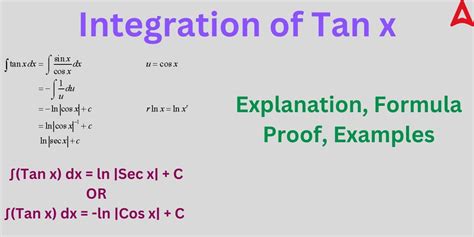
The integral of the tangent function, denoted as ∫tan(x) dx, is a fundamental concept in calculus that has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and mathematics. The tangent function, or tan(x), is defined as the ratio of the sine and cosine functions, i.e., tan(x) = sin(x) / cos(x). In this article, we will delve into the world of trigonometric integrals, exploring the integration of the tangent function, its derivation, and practical applications.
Key Points
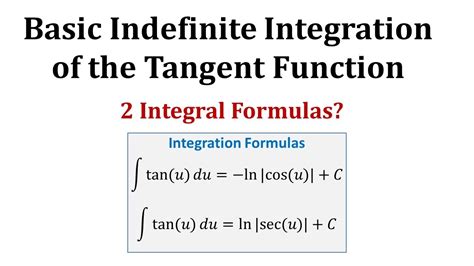
- The integral of the tangent function is -ln|cos(x)| + C, where C is the constant of integration.
- The derivation of this integral involves using the substitution method and the properties of logarithmic functions.
- The integral of the tangent function has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and mathematics, including the calculation of areas, volumes, and work done.
- Trigonometric identities, such as the Pythagorean identity, sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1, play a crucial role in deriving the integral of the tangent function.
- Understanding the integral of the tangent function is essential for solving problems in calculus, differential equations, and other areas of mathematics and science.
Derivation of the Integral of Tan(x)
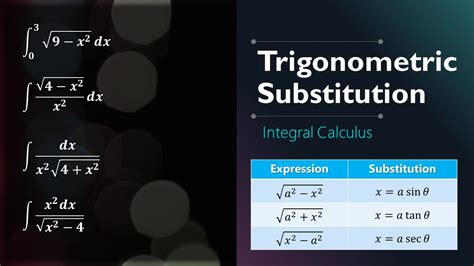
To derive the integral of the tangent function, we start by using the substitution method. Let’s substitute u = cos(x), which implies du/dx = -sin(x). Rearranging this expression, we get du = -sin(x) dx. Now, we can rewrite the integral of the tangent function as ∫tan(x) dx = ∫sin(x) / cos(x) dx. Substituting u = cos(x), we get ∫-du / u = -∫du / u. This is a standard integral, which evaluates to -ln|u| + C, where C is the constant of integration. Substituting back u = cos(x), we get -ln|cos(x)| + C, which is the final answer.
Trigonometric Identities and the Integral of Tan(x)
Trigonometric identities play a vital role in deriving the integral of the tangent function. One of the most important identities used in this derivation is the Pythagorean identity, sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1. This identity allows us to express the tangent function in terms of the sine and cosine functions, which are more easily integrable. Additionally, the identity tan(x) = sin(x) / cos(x) is used to rewrite the integral of the tangent function in a more manageable form.
| Trigonometric Identity | Description |
|---|---|
| Pythagorean Identity | sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1 |
| Tangent Identity | tan(x) = sin(x) / cos(x) |
| Sine Identity | sin^2(x) = 1 - cos^2(x) |
Applications of the Integral of Tan(x)
The integral of the tangent function has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and mathematics. One of the most significant applications is in the calculation of areas and volumes. For example, the integral of the tangent function can be used to calculate the area under a curve or the volume of a solid. Additionally, the integral of the tangent function is used in the calculation of work done by a force, which is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering.
Work Done by a Force
The work done by a force is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering. It is defined as the product of the force and the distance over which it is applied. The work done by a force can be calculated using the integral of the tangent function. For example, if a force F(x) is applied to an object over a distance x, the work done by the force can be calculated as W = ∫F(x) dx. If the force is a function of the tangent, i.e., F(x) = tan(x), then the work done by the force can be calculated as W = ∫tan(x) dx = -ln|cos(x)| + C, where C is the constant of integration.
What is the integral of the tangent function?
+The integral of the tangent function is -ln|cos(x)| + C, where C is the constant of integration.
What is the derivation of the integral of the tangent function?
+The derivation of the integral of the tangent function involves using the substitution method and the properties of logarithmic functions.
What are the applications of the integral of the tangent function?
+The integral of the tangent function has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and mathematics, including the calculation of areas, volumes, and work done.
Meta Description: Learn about the integral of the tangent function, its derivation, and practical applications in physics, engineering, and mathematics. Discover how to calculate the area under a curve, the volume of a solid, and the work done by a force using the integral of the tangent function.



