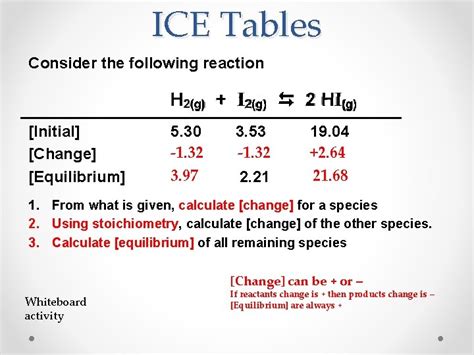
The world of chemistry can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding complex concepts like acid-base chemistry. One tool that has been a staple in chemistry education for decades is the ice table, also known as an ICE chart or ICE table. In this article, we will delve into the world of ice table chemistry, exploring what it is, how it works, and most importantly, how to make it easy to understand and apply.
What is an Ice Table?
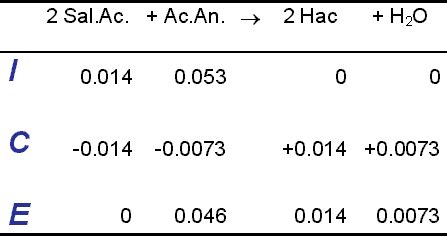
An ice table is a graphical representation of the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The acronym ICE stands for Initial, Change, and Equilibrium, which refers to the three stages of the reaction. The initial stage represents the concentrations of the reactants and products at the beginning of the reaction, the change stage represents the change in concentrations as the reaction proceeds, and the equilibrium stage represents the final concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium.
How to Set Up an Ice Table
Setting up an ice table involves several steps. First, you need to identify the chemical reaction and the equilibrium constant expression. Then, you need to determine the initial concentrations of the reactants and products. Next, you need to calculate the change in concentrations, which can be done using the equilibrium constant expression. Finally, you need to calculate the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants and products.
| Stage | Reactant 1 | Reactant 2 | Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 0.1 M | 0.2 M | 0 M |
| Change | -x | -x | +x |
| Equilibrium | 0.1 - x | 0.2 - x | x |
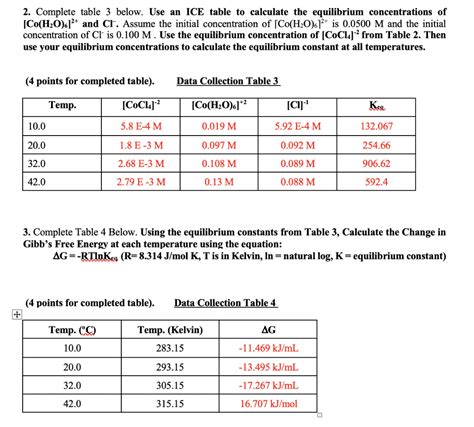
How to Use an Ice Table to Solve Equilibrium Problems

Once you have set up the ice table, you can use it to solve equilibrium problems. The key is to use the equilibrium constant expression to relate the concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium. By plugging in the values from the ice table into the equilibrium constant expression, you can solve for the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants and products.
Tips and Tricks for Working with Ice Tables
Working with ice tables can be challenging, but there are several tips and tricks that can make it easier. One tip is to use a systematic approach to setting up the ice table, making sure to include all the necessary information. Another tip is to use the equilibrium constant expression to check your work, making sure that the calculations are correct.
Key Points
- Ice tables are a graphical representation of the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
- The ice table is set up by identifying the chemical reaction, determining the initial concentrations, calculating the change in concentrations, and calculating the equilibrium concentrations.
- The equilibrium constant expression is used to relate the concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium.
- Working with ice tables requires a systematic approach and attention to detail.
- Ice tables can be used to solve a variety of equilibrium problems, including acid-base chemistry problems.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working with Ice Tables
When working with ice tables, there are several common mistakes to avoid. One mistake is to forget to include the units of the concentrations, which can lead to errors in the calculation. Another mistake is to use the wrong equilibrium constant expression, which can lead to incorrect calculations.
Real-World Applications of Ice Tables
Ice tables have a variety of real-world applications, including in the fields of chemistry, biology, and environmental science. For example, ice tables can be used to model the behavior of acid-base systems in the environment, which is essential for understanding and mitigating the effects of acid rain.
What is the purpose of an ice table in chemistry?
+The purpose of an ice table is to provide a graphical representation of the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products in a chemical reaction, making it easier to understand and solve equilibrium problems.
How do I set up an ice table for an acid-base reaction?
+To set up an ice table for an acid-base reaction, you need to identify the chemical reaction, determine the initial concentrations of the reactants and products, calculate the change in concentrations, and calculate the equilibrium concentrations.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with ice tables?
+Some common mistakes to avoid when working with ice tables include forgetting to include the units of the concentrations, using the wrong equilibrium constant expression, and not paying attention to the systematic approach to setting up the ice table.
In conclusion, ice tables are a powerful tool for understanding and solving equilibrium problems in chemistry. By following the tips and tricks outlined in this article, you can master the use of ice tables and become proficient in solving a variety of equilibrium problems. Remember to always pay attention to the units of the concentrations, use the correct equilibrium constant expression, and follow a systematic approach to setting up the ice table. With practice and patience, you can become an expert in using ice tables to solve equilibrium problems.