Hyperparathyroidism is a complex endocrine disorder characterized by the overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH) by the parathyroid glands. This hormone plays a crucial role in regulating calcium levels in the blood, and its excessive production can lead to a range of symptoms, including bone pain, kidney stones, and neurological disorders. While surgical removal of the affected parathyroid gland(s) is often the preferred treatment option, medication can also play a vital role in managing the condition, particularly in patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery or have mild symptoms.
The primary goal of hyperparathyroidism medication is to reduce PTH levels, alleviate symptoms, and prevent long-term complications. Several classes of medications are available, each with its own mechanism of action and potential side effects. For instance, calcimimetics work by mimicking the action of calcium on the parathyroid glands, thereby reducing PTH secretion. Cinacalcet is a commonly prescribed calcimimetic, which has been shown to effectively decrease PTH levels and improve clinical outcomes in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism.
Medication Options for Hyperparathyroidism
Several medication options are available for the treatment of hyperparathyroidism, including:
- Bisphosphonates: These medications, such as alendronate and zoledronic acid, can help reduce bone resorption and increase bone density, thereby alleviating bone pain and reducing the risk of fractures.
- Vitamin D analogs: These medications, such as calcitriol and paricalcitol, can help regulate calcium levels and reduce PTH secretion.
- Calcimimetics: As mentioned earlier, these medications work by mimicking the action of calcium on the parathyroid glands, thereby reducing PTH secretion.
Treatment Guidelines and Recommendations
The choice of medication and treatment approach depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, PTH levels, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Endocrine Society have established guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hyperparathyroidism, which emphasize the importance of individualized care and regular monitoring of PTH levels and clinical outcomes.
| Medication | Indication | Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Cinacalcet | Primary hyperparathyroidism | 30-90 mg twice daily |
| Alendronate | Osteoporosis and bone pain | 35-70 mg once weekly |
| Calcitriol | Secondary hyperparathyroidism | 0.25-1.0 mcg daily |

Key Points
- Hyperparathyroidism is a complex endocrine disorder characterized by the overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH).
- Medication can play a vital role in managing the condition, particularly in patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery or have mild symptoms.
- Calcimimetics, bisphosphonates, and vitamin D analogs are commonly prescribed medications for hyperparathyroidism.
- The choice of medication and treatment approach depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, PTH levels, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions.
- Regular monitoring of PTH levels and clinical outcomes is essential to ensure effective treatment and prevent long-term complications.
Future Directions and Emerging Therapies
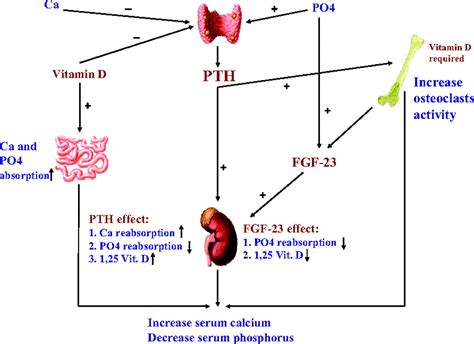
Research into the pathophysiology of hyperparathyroidism and the development of new therapeutic agents is ongoing. Emerging therapies, such as parathyroid hormone receptor antagonists and calcium-sensing receptor agonists, have shown promise in preclinical studies and may offer new treatment options for patients with hyperparathyroidism in the future.
In conclusion, the treatment of hyperparathyroidism requires a comprehensive approach, taking into account the patient's overall health status, medical history, and individual needs. Medication can play a vital role in managing the condition, and several classes of medications are available, each with its own mechanism of action and potential side effects. As our understanding of the pathophysiology of hyperparathyroidism continues to evolve, new therapeutic agents and treatment strategies may emerge, offering improved outcomes and quality of life for patients with this complex endocrine disorder.
What are the common symptoms of hyperparathyroidism?
+Common symptoms of hyperparathyroidism include bone pain, kidney stones, neurological disorders, and gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
How is hyperparathyroidism diagnosed?
+Hyperparathyroidism is typically diagnosed through a combination of laboratory tests, including serum calcium and PTH levels, and imaging studies such as ultrasound and sestamibi scans.
What are the treatment options for hyperparathyroidism?
+Treatment options for hyperparathyroidism include surgery, medication, and observation. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, PTH levels, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions.