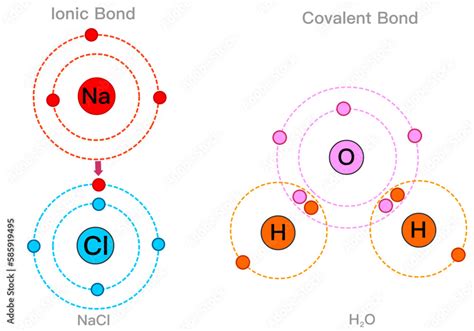
Water, chemically denoted as H2O, is a compound that has been extensively studied due to its unique properties and essential role in various biological, chemical, and physical processes. One of the fundamental aspects of water is the nature of its chemical bonding. The question of whether the bond in H2O is ionic or covalent is a subject of interest in chemistry, as understanding the type of bond provides insights into the compound's properties and behavior.
To address this question, it's essential to first understand the basic principles of ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges that are attracted to each other. This type of bond is common in compounds formed between metals and nonmetals. On the other hand, covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms, typically between nonmetal atoms. This sharing can result in a polar or nonpolar covalent bond, depending on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved.
Nature of the Bond in H2O
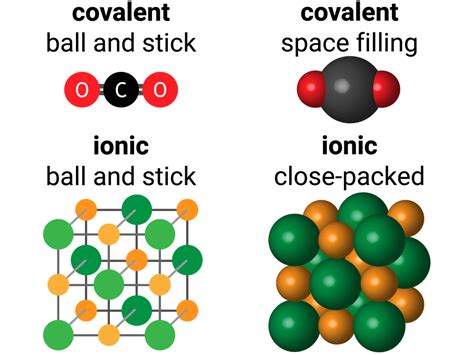
The water molecule (H2O) consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to a single oxygen atom. Oxygen is a nonmetal with a relatively high electronegativity value, which is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. Hydrogen, also a nonmetal, has a lower electronegativity compared to oxygen. When hydrogen and oxygen atoms form a bond, they share electrons, but due to the difference in electronegativity, the shared electrons are not equally distributed between the atoms. This results in a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom, leading to a polar covalent bond.
Polarity of the Water Molecule
The polarity of the water molecule is a direct consequence of the polar covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen. The oxygen atom, being more electronegative, pulls the shared electrons closer to itself, creating a partial negative charge (δ-). Conversely, the hydrogen atoms, having lost some electron density, carry a partial positive charge (δ+). This polarity gives water its unique chemical and physical properties, such as its high boiling point, solubility in a wide range of substances, and ability to form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules or different compounds.
| Atom | Electronegativity |
|---|---|
| Oxygen (O) | 3.44 |
| Hydrogen (H) | 2.20 |
In conclusion, the bond in H2O is covalent, specifically a polar covalent bond, due to the sharing of electrons between oxygen and hydrogen atoms and the difference in their electronegativities. This polarity is fundamental to the properties and behaviors of water, making it an indispensable compound in chemistry and biology.
Key Points
- The water molecule (H2O) consists of two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to a single oxygen atom.
- The bond between oxygen and hydrogen in H2O is a polar covalent bond due to the difference in electronegativity between the atoms.
- The polarity of the water molecule arises from the unequal distribution of shared electrons, resulting in partial positive charges on hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom.
- This polarity is responsible for many of water's unique properties, including its solubility, boiling point, and ability to form hydrogen bonds.
- Understanding the nature of the bond in H2O is essential for appreciating its role in chemical, biological, and physical processes.
Given the importance of water in various scientific disciplines, further exploration into its properties and behaviors can provide deeper insights into its applications and significance in both natural and industrial contexts.
What is the primary factor determining the polarity of the water molecule?
+The primary factor determining the polarity of the water molecule is the difference in electronegativity between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. Oxygen’s higher electronegativity pulls the shared electrons closer, resulting in a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charges on the hydrogen atoms.
How does the polarity of water influence its boiling point?
+The polarity of water molecules allows them to form hydrogen bonds with each other. These hydrogen bonds require energy to break, which is why water has a relatively high boiling point compared to other substances of similar molecular weight. The energy needed to overcome these intermolecular forces is directly related to the polarity of the water molecule.
What role does the covalent bond in H2O play in its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances?
+The covalent bond in H2O, particularly its polar nature, enables water to dissolve both ionic and polar covalent compounds. The partial positive charge on hydrogen atoms and the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom allow water molecules to interact with and solvate ions and polar molecules, making water an excellent solvent.