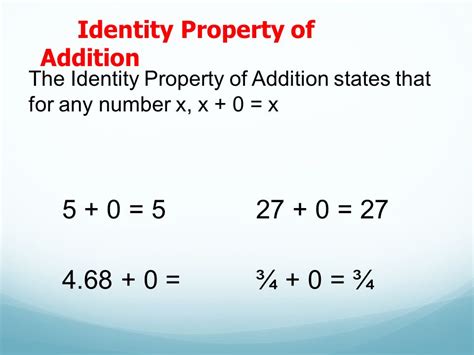
The identity property of addition is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the realm of arithmetic operations. It states that when the number zero is added to any given number, the result is always the original number. In mathematical terms, this can be expressed as: a + 0 = a, where 'a' represents any real number. This property is crucial because it provides a foundation for understanding the behavior of numbers under addition, allowing us to perform calculations with ease and precision.
Understanding the identity property of addition is essential for various mathematical operations, including solving equations and simplifying expressions. For instance, when simplifying an algebraic expression, the identity property of addition can be used to eliminate any terms that involve adding zero, thus streamlining the expression without altering its value. This property is also pivotal in proving other mathematical concepts and theorems, especially in algebra and calculus, where the concept of zero as an additive identity plays a central role.
Key Points
- The identity property of addition states that any number added to zero results in the original number.
- This property is represented by the equation: a + 0 = a, where 'a' can be any real number.
- It is fundamental for simplifying algebraic expressions and solving equations.
- The concept is crucial in various mathematical disciplines, including algebra and calculus.
- Understanding this property enhances the ability to perform mathematical operations with precision and clarity.
Applications and Importance
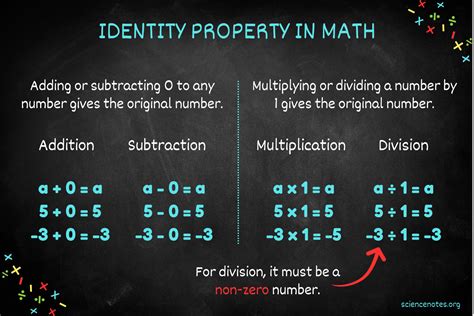
The identity property of addition has far-reaching implications and applications across different areas of mathematics and science. In algebra, for example, this property is used to solve linear equations by isolating the variable. By adding or subtracting the same value to both sides of an equation, one can manipulate the equation to find the value of the variable, with the understanding that adding zero does not change the value of the expression. Similarly, in calculus, the concept of limits and derivatives relies on the understanding of how functions behave as they approach certain values, with the additive identity playing a critical role in these definitions.
Mathematical Operations
In everyday mathematical operations, the identity property of addition is implicitly used. For instance, when calculating the sum of a series of numbers, if one of the numbers is zero, it does not affect the overall sum because adding zero to any number does not change its value. This property makes calculations simpler and more efficient, as it allows for the elimination of zero from any addition problem without altering the result.
| Mathematical Operation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Adding zero to a number | 5 + 0 | 5 |
| Subtracting zero from a number | 10 - 0 | 10 |
| Multiplying a number by one | 7 * 1 | 7 |

Comparison with Other Mathematical Properties

The identity property of addition is one of several fundamental properties in mathematics, including the commutative, associative, and distributive properties. While each of these properties has its unique role and application, the identity property stands out for its simplicity and its foundational role in defining the behavior of the number zero in addition. The commutative property of addition, for example, states that the order of the numbers being added does not change the result (a + b = b + a), but it does not address the concept of an additive identity. The associative property, which states that the order in which numbers are added does not affect the result (a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c), also relies on the understanding that adding zero does not change the value of an expression.
In contrast to addition, the identity property for multiplication states that any number multiplied by one remains unchanged (a * 1 = a). This highlights the distinction between additive and multiplicative identities in mathematics, with zero serving as the additive identity and one serving as the multiplicative identity. Understanding these properties and how they interrelate is essential for a deep comprehension of mathematical principles and their applications.
What is the identity property of addition?
+The identity property of addition states that when any number is added to zero, the result is the original number. It is mathematically represented as a + 0 = a, where 'a' can be any real number.
Why is the identity property of addition important?
+This property is crucial because it simplifies mathematical operations, particularly in algebra and calculus. It allows for the elimination of zero in addition problems, making calculations more efficient.
How does the identity property of addition compare to other mathematical properties?
+The identity property of addition is distinct from but complementary to other properties like the commutative, associative, and distributive properties. It specifically addresses the role of zero as an additive identity, which is fundamental to the structure of mathematics.
In conclusion, the identity property of addition is a foundational concept in mathematics that underpins many arithmetic operations and mathematical theories. Its understanding and application are essential for performing calculations accurately, solving equations, and grasping more advanced mathematical concepts. By recognizing the role of zero as the additive identity, individuals can deepen their comprehension of mathematical principles and enhance their ability to apply these principles in a variety of contexts.