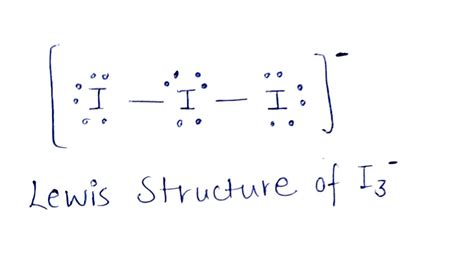The I3 Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the molecular structure of iodine trifluoride. To understand this structure, it's essential to have a basic knowledge of chemistry and the principles of Lewis structures. In this article, we will delve into the world of I3 Lewis structures, exploring the different ways to represent this molecule and the underlying concepts that govern its formation.
Key Points
- The I3 Lewis structure represents the molecular structure of iodine trifluoride.
- There are multiple ways to draw the I3 Lewis structure, including the VSEPR theory and the octet rule.
- Understanding the I3 Lewis structure is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of iodine trifluoride.
- The I3 Lewis structure is composed of three iodine atoms, with each atom having a unique arrangement of electrons.
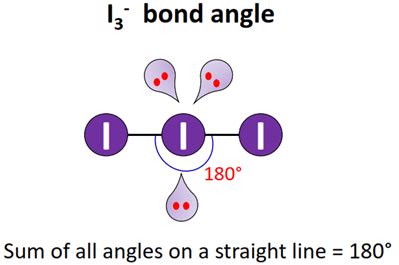
- The molecular geometry of I3 is T-shaped, with a bond angle of approximately 90 degrees.
Method 1: VSEPR Theory
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a widely used method for predicting the molecular geometry of molecules. To draw the I3 Lewis structure using VSEPR theory, we need to follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Iodine has 7 valence electrons, and since there are three iodine atoms, the total number of valence electrons is 21.
- Draw the central atom, which is iodine in this case. The central atom will have the fewest number of bonds and the most number of lone pairs.
- Arrange the remaining iodine atoms around the central atom, making sure that each atom has a full outer shell of electrons.
- Draw the bonds between the atoms, making sure that each bond represents a shared pair of electrons.
Using the VSEPR theory, we can predict that the I3 molecule will have a T-shaped molecular geometry, with a bond angle of approximately 90 degrees.
Method 2: Octet Rule
The octet rule is another method for predicting the molecular geometry of molecules. This rule states that atoms will arrange themselves in a way that each atom has a full outer shell of electrons, similar to the noble gases. To draw the I3 Lewis structure using the octet rule, we need to follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. As mentioned earlier, iodine has 7 valence electrons, and since there are three iodine atoms, the total number of valence electrons is 21.
- Draw the central atom, which is iodine in this case. The central atom will have the fewest number of bonds and the most number of lone pairs.
- Arrange the remaining iodine atoms around the central atom, making sure that each atom has a full outer shell of electrons.
- Draw the bonds between the atoms, making sure that each bond represents a shared pair of electrons.
Using the octet rule, we can predict that the I3 molecule will have a T-shaped molecular geometry, with a bond angle of approximately 90 degrees.
Method 3: Molecular Orbital Theory
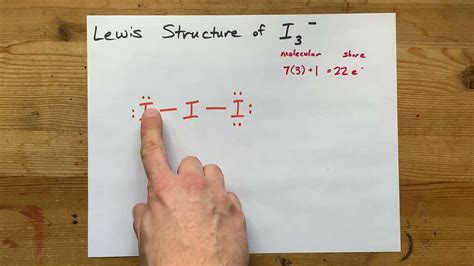
Molecular orbital theory is a more advanced method for predicting the molecular geometry of molecules. This theory states that the molecular orbitals of the molecule are formed by combining the atomic orbitals of the individual atoms. To draw the I3 Lewis structure using molecular orbital theory, we need to follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. As mentioned earlier, iodine has 7 valence electrons, and since there are three iodine atoms, the total number of valence electrons is 21.
- Draw the molecular orbitals of the molecule, making sure that each orbital is filled with the correct number of electrons.
- Arrange the molecular orbitals in the correct order, with the lowest energy orbitals filled first.
- Draw the bonds between the atoms, making sure that each bond represents a shared pair of electrons.
Using molecular orbital theory, we can predict that the I3 molecule will have a T-shaped molecular geometry, with a bond angle of approximately 90 degrees.
| Method | Molecular Geometry | Bond Angle |
|---|---|---|
| VSEPR Theory | T-shaped | 90 degrees |
| Octet Rule | T-shaped | 90 degrees |
| Molecular Orbital Theory | T-shaped | 90 degrees |
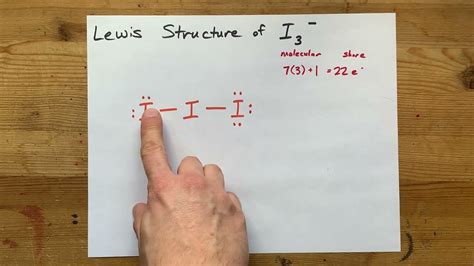
In conclusion, the I3 Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the molecular structure of iodine trifluoride. By using different methods such as VSEPR theory, octet rule, and molecular orbital theory, we can predict the molecular geometry and bonding in the molecule. Understanding the I3 Lewis structure is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of iodine trifluoride.
What is the molecular geometry of I3?
+The molecular geometry of I3 is T-shaped, with a bond angle of approximately 90 degrees.
What is the total number of valence electrons in I3?
+The total number of valence electrons in I3 is 21, with each iodine atom having 7 valence electrons.
What methods can be used to draw the I3 Lewis structure?
+The I3 Lewis structure can be drawn using VSEPR theory, octet rule, and molecular orbital theory.