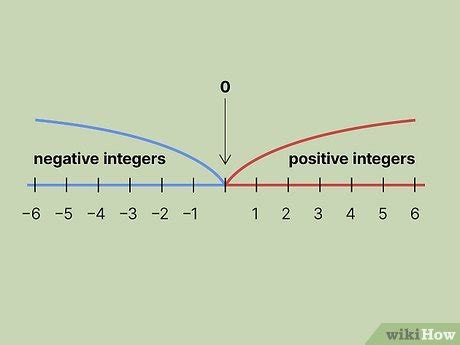
The question of whether 0 is a positive integer is a matter of debate among mathematicians and experts in various fields. To address this, let's first establish the definition of a positive integer. A positive integer is typically defined as an integer greater than zero. This definition is widely used in elementary arithmetic and is intuitive for most people. However, the inclusion or exclusion of zero as a positive integer can depend on the context and the specific mathematical or computational framework being used.
Mathematical Definition and Context

In standard mathematics, the set of positive integers is often denoted as ℕ+ or ℤ+ and includes all integers greater than zero: 1, 2, 3,…. This definition excludes zero, treating it as a special case that is neither positive nor negative but serves as the additive identity. The rationale behind excluding zero from the set of positive integers is to maintain consistency in various mathematical operations and properties, such as the behavior of inequalities and the definition of positive and negative numbers.
Contextual Variations
However, there are contexts in which zero might be included in discussions about positive integers, particularly when considering the broader set of non-negative integers, denoted as ℕ₀ or ℤ₀≥, which includes 0, 1, 2, 3,…. This set is relevant in combinatorics, graph theory, and other areas of mathematics where the distinction between positive and non-negative integers is crucial. In these contexts, including zero as part of the discussion does not necessarily imply it is considered a positive integer but rather acknowledges its role in the sequence of non-negative integers.
| Set Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| ℕ+ | Set of positive integers (1, 2, 3,...) |
| ℕ₀ | Set of non-negative integers (0, 1, 2, 3,...) |
| ℤ+ | Set of positive integers in the set of all integers |
| ℤ₀≥ | Set of non-negative integers in the set of all integers |

Key Points
- The standard definition of positive integers excludes zero, considering it as neither positive nor negative.
- Zero is part of the set of non-negative integers, which is crucial in certain mathematical contexts.
- The inclusion or exclusion of zero from positive integers depends on the mathematical framework or context.
- Understanding the distinction between positive and non-negative integers is essential for clarity in mathematical discussions.
- Contextual variations in the treatment of zero reflect the complexity and nuance of mathematical definitions.
Ultimately, whether 0 is considered a positive integer depends on the specific context and the definitions being applied. For most standard mathematical purposes, zero is not classified as a positive integer, but its role in the broader set of non-negative integers is recognized and utilized in various mathematical and computational contexts.
What is the standard definition of a positive integer?
+A positive integer is an integer greater than zero, typically denoted as 1, 2, 3,....
Is zero considered a non-negative integer?
+Yes, zero is considered a non-negative integer and is included in the set of non-negative integers, denoted as ℕ₀ or ℤ₀≥.
Why is the distinction between positive and non-negative integers important?
+The distinction is crucial for maintaining consistency in mathematical operations, definitions, and properties, especially in areas like combinatorics and graph theory.
In conclusion, the classification of zero as a positive integer is nuanced, depending on the mathematical context and definitions in use. Understanding these nuances is essential for clarity and precision in mathematical discussions and applications.