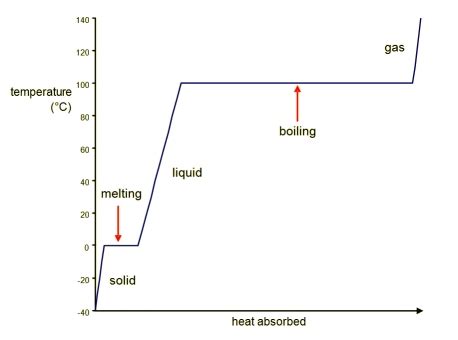
The boiling process is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, where a liquid is heated to its boiling point, resulting in the formation of vapor. The heat added during this process is crucial in understanding the thermodynamic principles involved. In this article, we will delve into the concept of heat added in the boiling process, exploring the theoretical foundations, practical applications, and key considerations.
To begin with, it is essential to understand the concept of latent heat, which is the energy required to change the state of a substance without altering its temperature. During the boiling process, the heat added to the liquid is used to overcome the intermolecular forces, allowing the molecules to transition from a liquid to a gas state. This process requires a significant amount of energy, which is known as the latent heat of vaporization. The latent heat of vaporization is a critical parameter in determining the amount of heat added during the boiling process.
Key Points
- The boiling process involves the addition of heat to a liquid, resulting in the formation of vapor.
- The latent heat of vaporization is a critical parameter in determining the amount of heat added during the boiling process.
- The heat added during boiling is used to overcome the intermolecular forces, allowing the molecules to transition from a liquid to a gas state.
- The boiling point of a liquid is influenced by factors such as pressure, temperature, and the presence of impurities.
- Understanding the heat added in the boiling process is crucial in various industrial applications, including power generation, refrigeration, and chemical processing.
Thermodynamic Principles

The thermodynamic principles involved in the boiling process can be understood by considering the first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. During the boiling process, the heat added to the liquid is converted into internal energy, which is used to overcome the intermolecular forces and allow the molecules to transition from a liquid to a gas state. The internal energy of the system increases as the heat is added, resulting in an increase in the temperature and pressure of the system.
Latent Heat of Vaporization
The latent heat of vaporization is a critical parameter in determining the amount of heat added during the boiling process. The latent heat of vaporization is the energy required to change the state of a substance from a liquid to a gas, without altering its temperature. The latent heat of vaporization is typically expressed in units of joules per kilogram (J/kg) and is a function of the temperature and pressure of the system. For example, the latent heat of vaporization of water at standard temperature and pressure (STP) is approximately 2256 kJ/kg.
| Substance | Latent Heat of Vaporization (kJ/kg) |
|---|---|
| Water | 2256 |
| Methanol | 1100 |
| Ethanol | 840 |
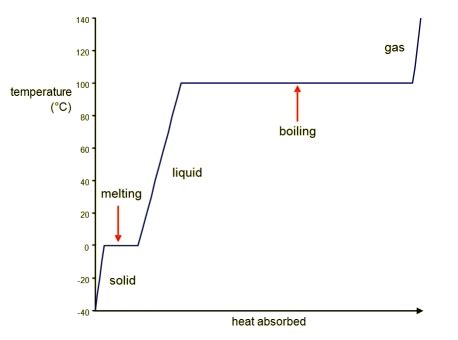
Practical Applications

The boiling process has numerous practical applications in various industries, including power generation, refrigeration, and chemical processing. In power generation, the boiling process is used to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. In refrigeration, the boiling process is used to absorb heat from a cold body, resulting in a cooling effect. In chemical processing, the boiling process is used to separate and purify substances based on their boiling points.
Industrial Boilers
Industrial boilers are designed to produce steam by boiling water, which is then used to drive turbines, pumps, and other equipment. The heat added during the boiling process is typically provided by the combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, or gas. The efficiency of the boiler is critical in determining the amount of heat added during the boiling process, as well as the overall energy efficiency of the system.
In conclusion, the heat added in the boiling process is a critical parameter in understanding the thermodynamic principles involved. The latent heat of vaporization is a key factor in determining the amount of heat added during the boiling process, and is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of impurities. Understanding the heat added in the boiling process is crucial in various industrial applications, including power generation, refrigeration, and chemical processing.
What is the latent heat of vaporization?
+The latent heat of vaporization is the energy required to change the state of a substance from a liquid to a gas, without altering its temperature.
What is the boiling point of water at standard temperature and pressure?
+The boiling point of water at standard temperature and pressure (STP) is 100°C or 212°F.
What are some practical applications of the boiling process?
+The boiling process has numerous practical applications in various industries, including power generation, refrigeration, and chemical processing.