Understanding and correctly using irregular past tense verbs is a fundamental aspect of mastering the English language. Unlike regular verbs, which follow a predictable pattern when forming their past tense (typically by adding -ed), irregular verbs have unique past tense forms that must be memorized. This can be a challenging task, especially for non-native speakers, due to the lack of a consistent rule that applies to all irregular verbs. However, with practice, patience, and the right approach, learners can improve their proficiency in using these verbs accurately.
Nature of Irregular Past Tense Verbs
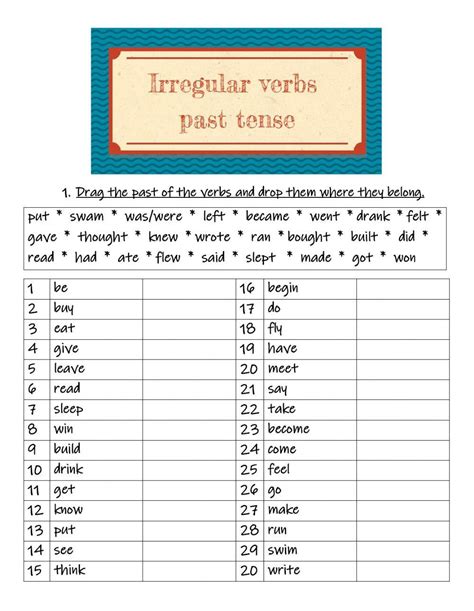
Irregular past tense verbs are those that do not follow the usual pattern of forming the past tense by adding -d or -ed to the base form of the verb. Instead, their past tense forms are often entirely different from their base forms and must be learned individually. For example, the verb “go” becomes “went” in the past tense, and “take” becomes “took”. The reasons behind these irregularities are rooted in the historical development of the English language, which has borrowed words from various languages, including Old English, Old Norse, French, and many others, each contributing its own grammatical quirks.
Common Irregular Past Tense Verbs
Some of the most commonly used irregular past tense verbs in English include “be” (was/were), “have” (had), “do” (did), “say” (said), “get” (got), and “make” (made). Mastering these verbs is crucial because they are frequently used in everyday conversation and writing. Learners can benefit from creating flashcards or making lists to help them memorize the base, past simple, and past participle forms of these verbs. For instance, the verb “eat” has “ate” as its past simple form and “eaten” as its past participle form.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| go | went | gone |
| take | took | taken |
| be | was/were | been |
| have | had | had |

Practical Applications and Challenges

Applying irregular past tense verbs correctly in sentences can be challenging, especially in contexts where the verb form changes based on the subject or the tense used. For instance, the verb “be” has different past tense forms (“was” for singular subjects and “were” for plural subjects), which can lead to errors if not used correctly. Practice exercises, such as filling in the blanks with the correct form of the verb or creating short stories using a variety of irregular verbs, can help learners overcome these challenges.
Tips for Mastery
To master irregular past tense verbs, learners should focus on consistent practice, using a variety of methods such as quizzes, writing prompts, and conversation exercises. Listening to and imitating native speakers can also provide valuable insights into how these verbs are used naturally in speech. Furthermore, understanding the nuances of English grammar, including the differences between the simple past, past perfect, and past continuous tenses, can help learners use irregular verbs more accurately in context.
Key Points
- Irregular past tense verbs do not follow a predictable pattern and must be memorized individually.
- Common irregular verbs like "go", "take", and "be" are frequently used and should be prioritized in learning.
- Grouping verbs into categories can aid in memorization.
- Practical application through writing and conversation exercises is crucial for mastery.
- Understanding English grammar nuances can help in accurate usage.
Overcoming Common Errors
One of the most common errors learners make when using irregular past tense verbs is confusing the past simple and past participle forms. For example, saying “I have went” instead of “I have gone” because “went” is the past simple form of “go”, while “gone” is the past participle form used with “have”. To overcome such errors, it’s essential to practice using these verbs in different contexts, such as in the present perfect, past perfect, and past simple tenses, and to receive feedback from instructors or language exchange partners.
Looking to the Future
As learners continue to practice and master irregular past tense verbs, they should also focus on how these verbs are used in real-life situations, including in formal and informal writing, and in different dialects of English. This can involve reading English literature, watching English movies, and engaging in conversations with native speakers. By doing so, learners not only improve their grammatical accuracy but also develop a deeper understanding of the linguistic and cultural nuances of the English language.
What is the best way to memorize irregular past tense verbs?
+The best way to memorize irregular past tense verbs is through consistent practice, using methods such as flashcards, quizzes, and writing exercises. Grouping verbs into categories based on their patterns can also aid in memorization.
How can I ensure I'm using irregular past tense verbs correctly in sentences?
+To ensure correct usage, practice filling in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in various sentence contexts. Additionally, listening to and imitating native speakers can provide valuable insights into natural usage.
What resources are available for learning irregular past tense verbs?
+Resources include grammar textbooks, online quizzes and exercises, language learning apps, and practice with a language exchange partner or tutor. Watching English media and reading English literature can also help.
In conclusion, mastering irregular past tense verbs is a key component of achieving proficiency in English. While it presents challenges due to the lack of a consistent formation rule, learners can overcome these challenges through dedicated practice, the use of effective memorization strategies, and a deep understanding of English grammar. By incorporating these verbs naturally into their language use, learners can enhance their communication skills, both in writing and in speech, and move closer to fluent expression in English.