The terms GB and MB are commonly used in the context of digital storage and data measurement. Understanding the difference between these two units is essential for managing and optimizing digital resources. In this article, we will delve into the GB vs MB size comparison, exploring their definitions, differences, and practical applications.
Key Points
- GB (Gigabyte) is a larger unit of digital storage compared to MB (Megabyte)
- 1 GB is equal to 1,024 MB
- GB is often used to measure the storage capacity of hard drives, solid-state drives, and flash drives
- MB is commonly used to measure the size of files, such as documents, images, and videos
- Understanding the difference between GB and MB is crucial for managing digital storage and optimizing data transfer
Definitions and Differences
A GB, or gigabyte, is a unit of digital information that represents 1,024 megabytes (MB). It is a larger unit of measurement compared to MB, which is often used to measure the size of individual files. The difference between GB and MB lies in their storage capacity, with GB being significantly larger. For example, a typical high-definition movie file can range from 1-5 GB in size, while a standard digital photo can range from 1-10 MB.
Practical Applications
In practical terms, GB is often used to measure the storage capacity of digital devices, such as hard drives, solid-state drives, and flash drives. For instance, a 1 TB (terabyte) hard drive can store approximately 1,024 GB of data. On the other hand, MB is commonly used to measure the size of individual files, such as documents, images, and videos. Understanding the difference between GB and MB is essential for managing digital storage, optimizing data transfer, and ensuring that devices have sufficient storage capacity.
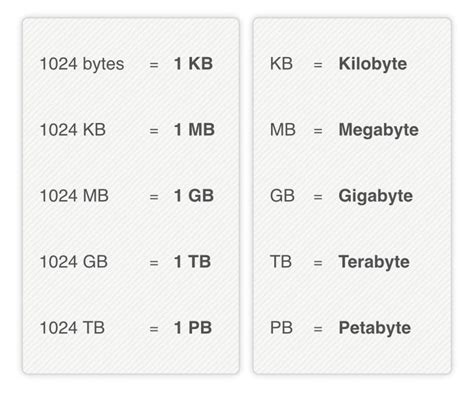
| Unit of Measurement | Storage Capacity |
|---|---|
| 1 MB | 1,024 kilobytes (KB) |
| 1 GB | 1,024 megabytes (MB) |
| 1 TB | 1,024 gigabytes (GB) |
Real-World Examples

In real-world scenarios, the GB vs MB size comparison plays a significant role in various applications. For instance, when downloading a large file, such as a software update or a high-definition movie, understanding the file size in GB or MB is essential for estimating the download time and ensuring that the device has sufficient storage capacity. Similarly, when purchasing a digital device, such as a smartphone or a laptop, understanding the storage capacity in GB or MB is crucial for determining the device’s ability to store and manage data.
Technical Specifications
From a technical perspective, the GB vs MB size comparison is based on the binary system, where 1 GB is equal to 2^30 bytes, and 1 MB is equal to 2^20 bytes. This binary system is the foundation of digital storage and data measurement, and understanding the technical specifications of GB and MB is essential for optimizing digital resources.
What is the main difference between GB and MB?
+The main difference between GB and MB is their storage capacity, with GB being significantly larger. 1 GB is equal to 1,024 MB.
How is GB used in practical applications?
+GB is often used to measure the storage capacity of digital devices, such as hard drives, solid-state drives, and flash drives. It is also used to measure the size of large files, such as high-definition movies and software updates.
What is the technical specification of GB and MB?
+1 GB is equal to 2^30 bytes, and 1 MB is equal to 2^20 bytes. This binary system is the foundation of digital storage and data measurement.
Meta Description: Understand the difference between GB and MB, and learn how to apply this knowledge in practical scenarios to optimize digital storage and data management. (149 characters)