The Middle East has long been a volatile region, with various nations vying for power and influence. Iran, in particular, has been at the forefront of regional politics, often finding itself at odds with neighboring countries and global superpowers. The Islamic Republic has a history of declaring war or engaging in conflict through various means, which can be both overt and covert. Understanding these methods is crucial for analyzing the region's geopolitical landscape and predicting potential future conflicts.
Key Points
- Iran's military strategy often involves a combination of conventional and unconventional tactics.
- The country's support for proxy forces is a key component of its foreign policy and military strategy.
- Cyber warfare has become an increasingly important tool for Iran, allowing it to attack adversaries without directly engaging in traditional combat.
- Iran's nuclear program remains a point of contention, with the country insisting it is for peaceful purposes while others suspect it may be aimed at developing nuclear weapons.
- Economic warfare, including sanctions and trade restrictions, is another method through which Iran can declare war without traditional military engagement.
Conventional Military Engagement

Iran’s conventional military is a significant force in the region, with a large army, navy, and air force. The country has been involved in several conflicts over the years, including the Iran-Iraq War from 1980 to 1988, which was one of the deadliest conflicts of the 20th century. Iran’s military doctrine emphasizes defense and deterrence, but it is capable of launching offensive operations. The use of conventional military force is the most traditional way Iran might declare war, involving direct combat with an adversary’s armed forces.
Proxy Wars and Asymmetric Warfare
Beyond conventional military engagement, Iran is known for its support of proxy forces and engagement in asymmetric warfare. This involves backing militant groups or militias in other countries to achieve strategic objectives without directly committing Iranian troops. Examples include Hezbollah in Lebanon and the Houthis in Yemen. Through these proxies, Iran can exert influence, destabilize enemies, and declare a form of war without the international community recognizing it as a traditional declaration of war. This tactic allows Iran to maintain plausible deniability while still pursuing its interests.
| Proxy Group | Country of Operation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Hezbollah | Lebanon | Influence in Lebanon, pressure on Israel |
| Houthis | Yemen | Control of Yemen, pressure on Saudi Arabia |
| Hashd al-Shaabi | Iraq | Influence in Iraq, resistance to ISIS and other groups |
Cyber Warfare

Cyber warfare represents a modern front in Iran’s military strategy, allowing the country to attack critical infrastructure, disrupt communications, and gather intelligence without the need for traditional military engagement. Iran has been accused of conducting numerous cyber attacks against adversaries, including the United States, Israel, and Saudi Arabia. This form of warfare enables Iran to declare a kind of war that is difficult to respond to conventionally, as it does not involve direct military action but can still have significant impacts on an adversary’s economy and security.
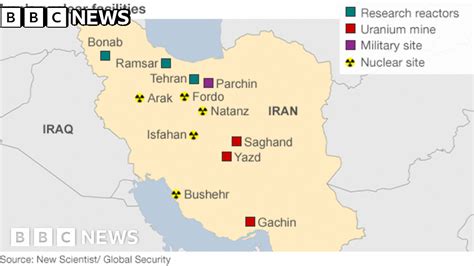
Nuclear Program and the Threat of Nuclear War
Iran’s nuclear program is a highly contentious issue, with the international community expressing concerns that it could be used to develop nuclear weapons. While Iran maintains that its program is for peaceful purposes, such as energy production and medical research, the possibility of nuclear weapon development cannot be ruled out. The threat of nuclear war, whether through the development of nuclear weapons or the attack on nuclear facilities, is a grave one, and Iran’s nuclear program is closely watched by the international community. The pursuit of nuclear capabilities can be seen as a form of declaring war, as it significantly raises the stakes and potential consequences of any conflict involving Iran.
Economic Warfare
Economic warfare, including the imposition and endurance of sanctions, is another method through which Iran can engage in conflict. Sanctions imposed by other countries, particularly the United States, have had significant effects on Iran’s economy, limiting its access to international markets and restricting the flow of goods and services. In response, Iran can employ its own economic warfare tactics, such as supporting terrorism, disrupting oil supplies, or engaging in currency manipulation, to harm its adversaries economically. This form of warfare can be just as damaging as traditional military conflict, affecting the livelihoods of citizens and the stability of governments.
What are the primary methods through which Iran declares war?
+Iran declares war through a variety of methods, including conventional military engagement, support for proxy forces, cyber warfare, development of its nuclear program, and economic warfare.
Why does Iran often prefer asymmetric warfare over conventional military engagement?
+Iran prefers asymmetric warfare because it allows the country to achieve strategic objectives without directly committing its military forces, thus avoiding the risks and consequences associated with conventional warfare.
How significant is cyber warfare in Iran's military strategy?
+Cyber warfare is increasingly significant in Iran's military strategy, offering a means to attack adversaries, disrupt their operations, and gain strategic advantages without the need for traditional military action.
In conclusion, Iran’s approach to declaring war is multifaceted, reflecting the country’s strategic adaptability and its desire to exert influence across the Middle East. Whether through conventional military means, proxy wars, cyber attacks, nuclear development, or economic warfare, Iran has demonstrated its willingness to engage in conflict to protect its interests and challenge its adversaries. Understanding these various methods is essential for navigating the complexities of Middle Eastern geopolitics and anticipating potential future conflicts in the region.



