The current global health landscape is marked by the constant emergence and re-emergence of viral infections, affecting populations worldwide. As of the latest reports, several viruses are presently circulating, impacting different regions and demographics. Understanding the nature of these viruses, their transmission modes, and the symptoms they cause is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures and treatment strategies.
Key Points
- The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, continues to evolve with new variants emerging, necessitating ongoing vigilance and adherence to public health guidelines.
- Influenza viruses, including seasonal flu and avian influenza, pose a significant threat, especially to vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with compromised immune systems.
- Monkeypox, a viral infection that can be transmitted from animals to humans and between humans, has seen increased cases in various parts of the world, highlighting the need for enhanced surveillance and control measures.
- Norovirus and other gastrointestinal viruses are common causes of outbreaks, particularly in closed environments like cruise ships, schools, and healthcare facilities, emphasizing the importance of strict hygiene practices.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a significant concern for infants and older adults, as it can lead to severe respiratory illnesses, underscoring the value of preventive measures such as vaccination when available.
Understanding the Current Viral Landscape
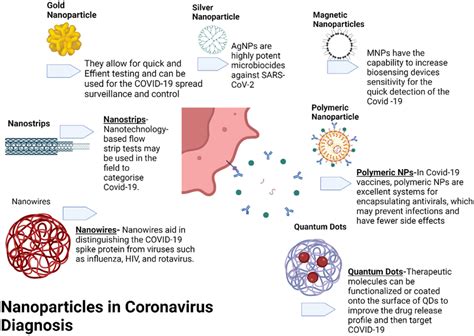
The global viral landscape is dynamic, with viruses constantly evolving and spreading. The COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, has introduced the world to the rapid spread and mutation of viruses. The SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for COVID-19, has shown a remarkable ability to mutate, leading to various variants with different transmissibility and virulence levels. This evolution necessitates continuous monitoring and updates to vaccination strategies and public health policies.
Viral Transmission and Prevention
Viruses can be transmitted through various routes, including respiratory droplets, contact with contaminated surfaces, vectors like mosquitoes, and direct contact with infected individuals. Understanding the transmission mode of each virus is key to devising effective preventive measures. For respiratory viruses like influenza and SARS-CoV-2, wearing masks, practicing good hygiene (such as frequent handwashing), and maintaining physical distancing can significantly reduce transmission rates. For viruses like norovirus, strict hygiene and surface cleaning are critical in preventing outbreaks.
| Virus | Transmission Mode | Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 | Respiratory droplets, contact | Masks, hand hygiene, physical distancing |
| Influenza | Respiratory droplets | Vaccination, masks, hand hygiene |
| Norovirus | Contaminated food/water, contact | Strict hygiene, surface cleaning |
Public Health Response and Future Directions
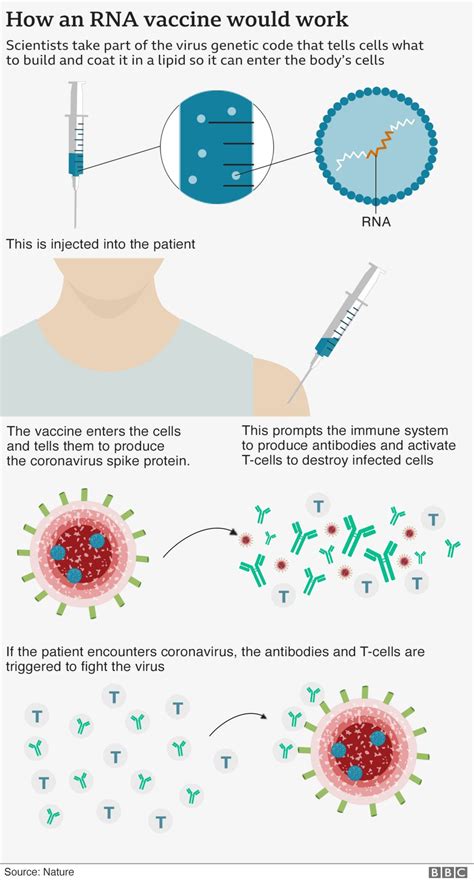
The response to viral outbreaks and pandemics requires a multifaceted approach, including enhanced surveillance, rapid diagnostics, effective treatment strategies, and the development and distribution of vaccines. Public health campaigns aimed at educating the population about preventive measures are also vital. Looking forward, investments in global health infrastructure, research into viral evolution and transmission, and the development of innovative diagnostic and therapeutic tools will be essential in preparing for and responding to future viral threats.
Global Cooperation and Preparedness
Given the interconnected nature of the world, global cooperation is indispensable in addressing viral outbreaks. International bodies like the World Health Organization (WHO) play a critical role in coordinating responses, sharing data, and providing guidelines for public health actions. Furthermore, investing in healthcare infrastructure, particularly in underserved areas, and promoting practices like One Health, which considers the health of humans, animals, and the environment as interconnected, can enhance preparedness and response capabilities.
What are the most common symptoms of viral infections?
+The symptoms of viral infections can vary widely depending on the virus. Common symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, and fatigue. Some viruses can also cause gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea and vomiting.
How can I protect myself from getting a viral infection?
+Protection against viral infections involves several strategies. Getting vaccinated against viruses like influenza and COVID-19 is highly effective. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and wearing a mask in crowded areas, can also significantly reduce your risk of infection.
What should I do if I think I have a viral infection?
+If you suspect you have a viral infection, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include rest, hydration, over-the-counter medications for symptom relief, and in some cases, antiviral medications.
In conclusion, the viral landscape is complex and ever-changing, with various viruses posing significant health risks to different populations. Understanding these viruses, their modes of transmission, and the measures to prevent their spread is crucial for individual and public health. Continued global cooperation, investment in health infrastructure, and advancements in medical science will be pivotal in managing and mitigating the impact of viral infections now and in the future.



