The distribution has various real-world applications, including quality control and medical research.
- Correct interpretation of calculated probabilities is essential for making informed decisions.
- The formula P(X = k) = [C(K, k) * C(N-K, n-k)] / C(N, n) is used to calculate probabilities.
In conclusion, the hypergeometric distribution is a powerful tool for statistical analysis, offering insights into the probability of success in scenarios involving sampling without replacement from a finite population. By grasping the fundamental principles, including the parameters of the distribution and how to apply them to real-world problems, practitioners can leverage this distribution to make more accurate predictions and informed decisions.
What is the primary difference between the hypergeometric and binomial distributions?
+The primary difference is that the hypergeometric distribution models sampling without replacement from a finite population, whereas the binomial distribution assumes sampling with replacement or from an infinite population.
How do you calculate the probability of success in the hypergeometric distribution?
+The probability is calculated using the formula P(X = k) = [C(K, k) * C(N-K, n-k)] / C(N, n), where C(a, b) denotes the number of combinations of ‘a’ items taken ‘b’ at a time.
What are some common applications of the hypergeometric distribution?
+Common applications include quality control, where it’s used to assess the probability of finding defective items in a sample, and medical research, for modeling the probability of success in clinical trials.