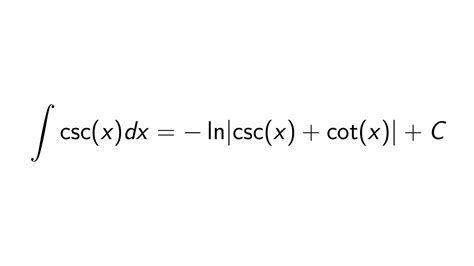The concept of integral calculus, particularly the integral of the cosecant function (csc), is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, playing a crucial role in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics. The integral of csc, denoted as ∫csc(x) dx, represents the antiderivative of the cosecant function. In this article, we will delve into five distinct ways to approach the integral of csc, exploring the intricacies of each method and highlighting their relevance to real-world applications.
Method 1: Integration by Substitution

One of the primary methods for solving the integral of csc involves the use of substitution, a technique where we replace a variable or an expression with another variable or expression to simplify the integral. For ∫csc(x) dx, we can use the substitution u = sin(x), which leads to du = cos(x) dx. However, to apply this substitution directly, we need to express csc(x) in terms of sin(x) and cos(x). Since csc(x) = 1/sin(x), we can manipulate the integral to fit the substitution, ultimately leading to the solution -ln|csc(x) + cot(x)| + C, where C is the constant of integration.
Derivation of the Integral of Csc Using Substitution
To derive the integral, we first express csc(x) in a form that is amenable to substitution. Recognizing that csc(x) = 1/sin(x), we can write the integral as ∫(1/sin(x)) dx. By using the substitution u = sin(x), we transform the integral into a form that can be directly integrated, considering the relationship between sin(x) and cos(x) to adjust the differential dx accordingly.
| Method | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Substitution | ∫csc(x) dx = -ln|csc(x) + cot(x)| + C | Using substitution to simplify the integral |
Method 2: Integration by Parts
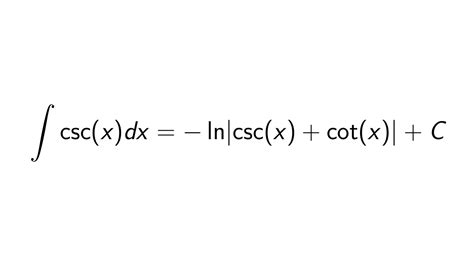
Another approach to solving the integral of csc involves the use of integration by parts, a technique that allows us to integrate the product of two functions. This method is based on the formula ∫u dv = uv - ∫v du, where u and v are functions of x. By carefully selecting u and dv, we can simplify the integral and solve it. However, the direct application of integration by parts to ∫csc(x) dx is less straightforward and typically involves recognizing the integral as a special case or applying trigonometric identities to transform it into a more manageable form.
Considerations for Integration by Parts
When considering integration by parts for the integral of csc, it’s essential to recognize the potential complexity and the need for clever selection of u and dv. This method, while powerful, may not always yield a straightforward solution for ∫csc(x) dx without additional manipulations or identities.
Key Points
- The integral of csc(x) can be approached through various methods, including substitution and integration by parts.
- Each method offers a unique perspective on solving the integral, with substitution being particularly effective for csc(x).
- Understanding the fundamental trigonometric relationships and identities is crucial for manipulating and solving integrals involving csc(x).
- The choice of method depends on the context and the specific form of the integral.
- Recognizing the integral of csc(x) as a standard form can simplify the solution process.
Method 3: Recognizing Standard Forms
A direct approach to solving the integral of csc involves recognizing it as a standard form, for which the antiderivative is well-known. The integral of csc(x) is a basic form that can be directly looked up or recognized from a table of integrals, yielding the solution -ln|csc(x) + cot(x)| + C. This method is the most straightforward and efficient, relying on familiarity with common integrals and their solutions.
Importance of Familiarity with Standard Forms
Familiarity with standard forms of integrals, including the integral of csc(x), is invaluable for efficiently solving problems in calculus and its applications. Recognizing these forms allows for the immediate identification of the antiderivative, streamlining the solution process.
Method 4: Using Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric identities can be leveraged to transform the integral of csc into a more manageable form. By expressing csc(x) in terms of other trigonometric functions, such as sin(x) and cos(x), and applying appropriate identities, we can simplify the integral. For instance, using the identity csc^2(x) = 1 + cot^2(x) can help in transforming the integral, although this method may lead to a more complex derivation compared to direct substitution or recognition of standard forms.
Application of Trigonometric Identities
The application of trigonometric identities to solve the integral of csc(x) highlights the importance of understanding and manipulating these identities in calculus. By recognizing and applying the appropriate identities, we can transform seemingly complex integrals into solvable forms.
Method 5: Numerical Integration
In cases where an analytical solution is not feasible or when dealing with complex functions, numerical integration methods can be employed to approximate the value of the integral of csc(x). Techniques such as the Riemann sum, trapezoidal rule, or Simpson’s rule can be used, offering an approximate solution based on the discretization of the area under the curve. While not providing an exact antiderivative, numerical methods are invaluable for applications where an approximation suffices.
Numerical Methods for Approximation
Numerical integration techniques offer a practical approach to approximating the integral of csc(x) when exact methods are not applicable. These methods, while subject to error, can provide a sufficiently accurate approximation for many real-world applications.
What is the most efficient method for solving the integral of csc(x)?
+The most efficient method typically involves recognizing the integral as a standard form, for which the antiderivative is well-known, yielding -ln|csc(x) + cot(x)| + C.
How do trigonometric identities assist in solving the integral of csc(x)?
+Trigonometric identities can transform the integral into a more manageable form by expressing csc(x) in terms of other trigonometric functions, facilitating the integration process.
What role does numerical integration play in solving the integral of csc(x)?
+Numerical integration provides an approximate solution when an analytical approach is not feasible, using techniques like the Riemann sum or Simpson's rule to discretize the area under the curve.
In conclusion, the integral of csc(x) can be approached through multiple methods, each offering unique insights and solutions. From the direct recognition of standard forms to the application of trigonometric identities and numerical integration techniques, the choice of method depends on the context, the specific form of the integral, and the desired level of precision. Understanding these methods not only deepens our grasp of calculus but also equips us with the flexibility to tackle a wide range of problems in mathematics and its applications.