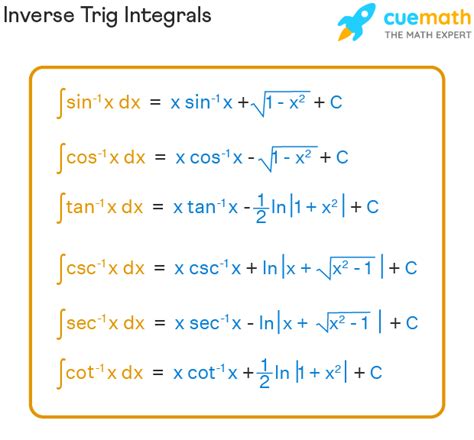
The realm of inverse trigonometric functions is a complex yet fascinating domain that has garnered significant attention in the mathematical community. As a fundamental concept in calculus, understanding the intricacies of inverse trig functions is crucial for navigating various mathematical and real-world applications. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of inverse trig functions, delving into their definitions, properties, and integration techniques, while also highlighting their practical implications and limitations.
Introduction to Inverse Trig Functions
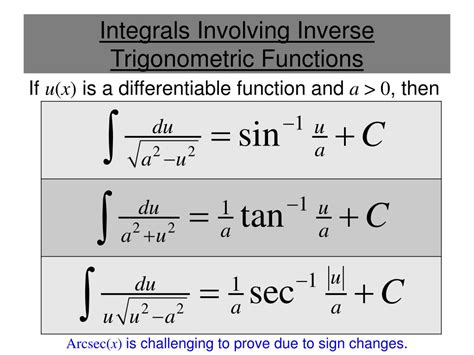
Inverse trigonometric functions, denoted as arcsin, arccos, and arctan, are the inverse operations of the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent, respectively. These functions play a pivotal role in calculus, particularly in the context of integration, as they enable the evaluation of definite integrals involving trigonometric expressions. The inverse trig functions are defined as follows: - y = arcsin(x) if and only if sin(y) = x - y = arccos(x) if and only if cos(y) = x - y = arctan(x) if and only if tan(y) = x Understanding the properties and ranges of these functions is essential for effective integration and application in various mathematical contexts.
Key Points
- Inverse trig functions are the inverse operations of trigonometric functions.
- They play a crucial role in calculus, particularly in integration.
- The range of arcsin(x) is [-π/2, π/2].
- The range of arccos(x) is [0, π].
- The range of arctan(x) is (-π/2, π/2).
Integration Techniques for Inverse Trig Functions
The integration of inverse trig functions can be approached through various techniques, including substitution, integration by parts, and the use of trigonometric identities. One of the primary methods involves utilizing the derivative of the inverse trig function to facilitate the integration process. For instance, the derivative of arcsin(x) is 1/√(1-x^2), which can be employed to integrate expressions involving this function. Similarly, the derivatives of arccos(x) and arctan(x) are -1/√(1-x^2) and 1/(1+x^2), respectively, and can be used in conjunction with integration techniques to evaluate complex expressions.
| Function | Derivative |
|---|---|
| arcsin(x) | 1/√(1-x^2) |
| arccos(x) | -1/√(1-x^2) |
| arctan(x) | 1/(1+x^2) |
Applications and Limitations of Inverse Trig Functions

Inverse trig functions have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, particularly in the context of solving equations and modeling periodic phenomena. However, they also have limitations, such as restricted ranges and potential singularities, which must be carefully considered when applying these functions. The understanding of these limitations is crucial for avoiding common pitfalls and ensuring the accuracy of mathematical models and calculations.
Practical Implications and Real-World Applications
The practical implications of inverse trig functions are far-reaching, with applications in navigation, physics, and engineering. For instance, the use of arctan(x) in computer graphics enables the calculation of angles and orientations, while the application of arcsin(x) in navigation facilitates the determination of positions and trajectories. The understanding of inverse trig functions is also essential in physics, particularly in the context of wave mechanics and signal processing, where these functions are used to model and analyze periodic phenomena.
What are the primary applications of inverse trig functions?
+The primary applications of inverse trig functions include navigation, physics, and engineering, particularly in the context of solving equations and modeling periodic phenomena.
What are the limitations of inverse trig functions?
+The limitations of inverse trig functions include restricted ranges and potential singularities, which must be carefully considered when applying these functions.
How are inverse trig functions used in calculus?
+Inverse trig functions are used in calculus to evaluate definite integrals involving trigonometric expressions, particularly in the context of integration by substitution and integration by parts.
In conclusion, the understanding of inverse trig functions is essential for navigating various mathematical and real-world applications. By grasping the definitions, properties, and integration techniques of these functions, individuals can develop a deeper appreciation for the complex interplay between trigonometric concepts and their practical implications. As the mathematical community continues to evolve, the significance of inverse trig functions will only continue to grow, underscoring the importance of a comprehensive understanding of these fundamental concepts.