Understanding the Concept of a Passing Grade

The notion of a passing grade can vary significantly across different educational institutions and systems. In many contexts, the letter grade “D” is considered the lowest passing grade. However, whether “D” is deemed a passing grade depends on the specific grading scale and policies of the institution or educator. To address this question comprehensively, let’s delve into the typical grading scales used in educational settings and explore the implications of a “D” grade.
Common Grading Scales
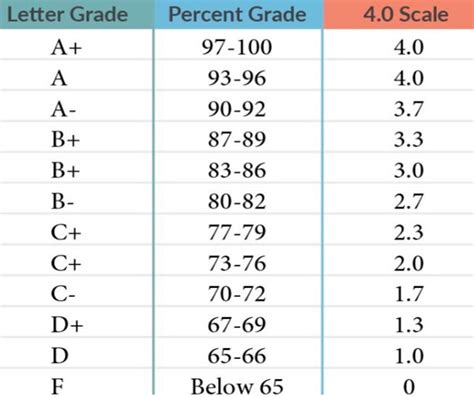
In the United States, for example, a common grading scale includes the letters A, B, C, D, and F, with A being the highest grade and F indicating failure. On this scale, grades A, B, and C are generally considered satisfactory, with D being a minimal passing grade. However, some institutions may have a plus/minus system, where a D+ might be seen as a slightly stronger passing grade than a D-, and some might not consider a D as passing at all, particularly in certain critical courses or programs.
| Grade | Percentage | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| A | 90-100% | Excellent |
| B | 80-89% | Good |
| C | 70-79% | Fair |
| D | 60-69% | Passing but minimal |
| F | Below 60% | Failing |
Implications of a “D” Grade
Achieving a “D” grade can have various implications depending on the context. In some cases, it may suffice to progress to the next level of study or to graduate, but it might not be sufficient for certain programs, scholarships, or professional certifications that require higher GPA thresholds. Furthermore, a “D” grade might not be seen as competitive for graduate school admissions or job applications where academic performance is a key selection criterion.
Strategies for Improvement
For students who receive a “D” grade, it’s essential to reflect on the reasons behind this outcome. This could involve seeking additional tutoring, adjusting study habits, or re-evaluating course loads. Many institutions offer resources such as academic support services, counseling, and flexible scheduling options to help students improve their academic performance.
Key Points
- The definition of a passing grade can vary significantly across different educational contexts.
- A "D" grade is often considered the minimum passing grade but may have different implications depending on the institution or program.
- Understanding the grading scale and policies of one's institution is crucial for navigating academic requirements and goals.
- Strategies for improvement after receiving a "D" grade include seeking additional academic support and re-evaluating study habits.
- Consulting with academic advisors can provide personalized guidance on academic progress and future opportunities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while a “D” grade may be considered passing in many educational settings, its implications can vary widely. Students should strive to achieve higher grades to open up more opportunities, but for those who do receive a “D,” understanding the reasons behind this outcome and seeking support for improvement can be crucial steps towards academic success.
What does a “D” grade typically represent in the grading scale?
+A “D” grade usually represents a passing but minimal performance, often corresponding to a percentage range of 60-69%.
Can a “D” grade affect future academic or professional opportunities?
+Yes, a “D” grade can have implications for future opportunities, such as graduate school admissions, job applications, or professional certifications, where higher grades are often preferred or required.
What strategies can students use to improve their grades after receiving a “D”?
+Students can seek additional tutoring, adjust their study habits, re-evaluate their course loads, and utilize academic support services offered by their institution to improve their grades.



