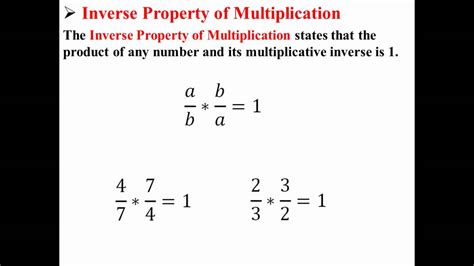
Mastering the concept of multiplication inverses is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, particularly in algebra and beyond. The multiplication inverse of a number is another number that, when multiplied by the original number, results in 1. This concept is crucial for solving equations and manipulating algebraic expressions. In this article, we will delve into five essential tips for understanding and working with multiplication inverses, providing a solid foundation for mathematical problem-solving.
Key Points
- Understanding the definition and purpose of multiplication inverses in mathematics.
- Learning how to find the multiplication inverse of a number.
- Applying multiplication inverses to solve linear equations.
- Using multiplication inverses in fraction operations and simplifications.
- Practicing with real-world examples and mathematical exercises to solidify understanding.
Understanding Multiplication Inverses

The concept of a multiplication inverse is straightforward: for any number a, its multiplication inverse is a number b such that a * b = 1. This concept is foundational in mathematics, especially when dealing with fractions, decimals, and algebraic equations. For instance, the multiplication inverse of 2 is 1⁄2 because 2 * 1⁄2 = 1. Understanding and identifying multiplication inverses is the first step in applying them effectively in mathematical problems.
Finding Multiplication Inverses
Finding the multiplication inverse involves simple division when dealing with numbers. For a number a, its inverse is 1/a. However, when dealing with variables or more complex expressions, the process might require algebraic manipulation. For example, to find the inverse of x, one would consider 1/x. In more complex scenarios, such as matrices, the process of finding an inverse is more intricate and involves specific formulas and operations.
| Number | Multiplication Inverse |
|---|---|
| 5 | 1/5 |
| 3/4 | 4/3 |
| x | 1/x |
Applying Multiplication Inverses to Solve Equations
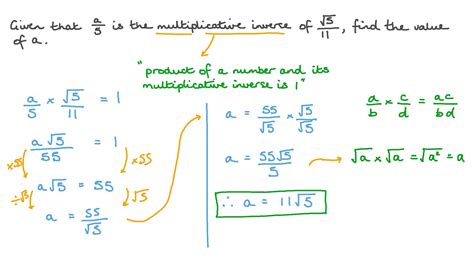
Multiplication inverses are particularly useful in solving linear equations. When an equation is in the form a*x = b, multiplying both sides by the inverse of a (which is 1/a) allows one to solve for x. This process effectively isolates x on one side of the equation, providing the solution. For example, given the equation 4x = 12, multiplying both sides by 1⁄4 yields x = 12(1⁄4) = 3.
Using Multiplication Inverses in Fraction Operations
In fraction operations, multiplication inverses play a critical role. When dividing by a fraction, it is equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal (or multiplication inverse). For instance, dividing by 3⁄4 is the same as multiplying by 4⁄3. This understanding is vital for simplifying complex fractions and performing arithmetic operations involving fractions.
Practicing with Examples and Exercises
Like any mathematical concept, mastery of multiplication inverses comes from practice. Engaging with a variety of problems, from simple arithmetic to more complex algebraic manipulations, helps solidify the understanding and application of multiplication inverses. Real-world examples, such as calculating proportions or scaling factors, can also provide practical insight into the utility and importance of multiplication inverses in everyday and professional contexts.
What is the multiplication inverse of a number?
+The multiplication inverse of a number a is another number b such that a * b = 1. For example, the multiplication inverse of 5 is 1/5.
How do you find the multiplication inverse of a fraction?
+To find the multiplication inverse of a fraction, you simply flip the fraction. For instance, the inverse of 3/4 is 4/3.
What is the role of multiplication inverses in solving linear equations?
+Multiplication inverses are used to isolate the variable in a linear equation. By multiplying both sides of the equation by the inverse of the coefficient of the variable, you can solve for the variable.
In conclusion, understanding and applying multiplication inverses is a critical skill in mathematics, enabling the solution of equations, manipulation of fractions, and performance of various algebraic operations. By mastering this concept and practicing its application, individuals can significantly enhance their mathematical proficiency and problem-solving capabilities.