The question of whether zero is a natural number has been a topic of debate among mathematicians and scholars for centuries. The answer to this question depends on the context and the definition of natural numbers being used. In this article, we will explore the different perspectives on this issue and examine the arguments for and against considering zero as a natural number.
Introduction to Natural Numbers

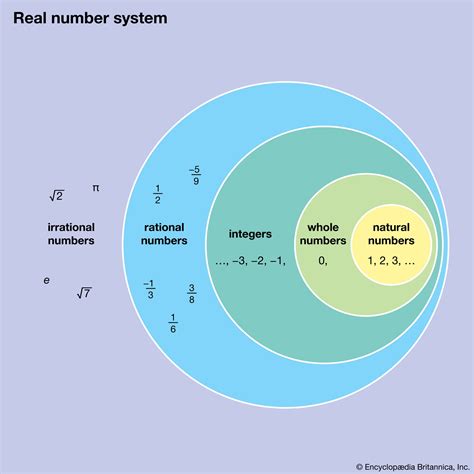
Natural numbers, also known as counting numbers, are a set of numbers that are used to count and order objects. The set of natural numbers is often denoted by the symbol ℕ and includes numbers such as 1, 2, 3, and so on. The definition of natural numbers can vary depending on the mathematical context, but it is generally accepted that natural numbers are positive integers that can be used to count and order objects.
Historical Perspective
In the past, zero was not considered a natural number. The ancient Greeks, for example, did not include zero in their set of natural numbers. The Greek mathematician Euclid, in his book “Elements,” defined natural numbers as “numbers that can be counted,” and he did not include zero in this definition. Similarly, the Indian mathematician Aryabhata, who is credited with the invention of zero, did not consider zero as a natural number in his work.
Modern Definition of Natural Numbers

In modern mathematics, the definition of natural numbers is more nuanced. Some mathematicians define natural numbers as positive integers, which would exclude zero. Others define natural numbers as non-negative integers, which would include zero. The set of natural numbers is often denoted by the symbol ℕ₀, which includes zero, and ℕ₁, which excludes zero.
Arguments For Including Zero as a Natural Number
There are several arguments that support including zero as a natural number. One argument is that zero is a fundamental concept in mathematics and is used extensively in mathematical operations such as addition and multiplication. Excluding zero from the set of natural numbers would create inconsistencies in mathematical formulas and equations. Another argument is that the set of natural numbers should be closed under addition, meaning that the sum of two natural numbers should also be a natural number. Since 0 + 1 = 1, which is a natural number, it can be argued that zero should be included in the set of natural numbers.
Arguments Against Including Zero as a Natural Number
On the other hand, there are also arguments against including zero as a natural number. One argument is that zero does not have the same properties as other natural numbers. For example, zero does not have a multiplicative inverse, meaning that there is no number that can be multiplied by zero to get 1. This property is unique to zero and sets it apart from other natural numbers. Another argument is that the concept of natural numbers is closely tied to the concept of counting, and zero does not represent a countable quantity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether zero is a natural number depends on the context and definition being used. While there are arguments for and against including zero as a natural number, the modern mathematical consensus is that zero is a natural number. The set of natural numbers, denoted by ℕ₀, includes zero and is used extensively in mathematical operations and formulas. However, it is also important to acknowledge the historical and philosophical perspectives that have shaped our understanding of natural numbers and to recognize the ongoing debate and discussion among mathematicians and scholars on this topic.
Key Points
- The definition of natural numbers can vary depending on the mathematical context.
- Zero was not considered a natural number in the past, but the modern mathematical consensus is that zero is a natural number.
- There are arguments for and against including zero as a natural number, including its fundamental role in mathematics and its unique properties.
- The set of natural numbers, denoted by ℕ₀, includes zero and is used extensively in mathematical operations and formulas.
- The concept of natural numbers is closely tied to the concept of counting, and zero does not represent a countable quantity.
| Set of Natural Numbers | Definition |
|---|---|
| ℕ₀ | Includes zero |
| ℕ₁ | Excludes zero |

What is the modern definition of natural numbers?
+The modern definition of natural numbers can vary depending on the context, but it is generally accepted that natural numbers are non-negative integers that can be used to count and order objects.
Why is zero included in the set of natural numbers?
+Zero is included in the set of natural numbers because it is a fundamental concept in mathematics and is used extensively in mathematical operations such as addition and multiplication.
What are the arguments against including zero as a natural number?
+The arguments against including zero as a natural number include its unique properties, such as not having a multiplicative inverse, and the fact that it does not represent a countable quantity.
Meta description suggestion: “Explore the debate on whether zero is a natural number and discover the arguments for and against its inclusion in the set of natural numbers.”