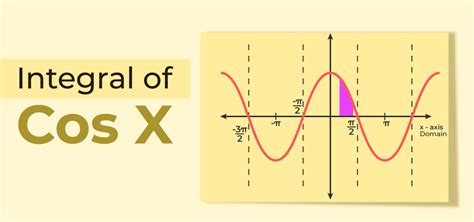
The integral of cos(x) is a fundamental concept in calculus, and it's essential to understand its derivation and application in various mathematical and real-world problems. The cosine function, denoted as cos(x), is a periodic function that oscillates between -1 and 1, and its integral is used to find the area under the curve. In this article, we'll delve into the world of trigonometric integrals, exploring the concept of the integral of cos(x), its derivation, and its significance in mathematics and physics.
Key Points
- The integral of cos(x) is sin(x) + C, where C is the constant of integration.
- The derivation of the integral of cos(x) involves the use of the fundamental theorem of calculus and the definition of the derivative of sin(x).
- The integral of cos(x) has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and mathematics, including the study of oscillations, waves, and signal processing.
- The concept of the integral of cos(x) can be extended to more complex functions, such as the integral of cos^n(x) and the integral of cos(x) with respect to other variables.
- Understanding the integral of cos(x) is crucial for solving problems in calculus, differential equations, and other areas of mathematics and physics.
Derivation of the Integral of Cos(x)
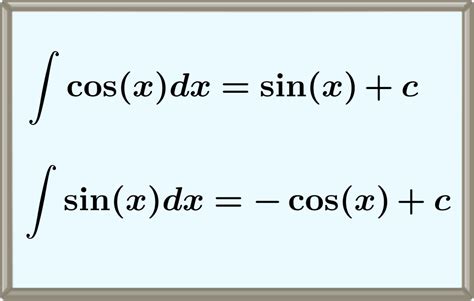
The integral of cos(x) can be derived using the fundamental theorem of calculus, which states that differentiation and integration are inverse processes. To derive the integral of cos(x), we can start with the definition of the derivative of sin(x), which is cos(x). Using the fundamental theorem of calculus, we can write:
∫cos(x) dx = ∫(d(sin(x))/dx) dx = sin(x) + C
where C is the constant of integration. This result shows that the integral of cos(x) is equal to sin(x) + C, which is a fundamental trigonometric identity.
Applications of the Integral of Cos(x)
The integral of cos(x) has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and mathematics. One of the most significant applications is in the study of oscillations and waves. The cosine function is used to model oscillations, and the integral of cos(x) is used to find the area under the curve, which represents the energy of the oscillation. Additionally, the integral of cos(x) is used in signal processing, where it’s used to filter and analyze signals.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Oscillations | The integral of cos(x) is used to model oscillations and find the area under the curve, which represents the energy of the oscillation. |
| Signal Processing | The integral of cos(x) is used to filter and analyze signals, where it's used to remove noise and extract relevant information. |
| Calculus | The integral of cos(x) is used to solve problems in calculus, such as finding the area under curves and solving differential equations. |
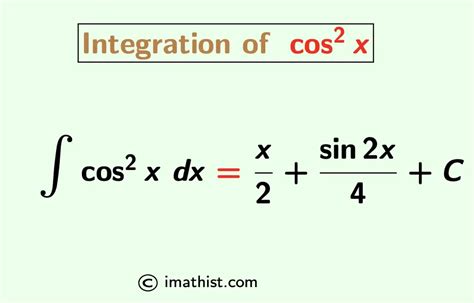
Extension to More Complex Functions
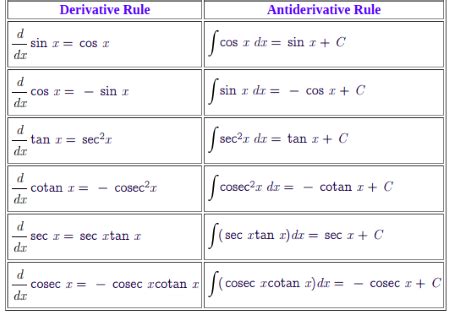
The concept of the integral of cos(x) can be extended to more complex functions, such as the integral of cos^n(x) and the integral of cos(x) with respect to other variables. These extensions are used to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under curves and solving differential equations. For example, the integral of cos^2(x) can be used to model the energy of an oscillation, while the integral of cos(x) with respect to time can be used to model the motion of an object.
Techniques for Evaluating the Integral of Cos(x)
There are several techniques for evaluating the integral of cos(x), including substitution, integration by parts, and integration by partial fractions. These techniques are used to solve problems in calculus and differential equations, and they’re essential for understanding the behavior of the cosine function. For example, substitution can be used to evaluate the integral of cos(x) by substituting x with a trigonometric function, such as sin(x) or tan(x).
What is the integral of cos(x)?
+The integral of cos(x) is sin(x) + C, where C is the constant of integration.
What are the applications of the integral of cos(x)?
+The integral of cos(x) has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and mathematics, including the study of oscillations, waves, and signal processing.
How is the integral of cos(x) derived?
+The integral of cos(x) is derived using the fundamental theorem of calculus, which states that differentiation and integration are inverse processes.
In conclusion, the integral of cos(x) is a fundamental concept in calculus, and its derivation and application are essential for understanding various mathematical and real-world problems. The concept of the integral of cos(x) can be extended to more complex functions, and its applications are diverse and widespread. By understanding the integral of cos(x), we can solve problems in calculus, differential equations, and other areas of mathematics and physics, and gain insights into the behavior of oscillations, waves, and signals.