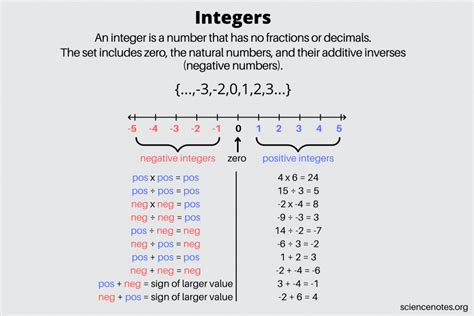
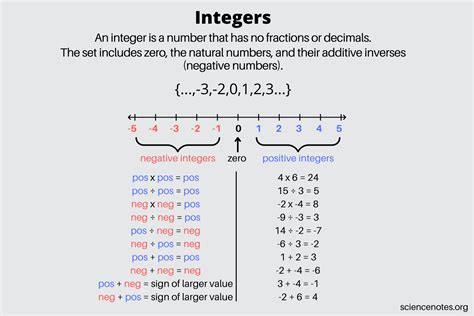
The question of whether 0 is an integer is a fundamental one in mathematics, and the answer is unequivocally yes. In the set of integers, which includes all whole numbers, both positive and negative, as well as zero, 0 is indeed considered an integer. This classification is based on the definition of integers as a set of numbers that includes..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,..., where 0 serves as the additive identity, meaning that for any integer x, x + 0 = x.
Definition and Properties of Integers

The definition of integers is central to understanding why 0 is classified as one. Integers are whole numbers, either positive, negative, or zero, without a fractional part. The set of integers is often denoted by the symbol ℤ, derived from the German word “Zahlen,” meaning numbers. The properties of integers, such as being closed under addition and multiplication (i.e., the sum and product of any two integers are also integers), further solidify 0’s place within this set, as 0 participates in these operations without violating their definitions.
Role of 0 in Mathematical Operations
0 plays a critical role in the algebraic structure of integers. As the additive identity, it does not change the value of any integer when added to it. For example, 5 + 0 = 5. Moreover, 0 is the additive inverse of itself, as 0 + 0 = 0, which aligns with the property that every integer has an additive inverse. This functional role of 0 in the system of integers underscores its integral (pun intended) nature within the set.
| Mathematical Operation | Example with 0 |
|---|---|
| Addition | 5 + 0 = 5 |
| Multiplication | 5 * 0 = 0 |
Implications and Applications
The recognition of 0 as an integer has far-reaching implications across various mathematical disciplines and their applications. In algebra, for instance, the concept of zero as an integer facilitates the formulation of equations and the solution of linear equations. In computer science, integers, including 0, are basic data types used in programming languages for performing arithmetic operations and making logical decisions.
Historical Perspective
Historically, the acceptance of 0 as a number and, more specifically, as an integer, was a gradual process. Ancient civilizations initially hesitated to embrace 0 due to its abstract nature and the challenge it posed to traditional notions of number and quantity. However, as mathematical concepts evolved, particularly with the development of the decimal system in India and its spread to the Middle East and Europe, the utility and necessity of 0 became increasingly apparent, leading to its universal acceptance as a fundamental component of the number system.
Key Points
- 0 is considered an integer based on the definition of integers as a set of whole numbers, including positive, negative numbers, and zero.
- The role of 0 as the additive identity and its participation in algebraic structures solidify its status as an integer.
- Historically, the recognition of 0 as a number and integer evolved over time, reflecting advancements in mathematical understanding and the need for a consistent number system.
- The inclusion of 0 as an integer is crucial for the coherence and functionality of arithmetic and algebraic systems.
- 0's status as an integer has significant implications for various mathematical disciplines and their applications in science and technology.
In conclusion, the classification of 0 as an integer is a cornerstone of mathematics, grounded in the definitions and properties of integers. This understanding is pivotal for the development and application of mathematical concepts across different fields, underscoring the fundamental nature of 0 within the number system.
What is the definition of an integer, and how does 0 fit into this definition?
+An integer is a whole number, either positive, negative, or zero, without a fractional part. 0 fits into this definition as it is a whole number that serves as the additive identity, meaning that for any integer x, x + 0 = x.
Why is 0 considered essential in mathematical operations involving integers?
+0 is essential because it acts as the additive identity, allowing for the completion of arithmetic operations without altering the value of other integers. Its role in equations and as a placeholder in the decimal system further emphasizes its importance.
How did the historical perception of 0 as a number and an integer evolve?
+The perception of 0 evolved gradually, from initial hesitation due to its abstract nature to universal acceptance as a fundamental component of the number system. This evolution was influenced by the development of the decimal system and the recognition of 0’s utility in mathematical operations.