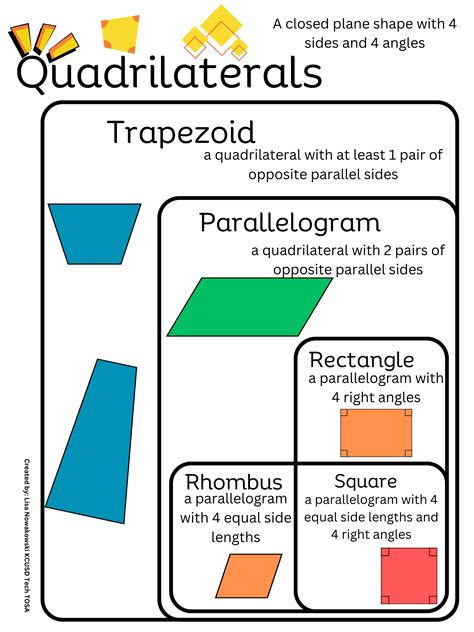
The trapezoid, a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides, is a fundamental shape in geometry. Its unique properties and characteristics make it a fascinating subject for study. With a rich history dating back to ancient civilizations, the trapezoid has been a crucial component in various architectural, engineering, and design applications. In this article, we will delve into five key facts about trapezoids, exploring their definitions, properties, and real-world implications.
Key Points
- The trapezoid is defined as a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides.
- Trapezoids can be classified into different types, including isosceles, scalene, and right trapezoids.
- The area of a trapezoid can be calculated using the formula: Area = (1/2) × (sum of parallel sides) × height.
- Trapezoids have numerous real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and design.
- The trapezoid's unique properties make it an essential shape in various mathematical and scientific contexts.
Definition and Classification of Trapezoids
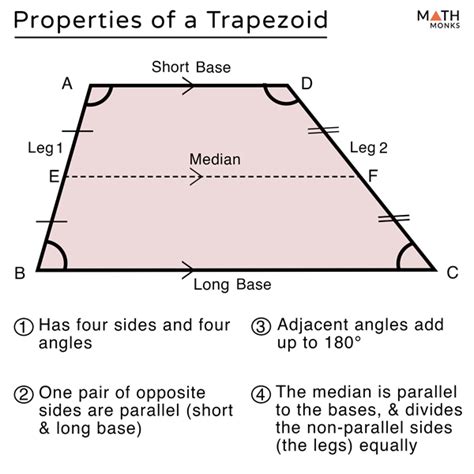
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. This definition encompasses a wide range of shapes, from the familiar trapezoid with two parallel sides to more complex shapes with multiple parallel sides. Trapezoids can be classified into different types, including isosceles, scalene, and right trapezoids. Isosceles trapezoids have two non-parallel sides of equal length, while scalene trapezoids have all sides of different lengths. Right trapezoids, on the other hand, have one right angle (90 degrees) and two parallel sides.
Properties of Trapezoids
Trapezoids exhibit several unique properties that make them useful in various mathematical and scientific contexts. One of the most important properties of a trapezoid is its ability to be divided into two triangles by drawing a diagonal. This property allows for the calculation of the trapezoid’s area using the formula: Area = (1⁄2) × (sum of parallel sides) × height. Additionally, trapezoids have a unique relationship with other geometric shapes, such as triangles, rectangles, and parallelograms.
| Type of Trapezoid | Properties |
|---|---|
| Isosceles Trapezoid | Two non-parallel sides of equal length |
| Scalene Trapezoid | All sides of different lengths |
| Right Trapezoid | One right angle (90 degrees) and two parallel sides |
Real-World Applications of Trapezoids

Trapezoids have numerous real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and design. In architecture, trapezoids are used in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures. For example, the ancient Egyptians used trapezoids in the construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza. In engineering, trapezoids are used in the design of mechanical systems, such as gears and levers. In design, trapezoids are used in the creation of logos, graphics, and other visual elements.
Mathematical and Scientific Implications
The trapezoid’s unique properties make it an essential shape in various mathematical and scientific contexts. In geometry, trapezoids are used to study the properties of quadrilaterals and to develop theorems and proofs. In trigonometry, trapezoids are used to study the relationships between angles and side lengths. In engineering, trapezoids are used to model and analyze complex systems, such as mechanical and electrical systems.
What is the definition of a trapezoid?
+A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides.
What are the different types of trapezoids?
+Trapezoids can be classified into different types, including isosceles, scalene, and right trapezoids.
What is the formula for calculating the area of a trapezoid?
+The area of a trapezoid can be calculated using the formula: Area = (1/2) × (sum of parallel sides) × height.
In conclusion, the trapezoid is a fascinating shape with unique properties and characteristics. Its definition, classification, and properties make it an essential component in various mathematical and scientific contexts. The trapezoid’s real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and design, demonstrate its importance and relevance in modern society. By understanding the trapezoid and its properties, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate and complex world of geometry and its applications.