Wavy hair is a unique and versatile hair texture that has fascinated many for centuries. As a trait influenced by genetics, understanding how wavy hair inheritance works can provide valuable insights into the complexities of human hair diversity. With advancements in genetic research, it has become possible to unravel the mysteries behind the inheritance patterns of wavy hair. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of wavy hair inheritance, exploring the genetic principles that govern its transmission from one generation to the next.
Introduction to Hair Texture Genetics

Human hair texture is primarily determined by the shape of the hair follicle, which is influenced by multiple genes. Wavy hair, characterized by its ’S’ shape, falls between straight and curly hair in terms of texture. The genetic basis of hair texture is complex, involving the interaction of several genes that control the structure and development of hair. Research has identified several key genes associated with hair texture, including those that influence the shape of the hair follicle and the structure of the hair shaft.
Key Points
- Wavy hair is influenced by multiple genetic factors, including the shape of the hair follicle and the structure of the hair shaft.
- The inheritance of wavy hair can follow both autosomal dominant and recessive patterns, depending on the specific genes involved.
- Genetic variations in the EDAR, FGFR2, and TRPS1 genes have been associated with hair texture, including wavy hair.
- Environmental factors, such as humidity and hair care practices, can also influence the expression of wavy hair.
- Understanding the genetics of wavy hair can provide insights into the development of hair care products and treatments tailored to specific hair textures.
Genetic Principles of Wavy Hair Inheritance
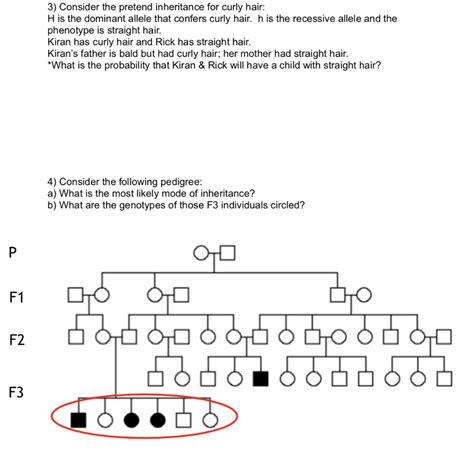
The inheritance of wavy hair is governed by the principles of Mendelian genetics, which describe how genes are passed from parents to offspring. Wavy hair can be inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner, depending on the specific genes involved. Autosomal dominant inheritance means that a single copy of the dominant allele is enough to express the trait, while autosomal recessive inheritance requires two copies of the recessive allele (one from each parent) to express the trait.
Role of Specific Genes
Several genes have been identified as playing a crucial role in determining hair texture, including the EDAR, FGFR2, and TRPS1 genes. Variations in these genes can influence the shape of the hair follicle and the structure of the hair shaft, leading to different hair textures. For example, mutations in the EDAR gene have been associated with hair texture variations, including wavy hair. Understanding the function and interaction of these genes can provide valuable insights into the genetic basis of wavy hair.
| Gene | Association with Hair Texture |
|---|---|
| EDAR | Variations associated with hair texture, including wavy hair |
| FGFR2 | Influences hair follicle development and hair texture |
| TRPS1 | Regulates hair shaft structure and texture |

Environmental Influences on Wavy Hair Expression
While genetics play a significant role in determining hair texture, environmental factors can also influence the expression of wavy hair. Humidity, temperature, and hair care practices can all impact the appearance and manageability of wavy hair. For example, high humidity can cause wavy hair to become frizzy, while certain hair care products can enhance or reduce wave definition. Understanding these environmental influences can help individuals with wavy hair optimize their hair care routines and product choices.
Practical Applications of Wavy Hair Genetics
The study of wavy hair genetics has practical implications for the development of hair care products and treatments. By understanding the genetic basis of wavy hair, manufacturers can create products tailored to the specific needs of individuals with this hair texture. Additionally, knowledge of the genetic factors influencing wavy hair can inform the development of personalized hair care recommendations, taking into account an individual’s unique genetic profile and environmental factors.
How is wavy hair inherited?
+Wavy hair can be inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner, depending on the specific genes involved. This means that a single copy of the dominant allele or two copies of the recessive allele (one from each parent) can express the trait.
What genes are associated with wavy hair?
+Several genes, including EDAR, FGFR2, and TRPS1, have been associated with hair texture, including wavy hair. Variations in these genes can influence the shape of the hair follicle and the structure of the hair shaft.
Can environmental factors influence wavy hair?
+Yes, environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and hair care practices can influence the expression and manageability of wavy hair. Understanding these factors can help individuals with wavy hair optimize their hair care routines.
In conclusion, the inheritance of wavy hair is a complex process influenced by multiple genetic and environmental factors. By understanding the genetic principles and specific genes associated with wavy hair, as well as the impact of environmental influences, individuals can better manage and care for their hair. The study of wavy hair genetics also has broader implications for the development of personalized hair care products and treatments, highlighting the importance of continued research into the genetics of human hair texture.



