No, aspirin and acetaminophen are not the same, although both are commonly used over-the-counter pain relievers and fever reducers. Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that works by blocking the production of certain natural substances that cause inflammation, pain, and fever in the body. It is often used to relieve headaches, reduce inflammation, and prevent blood clots.
Key Differences Between Aspirin and Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen, on the other hand, is primarily used to relieve pain and reduce fever. Unlike aspirin, acetaminophen does not have significant anti-inflammatory properties and is not typically used to treat inflammatory conditions such as arthritis. The exact mechanism of how acetaminophen works is not fully understood, but it is believed to affect the parts of the brain that regulate pain and temperature.
Comparison of Effects and Side Effects
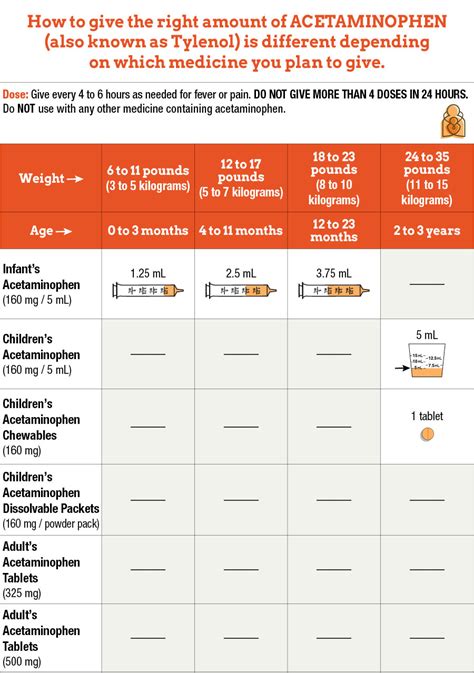
A key difference between the two medications is their side effect profiles. Aspirin can cause stomach upset, ulcers, and bleeding due to its effect on the stomach lining and its ability to thin the blood. Acetaminophen, when taken as directed, is generally easier on the stomach than aspirin. However, taking more than the recommended dose of acetaminophen can lead to liver damage, which is a serious side effect. The recommended dosage for adults for aspirin is typically 325-1000 mg every 4-6 hours, not to exceed 4000 mg in 24 hours, and for acetaminophen, it is 325-1000 mg every 4-6 hours, not to exceed 4000 mg in 24 hours.
| Medication | Primary Use | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Aspirin | Pain relief, inflammation, fever reduction, blood clot prevention | Stomach upset, ulcers, bleeding |
| Acetaminophen | Pain relief, fever reduction | Liver damage (with overdose), less stomach upset compared to aspirin |
Key Points
- Aspirin and acetaminophen are different medications with distinct uses and side effects.
- Aspirin is an NSAID used for pain relief, inflammation, fever reduction, and blood clot prevention, with potential side effects including stomach upset and bleeding.
- Acetaminophen is primarily used for pain relief and fever reduction, with a lower risk of stomach side effects but a risk of liver damage if taken in excess.
- It's essential to follow the recommended dosage for both medications and consult a healthcare professional, especially with underlying conditions or other medications.
- Understanding the differences between aspirin and acetaminophen can help in making informed decisions about pain management and reducing the risk of adverse effects.
In summary, while aspirin and acetaminophen can both be used for pain relief, they are not interchangeable due to their different mechanisms of action, uses, and potential side effects. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on which medication to use and how to use it safely.
Can I take aspirin and acetaminophen together?
+Generally, it’s not recommended to take aspirin and acetaminophen together without consulting a healthcare professional, as this can increase the risk of side effects. However, there are certain combinations and formulations available that include both, which should only be used under medical guidance.
How do I choose between aspirin and acetaminophen for my pain?
+The choice between aspirin and acetaminophen depends on the type of pain you’re experiencing and your individual health situation. For example, if you have an inflammatory condition like arthritis, aspirin might be more appropriate. For fever reduction or pain relief without inflammation, acetaminophen could be the better choice. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
What are the maximum safe dosages for aspirin and acetaminophen?
+The maximum safe dosage for adults for both aspirin and acetaminophen is 4000 mg in 24 hours, but this can vary based on individual factors such as weight, age, and other health conditions. It’s crucial to never exceed the recommended dosage without consulting a healthcare professional, as this can lead to serious side effects, including liver damage from acetaminophen and stomach ulcers or bleeding from aspirin.