The concept of inertia is a fundamental principle in physics, describing the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. When applied to a rod, inertia plays a crucial role in understanding its rotational motion and the distribution of mass. The inertia of a rod, also known as its moment of inertia, is a measure of its resistance to changes in its rotational motion. In this article, we will delve into the concept of inertia of a rod, exploring its definition, calculation, and significance in various physical systems.
Definition and Calculation of Inertia of a Rod
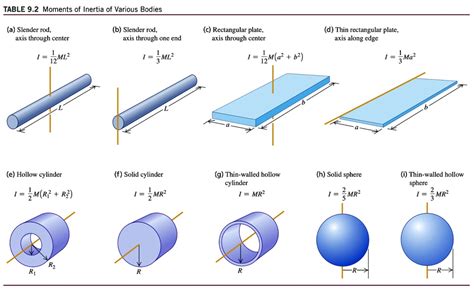
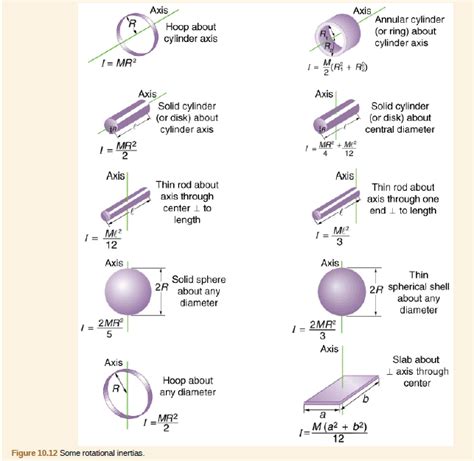
The moment of inertia of a rod is defined as the sum of the products of the mass elements of the rod and the square of their distances from the axis of rotation. Mathematically, it can be expressed as I = ∫r^2 dm, where I is the moment of inertia, r is the distance of the mass element from the axis of rotation, and dm is the mass element. For a uniform rod of length L and mass M, the moment of inertia about its center of mass can be calculated using the formula I = (1⁄12)ML^2.
Moment of Inertia about Different Axes
The moment of inertia of a rod depends on the axis of rotation. When the rod is rotated about its center of mass, the moment of inertia is minimum. However, when the rod is rotated about an axis perpendicular to its length and passing through one of its ends, the moment of inertia is maximum. This can be attributed to the fact that the mass elements of the rod are farther away from the axis of rotation, resulting in a greater resistance to changes in rotational motion. The moment of inertia about different axes can be calculated using the parallel axis theorem, which states that I = I_cm + Mh^2, where I_cm is the moment of inertia about the center of mass, M is the mass of the rod, and h is the distance between the axis of rotation and the center of mass.
| Axis of Rotation | Moment of Inertia |
|---|---|
| Center of Mass | (1/12)ML^2 |
| Perpendicular to length, passing through one end | (1/3)ML^2 |
| Parallel to length, passing through center of mass | 0 |
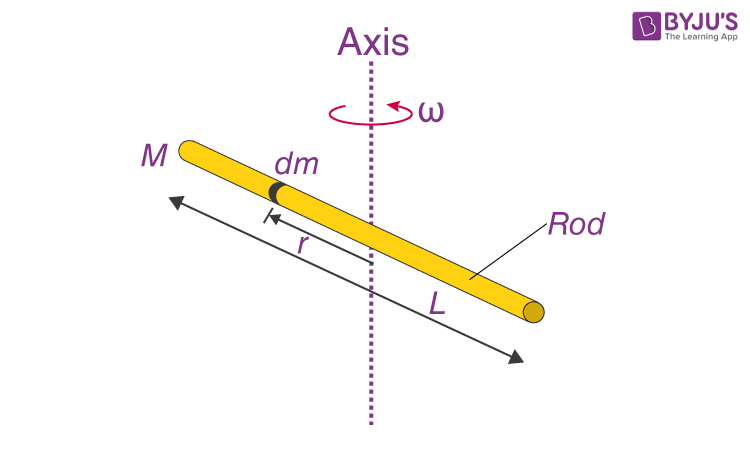
Significance of Inertia of a Rod in Physical Systems
The inertia of a rod has significant implications in various physical systems. In the design of flywheels, for instance, the moment of inertia of the rod plays a crucial role in determining its energy storage capacity. A flywheel with a higher moment of inertia can store more energy, resulting in a more efficient system. Similarly, in the design of gears and pendulums, the moment of inertia of the rod affects the rotational motion and the stability of the system.
Real-World Applications
The concept of inertia of a rod has numerous real-world applications. In the field of robotics, for example, the moment of inertia of a robotic arm is critical in determining its stability and precision. By carefully designing the mass distribution and axis of rotation of the robotic arm, engineers can optimize its performance and accuracy. Similarly, in the field of sports, the moment of inertia of a golf club or a baseball bat affects the athlete’s swing and the resulting trajectory of the ball.
Key Points
- The moment of inertia of a rod is a measure of its resistance to changes in rotational motion.
- The moment of inertia depends on the axis of rotation and the mass distribution of the rod.
- The parallel axis theorem can be used to calculate the moment of inertia about different axes.
- The moment of inertia is a critical parameter in designing rotational systems, such as flywheels and gears.
- The concept of inertia of a rod has numerous real-world applications, including robotics and sports.
FAQs
What is the moment of inertia of a uniform rod about its center of mass?
+The moment of inertia of a uniform rod about its center of mass is given by the formula I = (1⁄12)ML^2, where M is the mass of the rod and L is its length.
How does the moment of inertia of a rod affect its rotational motion?
+The moment of inertia of a rod affects its rotational motion by determining its resistance to changes in rotational motion. A higher moment of inertia results in a greater resistance to changes in rotational motion, while a lower moment of inertia results in a lower resistance.
What are some real-world applications of the concept of inertia of a rod?
+The concept of inertia of a rod has numerous real-world applications, including the design of flywheels, gears, and pendulums, as well as in the field of robotics and sports.
In conclusion, the inertia of a rod is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a critical role in understanding its rotational motion and the distribution of mass. By carefully calculating and designing the moment of inertia of a rod, engineers can optimize the performance and efficiency of various physical systems. Whether in the design of flywheels, gears, or robotic arms, the concept of inertia of a rod is essential in achieving precision and accuracy.