Medicaid is a complex and multifaceted healthcare program that is often misunderstood, particularly in terms of its target demographic. While it is true that Medicaid provides crucial healthcare coverage to low-income seniors, it is not exclusively a program for old people. In fact, Medicaid is designed to provide health insurance coverage to a wide range of individuals and families, including children, pregnant women, parents, and people with disabilities.
Established in 1965 as a joint federal-state program, Medicaid has evolved over the years to address the diverse healthcare needs of its beneficiaries. According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), as of 2022, Medicaid covers over 82 million people, including approximately 7.2 million low-income seniors who are dually eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare. This dual eligibility is crucial, as it allows these individuals to access a comprehensive range of healthcare services, including long-term care, prescription medications, and preventive care.
Key Points
- Medicaid is a healthcare program that provides coverage to low-income individuals and families, including children, pregnant women, parents, and people with disabilities.
- Medicaid is not exclusively a program for old people, although it does provide crucial coverage to low-income seniors.
- Approximately 7.2 million low-income seniors are dually eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare, allowing them to access a comprehensive range of healthcare services.
- Medicaid plays a critical role in addressing healthcare disparities and promoting health equity, particularly among vulnerable populations.
- The program's eligibility criteria and benefits vary from state to state, reflecting the diverse healthcare needs and priorities of different regions.
Medicaid Eligibility and Benefits
Medicaid eligibility is determined by a combination of factors, including income, family size, and disability status. In general, individuals with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level (FPL) are eligible for Medicaid, although some states have expanded their programs to cover individuals with higher incomes. The benefits provided by Medicaid are comprehensive and include hospital care, physician services, prescription medications, and long-term care, among others.
It is worth noting that Medicaid plays a critical role in addressing healthcare disparities and promoting health equity, particularly among vulnerable populations. By providing access to affordable healthcare services, Medicaid helps to reduce health disparities and improve health outcomes for low-income individuals and families. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), Medicaid expansion has been associated with significant reductions in mortality rates and improvements in health outcomes, particularly among low-income adults.
Medicaid and Long-Term Care
One of the most important benefits provided by Medicaid is long-term care, which includes services such as nursing home care, home health care, and adult day care. These services are essential for individuals who require ongoing support and care, particularly those with disabilities or chronic illnesses. According to the National Association of States United for Aging and Disabilities (NASUAD), Medicaid pays for approximately 50% of all long-term care services provided in the United States, making it a critical component of the nation’s healthcare system.
| Category | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hospital Care | Coverage for inpatient and outpatient hospital services |
| Physician Services | Coverage for primary and specialty care physician services |
| Prescription Medications | Coverage for prescription medications, including generics and brand-name drugs |
| Long-Term Care | Coverage for nursing home care, home health care, and adult day care |

Medicaid Expansion and the Affordable Care Act
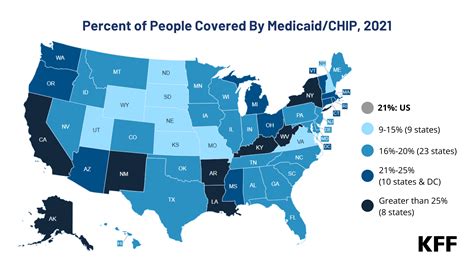
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, has had a significant impact on Medicaid, particularly with regards to expansion. Under the ACA, states have the option to expand their Medicaid programs to cover individuals with incomes up to 138% of the FPL. To date, 38 states and the District of Columbia have expanded their Medicaid programs, resulting in millions of newly eligible individuals gaining access to healthcare coverage.
According to a report by the Kaiser Family Foundation, Medicaid expansion has been associated with significant reductions in uninsurance rates, particularly among low-income adults. Additionally, expansion has helped to reduce healthcare disparities and promote health equity, particularly among communities of color. However, some states have chosen not to expand their Medicaid programs, leaving thousands of low-income individuals without access to affordable healthcare coverage.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its many successes, Medicaid faces numerous challenges, including funding constraints, bureaucratic complexities, and limited provider participation. To address these challenges, policymakers and healthcare leaders must work together to promote Medicaid reform, improve program efficiency, and enhance provider reimbursement rates. Additionally, there are opportunities for Medicaid to play a more prominent role in promoting population health, particularly through the use of value-based payment models and community-based initiatives.
What is Medicaid, and how does it differ from Medicare?
+Medicaid is a joint federal-state program that provides healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families, while Medicare is a federal program that provides coverage to seniors and individuals with disabilities.
Who is eligible for Medicaid, and what benefits does it provide?
+Medicaid eligibility varies by state, but generally includes individuals with incomes up to 138% of the FPL. Benefits include hospital care, physician services, prescription medications, and long-term care, among others.
How has the Affordable Care Act impacted Medicaid, and what are the implications for healthcare reform?
+The ACA has expanded Medicaid to cover millions of newly eligible individuals, resulting in significant reductions in uninsurance rates and healthcare disparities. However, the future of Medicaid remains uncertain, and policymakers must work together to promote program sustainability and reform.
In conclusion, Medicaid is a vital component of the US healthcare system, providing access to affordable healthcare services for millions of low-income individuals and families. While it is not exclusively a program for old people, Medicaid plays a critical role in addressing the healthcare needs of low-income seniors, particularly those who are dually eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, it is essential to recognize the importance of Medicaid in promoting health equity and improving health outcomes for vulnerable populations.