Fermentation, a metabolic process, has been utilized for centuries in the production of various food products and beverages, such as wine, beer, and yogurt. At its core, fermentation is an anaerobic process, meaning it occurs in the absence of oxygen. This process involves the conversion of sugars into acids, gases, or alcohol by microorganisms like yeast or bacteria. The anaerobic nature of fermentation is crucial, as the absence of oxygen allows these microorganisms to thrive and produce the desired end products.
Understanding the Anaerobic Process of Fermentation
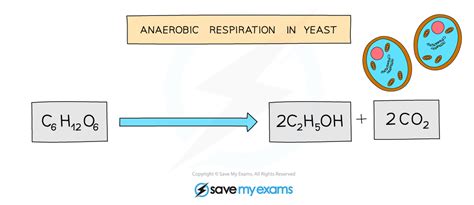
The anaerobic process of fermentation is complex and involves several biochemical reactions. It begins with the breakdown of sugars by enzymes, which are then converted into pyruvate through glycolysis. In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is further metabolized into various end products, such as lactic acid, ethanol, or carbon dioxide, depending on the type of microorganism involved. For example, in the production of yogurt, lactic acid bacteria convert the lactose in milk into lactic acid, which gives yogurt its characteristic taste and texture. Similarly, in the brewing of beer, yeast ferments the sugars in grains to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Types of Fermentation
There are several types of fermentation, each producing different end products. Lactic acid fermentation, for instance, is used in the production of yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi, and involves the conversion of sugars into lactic acid. Ethanol fermentation, on the other hand, is used in the production of beer and wine, and involves the conversion of sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide. Another type of fermentation is acetone-butanol fermentation, which is used in the production of solvents and involves the conversion of sugars into acetone, butanol, and ethanol.
| Type of Fermentation | End Products | Microorganisms Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Lactic Acid Fermentation | Lactic Acid | Lactic Acid Bacteria |
| Ethanol Fermentation | Ethanol, Carbon Dioxide | Yeast |
| Acetone-Butanol Fermentation | Acetone, Butanol, Ethanol | Clostridium acetobutylicum |

Key Points
- Fermentation is an anaerobic process that involves the conversion of sugars into acids, gases, or alcohol by microorganisms.
- The absence of oxygen is crucial for the process, as it allows microorganisms to thrive and produce the desired end products.
- There are several types of fermentation, including lactic acid fermentation, ethanol fermentation, and acetone-butanol fermentation.
- The end products of fermentation depend on the type of microorganism involved and the specific biochemical reactions that occur.
- Fermentation has significant applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and biofuel industries.
Applications of Fermentation
Fermentation has a wide range of applications, from the production of food and beverages to the production of pharmaceuticals and biofuels. In the food industry, fermentation is used to produce yogurt, cheese, sauerkraut, and kimchi, among other products. In the pharmaceutical industry, fermentation is used to produce antibiotics, vaccines, and other medicines. In the biofuel industry, fermentation is used to produce ethanol and butanol, which can be used as alternatives to fossil fuels.
Future of Fermentation
The future of fermentation is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving the efficiency and sustainability of fermentation processes. New technologies, such as genetic engineering and bioreactor design, are being developed to enhance the productivity and yield of fermentation processes. Additionally, there is a growing interest in the use of fermentation for the production of biofuels and other sustainable products.
What is fermentation, and how does it occur?
+Fermentation is a metabolic process that involves the conversion of sugars into acids, gases, or alcohol by microorganisms. It occurs in the absence of oxygen and involves a series of biochemical reactions that result in the production of end products such as lactic acid, ethanol, or carbon dioxide.
What are the different types of fermentation?
+There are several types of fermentation, including lactic acid fermentation, ethanol fermentation, and acetone-butanol fermentation. Each type of fermentation involves the conversion of sugars into different end products and is used in the production of various food products, beverages, and other products.
What are the applications of fermentation?
+Fermentation has a wide range of applications, from the production of food and beverages to the production of pharmaceuticals and biofuels. It is used in the production of yogurt, cheese, sauerkraut, and kimchi, among other food products, and is also used in the production of antibiotics, vaccines, and other medicines.
In conclusion, fermentation is a complex and fascinating process that has been utilized for centuries in the production of various food products and beverages. The anaerobic process of fermentation is crucial for the production of these products, and understanding the biochemical reactions involved can help in the development of new products and processes. With ongoing research and development aimed at improving the efficiency and sustainability of fermentation processes, the future of fermentation is promising, and its applications are expected to continue to grow and expand into new areas.