Wellbutrin, also known by its generic name bupropion, is a medication that has been widely used for the treatment of major depressive disorder and seasonal affective disorder. One of the common questions surrounding Wellbutrin is whether it is a stimulant. To address this, it's essential to understand the pharmacological profile of bupropion and how it differs from traditional stimulants.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
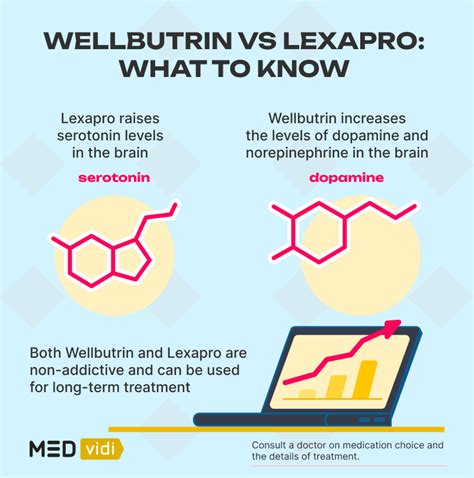
Wellbutrin works as a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI), meaning it increases the levels of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain by blocking the reabsorption of these chemicals. This mechanism of action is distinct from that of traditional stimulants like amphetamines or cocaine, which typically work by releasing large amounts of dopamine and norepinephrine into the synaptic cleft. While both types of drugs can increase the availability of these neurotransmitters, the way they achieve this and their overall effects on the body and brain are different.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
The stimulant-like effects of Wellbutrin, such as increased energy and alertness, can sometimes lead to confusion about its classification. However, it does not possess the same high potential for abuse or the intense stimulatory effects seen with drugs like methamphetamine or Ritalin. Bupropion’s pharmacokinetic profile, including its slower onset of action and lower peak levels of dopamine release, contributes to its lower abuse potential compared to traditional stimulants.
| Characteristic | Wellbutrin (Bupropion) | Traditional Stimulants |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Norepinephrine-Dopamine Reuptake Inhibition | Release of Dopamine and Norepinephrine |
| Abuse Potential | Lower | Higher |
| Onset of Action | Slower | Faster |
| Clinical Use | Depression, Smoking Cessation | ADHD, Narcolepsy |
Key Points
- Wellbutrin (bupropion) is primarily a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor, not a traditional stimulant.
- It has a lower potential for abuse compared to traditional stimulants.
- The medication is used for treating depression and aiding in smoking cessation, among other uses.
- Its effects, such as increased energy, are due to its impact on neurotransmitter levels but are distinct from the intense stimulatory effects of drugs like amphetamines.
- Understanding the pharmacological differences between Wellbutrin and traditional stimulants is essential for its appropriate use and management.
Comparative Analysis with Traditional Stimulants
A comparative analysis between Wellbutrin and traditional stimulants reveals significant differences in their pharmacological profiles, clinical applications, and potential for abuse. Traditional stimulants, such as those used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), work by immediately releasing large amounts of dopamine and norepinephrine into the synaptic cleft, leading to rapid increases in alertness, energy, and focus. In contrast, Wellbutrin’s action is more nuanced, involving the inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters, which results in a slower and more sustained increase in their availability.
Clinical Implications and Applications
The clinical implications of Wellbutrin’s mechanism of action are significant. Its use in the treatment of major depressive disorder, for example, is based on its ability to increase dopamine and norepinephrine levels, which can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Additionally, its application in smoking cessation programs, such as the brand-name product Zyban, leverages its ability to affect neurotransmitter levels, helping to mitigate withdrawal symptoms and cravings associated with nicotine cessation.
Is Wellbutrin considered a controlled substance?
+No, Wellbutrin is not classified as a controlled substance in the same category as traditional stimulants. It is available by prescription for the treatment of depression and smoking cessation.
Can Wellbutrin be used to treat ADHD?
+While Wellbutrin can have stimulant-like effects, it is not primarily approved for the treatment of ADHD. However, it may be used off-label for this purpose in certain cases, under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
What are the common side effects of Wellbutrin?
+Common side effects of Wellbutrin include dry mouth, nausea, insomnia, and increased anxiety. It's essential to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider before starting the medication.
In conclusion, while Wellbutrin shares some properties with traditional stimulants, its unique mechanism of action, clinical applications, and lower potential for abuse distinguish it from this category of drugs. Understanding these differences is crucial for the appropriate use and management of Wellbutrin in clinical practice.