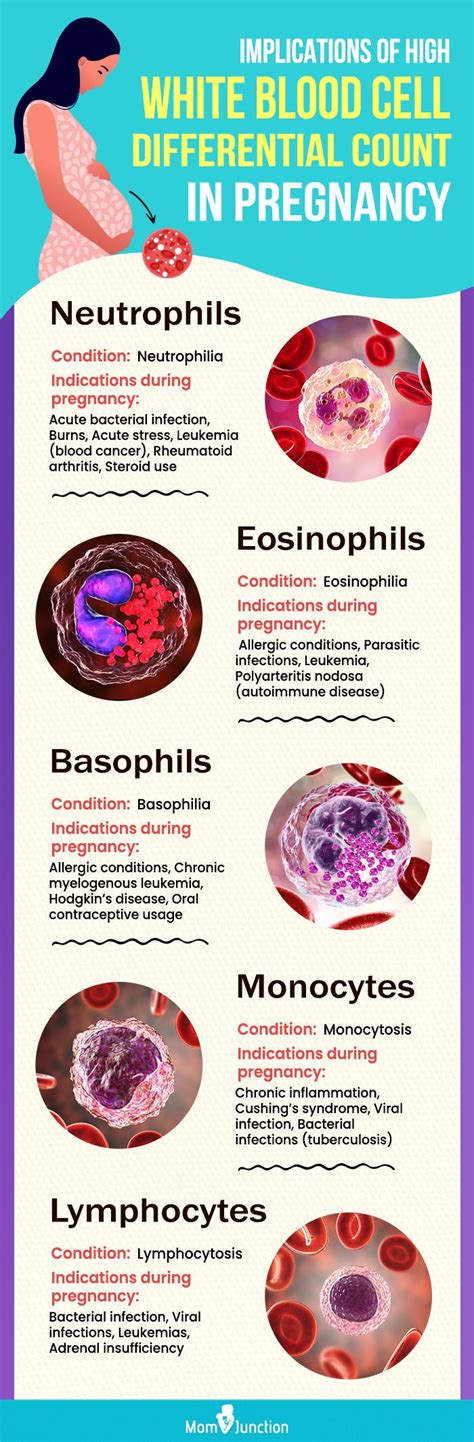
During pregnancy, the body undergoes numerous physiological changes to support the growth and development of the fetus. One such change is the alteration in blood cell counts, including an increase in neutrophils. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system, helping to fight off infections and inflammation. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind increased neutrophils during pregnancy, their implications, and the potential effects on maternal and fetal health.
Key Points
- Increased neutrophils during pregnancy are a normal physiological response to support the growing fetus and prepare the mother's body for childbirth.
- Elevated neutrophil counts can indicate an underlying infection or inflammation, requiring prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
- Neutrophilia can increase the risk of pregnancy-related complications, such as preterm labor, preeclampsia, and gestational diabetes.
- Regular prenatal check-ups and monitoring of neutrophil counts can help identify potential issues and ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
- Research suggests that increased neutrophils during pregnancy may be associated with changes in the maternal microbiome, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiota during this critical period.
Physiological Changes in Neutrophil Counts During Pregnancy

Neutrophil counts typically increase during pregnancy, with a median increase of 30-50% above non-pregnant levels. This rise in neutrophils is thought to be a normal physiological response to support the growing fetus and prepare the mother’s body for childbirth. The exact mechanisms behind this increase are not fully understood but are believed to involve hormonal changes, such as the rise in estrogen and progesterone levels, which can stimulate the production of neutrophils in the bone marrow.
Causes of Increased Neutrophils During Pregnancy
While an increase in neutrophils is a normal occurrence during pregnancy, there are several factors that can contribute to elevated neutrophil counts. These include:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause a significant increase in neutrophil counts as the body responds to the invading pathogens.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation, such as that seen in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, can also lead to elevated neutrophil counts.
- Pregnancy-related complications: Conditions like preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and preterm labor can all be associated with increased neutrophil counts.
| Neutrophil Count Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Normal (non-pregnant): 1,500-8,000 cells/μL | No infection or inflammation present |
| Mild neutrophilia (pregnant): 8,000-12,000 cells/μL | May indicate a mild infection or inflammation |
| Moderate neutrophilia (pregnant): 12,000-18,000 cells/μL | Suggests a moderate infection or inflammation |
| Severe neutrophilia (pregnant): >18,000 cells/μL | Indicates a severe infection or inflammation, requiring prompt medical attention |

Clinical Implications of Increased Neutrophils During Pregnancy
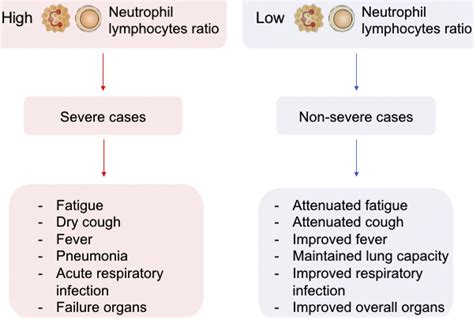
Elevated neutrophil counts during pregnancy can have significant clinical implications. For example, severe neutrophilia (neutrophil counts >18,000 cells/μL) has been associated with an increased risk of pregnancy-related complications, such as preterm labor, preeclampsia, and gestational diabetes. Additionally, neutrophilia can increase the risk of fetal growth restriction and low birth weight.
Management and Treatment of Increased Neutrophils During Pregnancy
The management and treatment of increased neutrophils during pregnancy depend on the underlying cause. If an infection is present, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed to treat the underlying condition. In cases of chronic inflammation, anti-inflammatory medications or immunosuppressants may be used to reduce inflammation and prevent complications. In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular exercise, can help support the immune system and reduce the risk of complications.
What are the normal neutrophil count ranges during pregnancy?
+Normal neutrophil count ranges during pregnancy vary, but a general range is 5,000-15,000 cells/μL. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the normal range for individual cases.
Can increased neutrophils during pregnancy be a sign of an underlying infection?
+Yes, increased neutrophils during pregnancy can be a sign of an underlying infection. If an infection is suspected, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
How can I reduce my risk of complications associated with increased neutrophils during pregnancy?
+Regular prenatal check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following a balanced diet can help reduce the risk of complications associated with increased neutrophils during pregnancy. Additionally, staying hydrated, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress can also support the immune system and reduce the risk of complications.
In conclusion, increased neutrophils during pregnancy are a normal physiological response to support the growing fetus and prepare the mother’s body for childbirth. However, elevated neutrophil counts can also indicate an underlying infection or inflammation, requiring prompt medical attention to prevent complications. Regular prenatal check-ups, monitoring of neutrophil counts, and a thorough medical history can help identify potential issues and ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby. By understanding the causes, clinical implications, and management of increased neutrophils during pregnancy, healthcare providers can provide optimal care and support for pregnant women, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for both mother and baby.