The concept of infinitely many solutions is a profound and intriguing idea that has far-reaching implications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering. In essence, it refers to the existence of an endless number of solutions to a particular problem or equation, which can be both fascinating and overwhelming. To delve into this topic, it's essential to establish a solid foundation in the underlying principles and terminology.
Mathematical Foundations
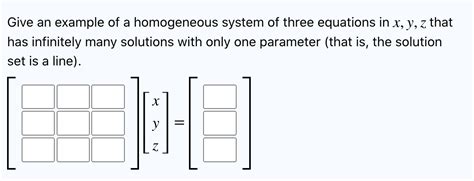
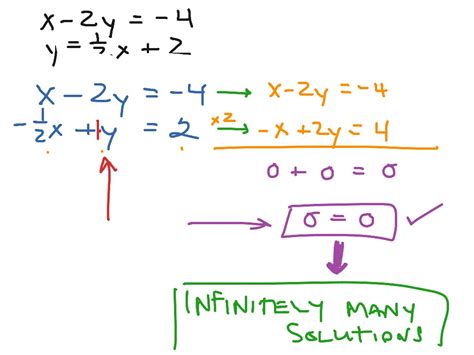
In mathematics, the concept of infinitely many solutions often arises in the context of algebraic equations, differential equations, and optimization problems. For instance, consider a linear equation of the form ax + by = c, where a, b, and c are constants. If the equation has a non-trivial solution, it can be shown that there are infinitely many solutions, which can be expressed as a linear combination of the base solutions. This is a fundamental concept in linear algebra, and it has significant implications for solving systems of equations and analyzing the properties of linear transformations.
Algebraic Equations and Group Theory
Group theory provides a powerful framework for analyzing the symmetries and structure of algebraic equations. In particular, the concept of a group action can be used to describe the symmetries of a solution set, which can lead to the discovery of infinitely many solutions. For example, consider the equation x^2 + y^2 = 1, which represents a circle in the Cartesian plane. The group of rotations around the origin acts on the solution set, generating infinitely many solutions that can be obtained by rotating the initial solution.
| Equation Type | Number of Solutions |
|---|---|
| Linear Equation | Infinitely Many |
| Quadratic Equation | 0, 1, or 2 |
| Cubic Equation | 1 or 3 |
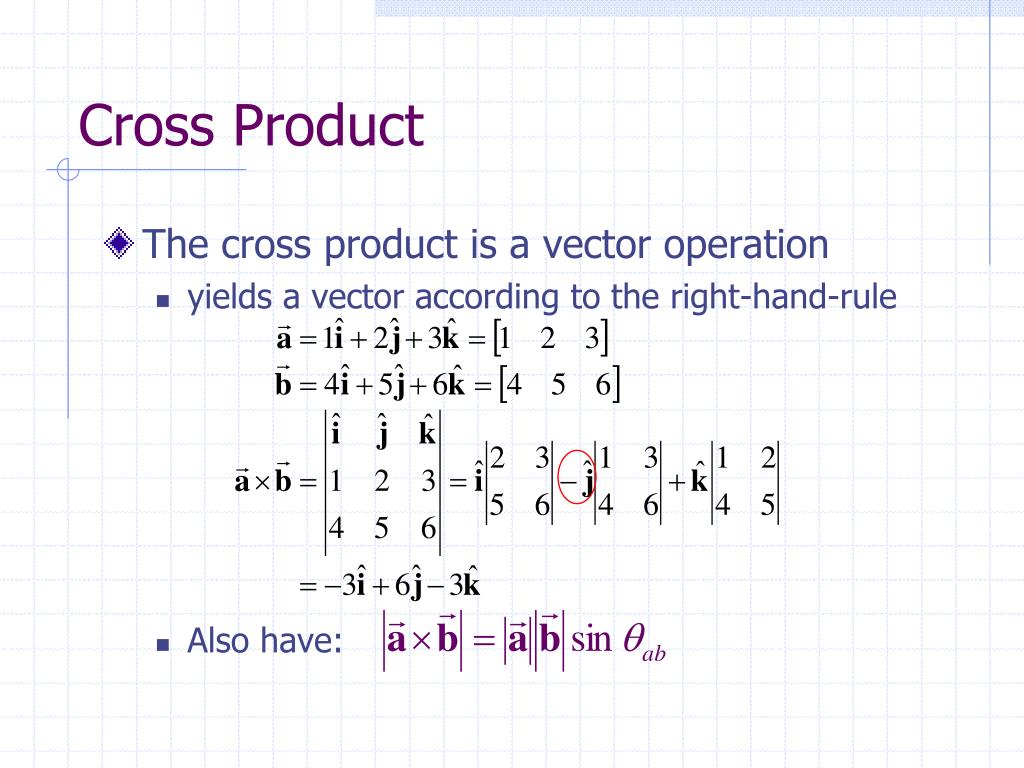
Physical Applications and Implications
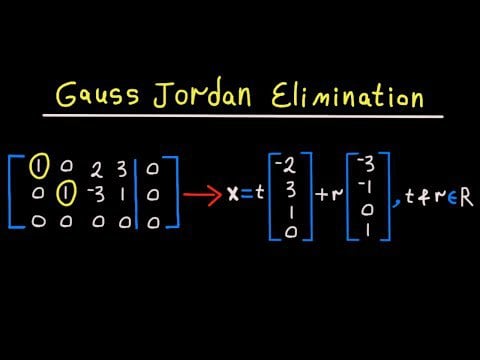
In physics and engineering, infinitely many solutions can arise in the context of differential equations, which describe the behavior of complex systems over time. For example, the wave equation, which governs the propagation of waves in a medium, can have infinitely many solutions, each corresponding to a different initial condition or boundary condition. This has significant implications for understanding the behavior of physical systems, such as the vibration of strings, the propagation of electromagnetic waves, and the flow of fluids.
Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems
Differential equations can be used to model a wide range of physical phenomena, from the motion of particles to the behavior of complex systems. In many cases, the solution to a differential equation depends on the boundary conditions, which can be specified in various ways. The existence of infinitely many solutions can make it challenging to determine the properties of the solution set, but it also provides a rich framework for exploring the behavior of physical systems under different conditions.
Key Points
- Infinitely many solutions can arise in various mathematical and physical contexts.
- The concept of group theory provides a powerful framework for analyzing the symmetries and structure of algebraic equations.
- Differential equations can have infinitely many solutions, depending on the boundary conditions and initial conditions.
- The existence of infinitely many solutions can make it challenging to determine the properties of the solution set, but it also provides a rich framework for exploration and discovery.
- Physical applications of infinitely many solutions include the behavior of waves, the vibration of strings, and the flow of fluids.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the concept of infinitely many solutions is a profound and intriguing idea that has far-reaching implications in various fields. By exploring the mathematical foundations, physical applications, and implications of infinitely many solutions, we can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying principles and structure of complex systems. As we continue to advance our knowledge and understanding of these phenomena, we may uncover new patterns and relationships that can inform and inspire future discoveries.
What are some common examples of infinitely many solutions in mathematics?
+Some common examples of infinitely many solutions in mathematics include linear equations, quadratic equations with no real solutions, and differential equations with non-trivial solutions.
How do infinitely many solutions arise in physical applications?
+Infinitely many solutions can arise in physical applications, such as the behavior of waves, the vibration of strings, and the flow of fluids, due to the presence of differential equations and boundary value problems.
What are some potential challenges and opportunities associated with infinitely many solutions?
+The existence of infinitely many solutions can be both a blessing and a curse, providing a rich landscape for exploration and discovery, but also making it challenging to determine the properties of the solution set as a whole.