Iron(II) oxide, also known as ferrous oxide, is a chemical compound with the formula FeO. It is a black solid with a metallic luster and is highly reactive. Iron(II) oxide is an important compound in the field of materials science and is used in a variety of applications, including the production of steel, catalysts, and pigments.
Physical Properties
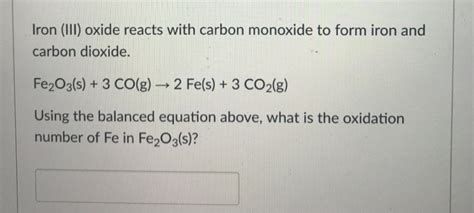
Iron(II) oxide has a number of distinct physical properties that make it useful for a range of applications. It has a melting point of 1377°C and a boiling point of 3270°C, making it a relatively stable compound at high temperatures. Iron(II) oxide is also highly dense, with a density of 5.7 g/cm³, which makes it useful for applications where high mass is required.
One of the most distinctive physical properties of iron(II) oxide is its color. It is a black solid with a metallic luster, which makes it useful as a pigment in a range of applications, including paints, coatings, and plastics. Iron(II) oxide is also highly opaque, which makes it useful for applications where high levels of light absorption are required.
Crystal Structure
Iron(II) oxide has a crystal structure that is based on the sodium chloride (NaCl) structure. In this structure, the iron ions are arranged in a cubic lattice, with each iron ion surrounded by six oxygen ions. The oxygen ions are arranged in a cubic lattice, with each oxygen ion surrounded by six iron ions. This crystal structure gives iron(II) oxide its high density and stability.| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1377°C |
| Boiling Point | 3270°C |
| Density | 5.7 g/cm³ |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic |
Chemical Properties

Iron(II) oxide is highly reactive, which makes it useful for a range of chemical applications. It is highly susceptible to oxidation, which makes it useful as a reducing agent in a range of chemical reactions. Iron(II) oxide is also highly reactive with acids, which makes it useful for applications where high levels of acidity are required.
One of the most distinctive chemical properties of iron(II) oxide is its ability to undergo a range of chemical reactions. It can react with oxygen to form iron(III) oxide, which is a highly stable compound. Iron(II) oxide can also react with acids to form iron salts, which are highly soluble in water.
Reactivity
Iron(II) oxide is highly reactive, which makes it useful for a range of chemical applications. It is highly susceptible to oxidation, which makes it useful as a reducing agent in a range of chemical reactions. Iron(II) oxide is also highly reactive with acids, which makes it useful for applications where high levels of acidity are required.Key Points
- Iron(II) oxide has a melting point of 1377°C and a boiling point of 3270°C.
- Iron(II) oxide is highly dense, with a density of 5.7 g/cm³.
- Iron(II) oxide has a crystal structure based on the sodium chloride (NaCl) structure.
- Iron(II) oxide is highly reactive, which makes it useful for a range of chemical applications.
- Iron(II) oxide can react with oxygen to form iron(III) oxide, which is a highly stable compound.
Applications
Iron(II) oxide has a range of applications, including the production of steel, catalysts, and pigments. It is highly useful as a reducing agent in a range of chemical reactions, and its high density makes it useful for applications where high mass is required.One of the most significant applications of iron(II) oxide is in the production of steel. Iron(II) oxide is used as a reducing agent in the blast furnace, where it reacts with carbon to form iron. This iron is then used to produce steel, which is a highly versatile and widely used material.
Pigments
Iron(II) oxide is also highly useful as a pigment in a range of applications, including paints, coatings, and plastics. Its high opacity and metallic luster make it useful for applications where high levels of light absorption are required.What is the melting point of iron(II) oxide?
+The melting point of iron(II) oxide is 1377°C.
What is the crystal structure of iron(II) oxide?
+The crystal structure of iron(II) oxide is based on the sodium chloride (NaCl) structure.
What are the applications of iron(II) oxide?
+Iron(II) oxide has a range of applications, including the production of steel, catalysts, and pigments.
Meta Description: Iron(II) oxide properties, including physical and chemical properties, crystal structure, and applications. Learn about the uses of iron(II) oxide in steel production, catalysts, and pigments.